Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Functional Groups.
Uploaded by
Ravu ArunCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functional Groups.
Uploaded by
Ravu ArunCopyright:
Available Formats
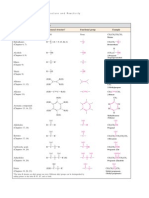
Important organic chemical FUNCTIONAL GROUPS found in biological molecules (R = any organic group) This page is for reference.
Learn these only as they are discussed in class. They should be memorized so we can talk about them easily. NAME
hydroxyl: aldehyde: detail:
GROUP
-OH -CHO O || -C-H -COOH
CHEMICAL EXAMPLE
ethanol: CH3-CH2-OH acetaldehyde: CH3-CHO
COMMENT
polar polar
BIOLOGICAL EXAMPLE
sugars (e.g., fructose) glucose
carboxylic acid: detail:
acetic acid: CH3-COOH
-
charged (ionized)
fatty acid (e.g., oleate)
O O O <---> || || <---> || -C-O -C-OH -C-O -NH2 (-NH3+) -COO || -C-O-COOR O || -C-O-R -CONH2 O || -C-NH2 -SH -S-S2-mercaptoethanol: HO-CH2-CH2-SH R-S-S-R reducing agent protein (cysteine) crosslinks in proteins protein (cystine) acetamide: CH3-CONH2 polar, not charged proteins (e.g., asparagine) ethyl ether: CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3 methyl ester of acetic acid: CH3-CO-OCH3 not so polar (symmetric) polar. not charged some lipids fats (e.g., triglycerides) acetone: CH3-CO-CH3 polar metabolic intermediate (e.g., pyruvic acid) methyl amine: CH3-NH2 charged (ionized) amino acid (e.g., glycine)
amine: detail: ketone: detail:
ether: ester: detail:
amide: detail:
sulfhydryl: disulfide:
phenyl:
phenol: C6H5-OH, -OH
hydrophobic
proteins (phenylalanine)
anhydride
O O|| | -C-O-P=O
|
3-phosphogyceric acid: HOCH-CHOH-CO-OP03--
2 acids joined
intermediary metabolites
O-N-C-NH2 H || NH2+
+
guanidino
arginine: H3N-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH-C-NH2 | || COONH2+
charged
proteins (arginine)
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Priority Table of Functional Groups of Organic ChemistryDocument1 pagePriority Table of Functional Groups of Organic ChemistryArut SelvanNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument1 pageFunctional GroupsKevin YeNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Functional GroupsDocument3 pagesAppendix: Functional GroupsbibronsNo ratings yet
- Common Functional GroupsDocument1 pageCommon Functional Groupszeeshan876No ratings yet
- Notes Functional GroupsDocument5 pagesNotes Functional GroupsFrank GaoNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 2Document13 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 2ridwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document50 pagesLecture 1Maria Cleo Conde PasionNo ratings yet
- كيمياء حيوية الوحدة التانيةDocument50 pagesكيمياء حيوية الوحدة التانيةasem sawalmehNo ratings yet
- ch10 Reactions Worksheet and Key 05 7 09Document13 pagesch10 Reactions Worksheet and Key 05 7 09api-304182646No ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument2 pagesFunctional GroupsshosteveNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument56 pagesPROTEINSJoltPacy100% (1)
- Nomenclature (One Shot) Class Notes PDFDocument68 pagesNomenclature (One Shot) Class Notes PDFaryanpw905No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nomenclature - Reaction Classification 2Document55 pagesChapter 1 - Nomenclature - Reaction Classification 2Duong Hoang Thoai ChauNo ratings yet
- Hidrati de CarbonDocument46 pagesHidrati de Carbonanon_887394303No ratings yet
- Table of Common Functional GroupsDocument10 pagesTable of Common Functional GroupsAngelica Mae Lasam100% (1)
- Notes - Chapt.25 Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument51 pagesNotes - Chapt.25 Amino Acids and PeptidesSiddarth PalletiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument33 pagesCarboxylic AcidRika Yulliyani RNo ratings yet
- Non Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticDocument4 pagesNon Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticRob FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Carboxilc Acids and EstersDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Carboxilc Acids and EstersKasun WekasingheNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument3 pagesFunctional Groupsrache1505No ratings yet
- Peptide PPT 1Document26 pagesPeptide PPT 1sheetal_5012No ratings yet
- Hidrati de Carbon 2012Document66 pagesHidrati de Carbon 2012anon_887394303No ratings yet
- 8.0 Hydroxy Compounds Pemurniaan by LiyaaaDocument99 pages8.0 Hydroxy Compounds Pemurniaan by LiyaaaNURUL HIDAYAH SAIFUL ANUARNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - NomenclatureDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 - NomenclatureKesavan KomandurNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids: R-COH Aldehyde R-CO-R Ketone R-CoohDocument17 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids: R-COH Aldehyde R-CO-R Ketone R-CoohMoshe Cohen'sNo ratings yet
- Esters PresentationDocument9 pagesEsters PresentationClarissa100% (2)
- IUPAC HandoutDocument9 pagesIUPAC HandoutjanellamaikaNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature 1 5Document5 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature 1 5Ömer KhanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratesshajmalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistryauni ramizahNo ratings yet
- Organic Short Notes: Functiona L Group Formula - Suffi XDocument2 pagesOrganic Short Notes: Functiona L Group Formula - Suffi XSahanNivanthaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry - Classification - Properties: Reactions: ¡Biologically Different! ¡Biologically Different!Document8 pagesStereochemistry - Classification - Properties: Reactions: ¡Biologically Different! ¡Biologically Different!Alberto CancelaNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature AllDocument83 pagesNomenclature AllLabib HasnainNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetoneDocument39 pagesAldehyde and KetoneCitra Siti PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Hidrati de CarbonDocument56 pagesHidrati de CarbonLoredana BradovaNo ratings yet
- AlcoholsDocument9 pagesAlcoholsShreya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Alcohol - WikipediaDocument14 pagesAlcohol - WikipediaMorteza YazdaniNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ether 06-12-2020Document51 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ether 06-12-2020gaganshishodia2No ratings yet
- FPPTDocument28 pagesFPPTGowsalyaNo ratings yet
- Try To Answer: IsopropylbenzeneDocument33 pagesTry To Answer: IsopropylbenzeneRoxanne Sioco100% (1)
- Student Copy True Lipids TrueDocument113 pagesStudent Copy True Lipids TrueSree Balaji Srinivas KatakamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 3 PDFNazir KhanNo ratings yet
- Review BifunctionalDocument18 pagesReview BifunctionalMelva Hilderia SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Himilo University Course Name: Organic ChemistryDocument37 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Himilo University Course Name: Organic ChemistryAbdulkarim FagaaseNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PartDocument22 pagesBiomolecules PartYashNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Major Classes of Organic CompoundsDocument42 pages3.0 Major Classes of Organic CompoundsAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- AVCL 9A Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument8 pagesAVCL 9A Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersGiane MadrigalNo ratings yet
- CHEM1102 Lecture Notes 12Document18 pagesCHEM1102 Lecture Notes 12Callum BiggsNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups 4Document12 pagesFunctional Groups 4isel melianiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.4 Nomenclature and Isomerism in Organic Chemistry New Functional Groups Review of AS Isomerism Optical IsomerismDocument20 pagesTopic 4.4 Nomenclature and Isomerism in Organic Chemistry New Functional Groups Review of AS Isomerism Optical IsomerismRyantyler13No ratings yet
- E22' Act 6. Functional Groups IDDocument3 pagesE22' Act 6. Functional Groups IDisojdosNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupDocument10 pagesFunctional Groupbalweg mackyNo ratings yet
- 12 - Nomenclature Questions TPP by Sir ShafeyDocument4 pages12 - Nomenclature Questions TPP by Sir Shafeyaftabhajano080No ratings yet
- Basic Hydrocarbons:: RH CC R R R R CC R R R R R R R RDocument2 pagesBasic Hydrocarbons:: RH CC R R R R CC R R R R R R R RyoonnyungleeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Organic ChemistryDocument32 pagesAlcohols, Organic Chemistryclassy43390% (1)
- Guide to Trivial Names, Trade Names and Synonyms for Substances Used in Analytical Nomenclature: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analytical Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandGuide to Trivial Names, Trade Names and Synonyms for Substances Used in Analytical Nomenclature: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Analytical Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2014-15Document88 pagesAnnual Report 2014-15Ravu ArunNo ratings yet
- PONGAMIA OIL Powerpoint PresentationDocument20 pagesPONGAMIA OIL Powerpoint PresentationRavu Arun67% (3)
- Exam Calender English 2016 PDFDocument1 pageExam Calender English 2016 PDF123456789cisco123456789No ratings yet
- 14th Finance Commission PDFDocument6 pages14th Finance Commission PDFRavu ArunNo ratings yet
- Pharm D (Revised) ADocument97 pagesPharm D (Revised) ARajesh AkkiNo ratings yet