Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6: Air Pressure 6.1 Air Pressure
Uploaded by
Elen UningOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6: Air Pressure 6.1 Air Pressure
Uploaded by
Elen UningCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 6 : AIR PRESSURE 6.1 AIR PRESSURE 1.
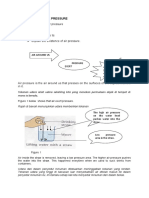
Air has mass and it exerts pressure on the surfaces of all objects. 2. Air has particles that are continually moving and colliding with things on Earth. These collisions produce air pressure or atmospheric pressure. Kinetic Theory of Gas A gas consists of many particles which are ________________ from each other. The particles move freely in all ____________________ . The particles continuously collide with the each other and the walls of the container at all time. A force is exerted by the particles on the walls of the container. The force produces a _______________ on the walls of the container.
3. Factors that affect the air pressure: a) Volume of air b) Temperature of air Factor Volume Relationship Explanation
Temperature
Gas pressure increases when: 1. The number of gas particles is increased (adding gas) 2. The volume of the container is decreased (gas is compressed) 3. The gas is heated
4. Features of air pressure are: a) It acts in all directions b) It changes from one place to another c) The higher the altitude, the lower is the air pressure.
5. Examples of air pressure: The cardboard will stay in place when the hand is removed as air pressure pushes the cardboard against the mouth of the glass.
Sucking the straw will reduce air pressure in the box while the higher air pressure crushes the wall of the box.
When the steam in the can is cooled, the air pressure in the can reduces. The higher pressure outside crashed the can.
Pumping air out of the bottle reduces the pressure in it and causes the balloon to expand.
6.2 APPLICATION OF THE PRINCIPLE OF AIR PRESSURE 1. Devices that use the principle of air pressure: a) Suction pump to unblock a clogged sink or pipe b) Rubber suckers - to hang objects c) Drinking straw - to suck up liquid from a container d) Dropper to transfer small amount of liquid e) Syringe for sucking liquid in and then forcing it out in a small stream f) Spraying pump to release liquid as a spray of tiny droplets g) Siphon to transfer water from a container at a higher level to a container at a lower level
Dropper
Drinking straw
Rubber sucker
Spraying Pump
Syringe
2. Using the principle of air pressure to solve daily problems: a) Clearing a blocked pipe - When the suction pump is pushed down, the air inside is pushed out, leaving a low pressure area. - The higher air pressure outside presses on the rubber cup and makes it stick to the surface of the sink. - When the suction pump is pulled upwards, the higher pressure inside the pipe pushes out the dirt that clogged it.
b) Pouring condensed milk - Air pressure that pushes air into one hole will also push the milk out of the other hole. - Two holes need to be punched on a milk tin before the contents can be poured out.
3. Gas under high pressure a) Gas will become liquid under high pressure and when it is cooled. b) The liquid becomes gas again when the pressure is released from the container. c) This enables gas to be stored easily as it reduces storage space, has more content and easily transported. d) Examples: i. Gas cylinders - Petroleum gas or natural gas is compressed to become liquid in a gas tank or cylinder - Other gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and nitrogen are also stored in cylinders for industrial use ii. Aerosol cans - Insecticides, perfume, hair sprays and paints are stored under high pressure in aerosol can. - When the pressure is released by pressing on the knob, the liquid comes out as a spray. e) Safety precautions when using gas cylinders: i. Place the gas containers upright ii. Do not place the tank near a heat source iii. Never dispose a used aerosol can in a fire iv. Do not smoke near the gas cylinder
You might also like
- 71+10 New Science Project Junior (with CD): learning science - the fun wayFrom Everand71+10 New Science Project Junior (with CD): learning science - the fun wayNo ratings yet
- Nota Air Pressure (Sains)Document7 pagesNota Air Pressure (Sains)Damairin SelangorNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure: Science - Form 2Document6 pagesAir Pressure: Science - Form 2BHASKARNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureDocument16 pages6.1 Air Pressure Learning Objective: Understanding Air PressureAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureDocument3 pages6.1 Kinetic Energy of Gases and Air PressureNg AliceNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure - Form 2Document5 pagesAir Pressure - Form 2Meggala MorganNo ratings yet
- Modul 11 - Air PressureDocument14 pagesModul 11 - Air PressureMastura AhmadNo ratings yet
- Air Pressure ExplainedDocument4 pagesAir Pressure ExplainedSanjana ShahNo ratings yet
- Gases properties laws technologiesDocument4 pagesGases properties laws technologiesCris CorsinoNo ratings yet
- Application of Air Pressure PrinciplesDocument19 pagesApplication of Air Pressure PrinciplesAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Air PressureDocument8 pagesForm 2 Air PressureCeline YingNo ratings yet
- Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.3Document15 pagesChapter Pressure:Lesson 3.3Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Gas PressureDocument10 pages3.3 Gas PressureNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Principles Air Pressure Form 2Document3 pagesPrinciples Air Pressure Form 2kaveesh_93No ratings yet
- Understanding Pressure: Applications of Pressure in Everyday LivingDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Pressure: Applications of Pressure in Everyday Livingredz45No ratings yet
- 3.3 Atmospheric and Gas Pressure 2012Document12 pages3.3 Atmospheric and Gas Pressure 2012cikgusuriyati100% (1)
- Mozac 3.3Document33 pagesMozac 3.3Pauling ChiaNo ratings yet
- G10 Q4 W1-W2-Behavior of GasesDocument19 pagesG10 Q4 W1-W2-Behavior of GasesJB DarNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureDocument17 pages6.1 Understanding Air Pressure Learning Outcomes: The Students Will Be Able To: Explain The Existence of Air PressureabdullmalikNo ratings yet
- Summative 4.4 Avogadro and IdealDocument14 pagesSummative 4.4 Avogadro and Idealelsie tequinNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test in Grade 10Document8 pagesChapter Test in Grade 10Maestro de Grapico100% (2)
- Air PressureDocument21 pagesAir PressureNoredah JamiaanNo ratings yet
- 18 Determination of O2 in AirDocument2 pages18 Determination of O2 in AirEva Hasanah Z.No ratings yet
- Air Around Us NBW (1) - Converted - 230124 - 225639Document5 pagesAir Around Us NBW (1) - Converted - 230124 - 225639KAMAKSHI DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Air and WaterDocument3 pagesAir and Waterjanhazo9No ratings yet
- SCIENCE-10-Q4-SLM4.kenitic-moleculartheoryDocument12 pagesSCIENCE-10-Q4-SLM4.kenitic-moleculartheorysharlenelawig5No ratings yet
- 3 Forces and PressureDocument24 pages3 Forces and PressureAbdiwahabSaedIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Form Two Science Module Air Pressure Concept MapDocument7 pagesForm Two Science Module Air Pressure Concept MapintanNo ratings yet
- Gas Pressure: Which Far Apart and in Random Motion at High SpeedDocument21 pagesGas Pressure: Which Far Apart and in Random Motion at High SpeedPooja UdupaNo ratings yet
- Cyclones WorksheetDocument4 pagesCyclones WorksheetPrasanjeet DebNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11: Pressure (Part - 3)Document3 pagesChapter - 11: Pressure (Part - 3)ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- HS Standard 5 2017Document8 pagesHS Standard 5 2017Not PrxNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 Behavior of GasesDocument2 pagesSummative Test 1 Behavior of GasesPangangan NHS100% (8)
- Chemistry Laboratory FormatDocument15 pagesChemistry Laboratory FormatAbesamis RanmaNo ratings yet
- monLabOperations 1Document12 pagesmonLabOperations 1Jayson Ace EnadNo ratings yet
- ProjectproposalDocument2 pagesProjectproposalapi-242285436No ratings yet
- G8 Lesson 5 - ChemistryDocument1 pageG8 Lesson 5 - Chemistryوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- ProjectproposalDocument3 pagesProjectproposalapi-264665509No ratings yet
- G. D. Goenka International School: Date: SUBJECT: Science Class: Viii TOPIC: Pressure Total No. of Pages:2Document2 pagesG. D. Goenka International School: Date: SUBJECT: Science Class: Viii TOPIC: Pressure Total No. of Pages:2Anonymous JhAwDJ9L7No ratings yet
- Uses and Applications of The Different Gas LawsDocument8 pagesUses and Applications of The Different Gas LawsWin7Addict100% (30)
- Activity 2 A Common Laboratory TechniquesDocument8 pagesActivity 2 A Common Laboratory TechniquesJearzy RufoNo ratings yet
- Che 205 Practice Questions 1Document9 pagesChe 205 Practice Questions 1Sunday EdemaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Evaporation of LiquidsDocument14 pagesRate of Evaporation of LiquidsiulefwlbNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Report: Datasheet B. The Bunsen BurnerDocument10 pagesInorganic Chemistry Laboratory Report: Datasheet B. The Bunsen Burnerkim allysaNo ratings yet
- Behavior of GasesDocument44 pagesBehavior of Gasesapi-668571149No ratings yet
- Laporan Fisika "Water Rocket"Document6 pagesLaporan Fisika "Water Rocket"Nur Cahyati100% (1)
- Air Conditioner Model: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoDocument13 pagesAir Conditioner Model: Andrea Badua Period 2 Physics Ms. BuenconsejoAndrea Badua100% (2)
- Soda Can Solar Air HeaterDocument8 pagesSoda Can Solar Air HeaterMatthew Zaragoza100% (1)
- 4q Science 10 PTDocument2 pages4q Science 10 PTBecky ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Air and Water WorkbookDocument6 pagesAir and Water Workbooksubhasmitaptr9No ratings yet
- Types of compressors and their advantages and disadvantagesDocument4 pagesTypes of compressors and their advantages and disadvantagesAj Ax100% (1)
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsMohamed Jameel77% (31)
- Thermo Activity ReportDocument5 pagesThermo Activity ReportNikhilNo ratings yet
- Printable Concrete ProceduresDocument6 pagesPrintable Concrete ProceduresAlfred Harvey ElacionNo ratings yet
- Respiration: The Big Idea: Explore Different Aspects of The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiration: The Big Idea: Explore Different Aspects of The Respiratory SystemYerick MartinezNo ratings yet
- EvaporationDocument32 pagesEvaporationSomesh Mahajan100% (1)
- Activity 2 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning cycle-MORADO, NANETTEDocument3 pagesActivity 2 - Refrigeration and Air Conditioning cycle-MORADO, NANETTENanette Morado100% (1)
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- March Exam Science F3 KSSMDocument29 pagesMarch Exam Science F3 KSSMElen UningNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 8Document16 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 8Elen UningNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper2 Term 1Document17 pagesPhysics Paper2 Term 1Elen UningNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Objective QuestionsDocument12 pagesScience Form 2 Objective QuestionsElen UningNo ratings yet
- FINAL TERM EXAMINATION FORM 4 2016 PHYSICSDocument21 pagesFINAL TERM EXAMINATION FORM 4 2016 PHYSICSElen UningNo ratings yet
- Final Term Examination Form 4 2016 PhysicsDocument14 pagesFinal Term Examination Form 4 2016 PhysicsElen UningNo ratings yet
- SC Chapter 7 DynamicsDocument3 pagesSC Chapter 7 DynamicsElen UningNo ratings yet
- Yearly Scheme of Work - Biology Form 4 - 2019Document40 pagesYearly Scheme of Work - Biology Form 4 - 2019Elen UningNo ratings yet
- FINAL TERM EXAMINATION FORM 4 2016 PHYSICSDocument21 pagesFINAL TERM EXAMINATION FORM 4 2016 PHYSICSElen UningNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Air Pressure 6.1 Air PressureDocument4 pagesChapter 6: Air Pressure 6.1 Air PressureElen UningNo ratings yet
- Section A (20 Marks)Document8 pagesSection A (20 Marks)Elen UningNo ratings yet
- Science Support & MovementDocument4 pagesScience Support & MovementElen UningNo ratings yet
- Maths Mid TermDocument3 pagesMaths Mid TermElen UningNo ratings yet