Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Mechanics - Problem Set
Uploaded by
Karl GemayelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Mechanics - Problem Set
Uploaded by
Karl GemayelCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Problems Chapter 5 5. An electron of mass 9.11 1031 kg has an initial speed of 3.00 105 m/s.
s. It travels in a straight line, and its speed increases to 7.00 105 m/s in a distance of 5.00 cm. Assuming its acceleration is constant, (a) determine the force exerted on the electron and (b) compare this force with the weight of the electron, which we neglected.
F = 5.00 3.00 N , and F3 = 45.0 N , act on an object to give it i j i 2 2
an acceleration of magnitude 3.75 m/s . (a) What is the direction of the acceleration? (b) What is the mass of the object? (c) If the object is initially at rest, what is its speed after 10.0 s? (d) What are the velocity components of the object after 10.0 s?
i j 14. Three forces, given by F1 = 2.00 + 2.00 N ,
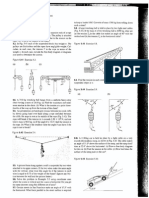
21. The systems shown in Figure P5.21 are in equilibrium. If the spring scales are calibrated in newtons, what do they read? (Neglect the masses of the pulleys and strings, and assume the incline in part (c) is frictionless.)
Figure P5.21
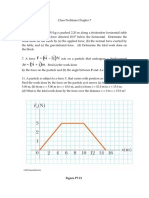
27. In the system shown in Figure P5.31, a horizontal force Fx acts on the 8.00-kg object. The horizontal surface is frictionless. (a) For what values of Fx does the 2.00-kg object accelerate upward? (b) For what values of Fx is the tension in the cord zero? (c) Plot the acceleration of the 8.00-kg object versus Fx. Include values of Fx from 100 N to +100 N.
Figure P5.31
36. A woman at an airport is towing her 20.0-kg suitcase at constant speed by pulling on a strap at an angle above the horizontal (Fig. P5.40). She pulls on the strap with a 35.0-N force, and the friction force on the suitcase is 20.0 N. Draw a free-body diagram of the suitcase. (a) What angle does the strap make with the horizontal? (b) What normal force does the ground exert on the suitcase?
Figure P5.40
You might also like
- GP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsDocument14 pagesGP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsUmbina Gescery100% (1)
- Assignment 3 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 PDFAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- Physics 4A Chapter 5 HW ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics 4A Chapter 5 HW Problemstannguyen8No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Solution PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment 3 Solution PDFAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- WS 1Document7 pagesWS 1melatsime609No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Muhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Serway and Jewett: 7 Edition 8 Edition Problems 1 5-14 5-16 2 5-43 5-47 3 6-10 6-6 4 6-13 6-14 5 6-15 6-17Document2 pagesSerway and Jewett: 7 Edition 8 Edition Problems 1 5-14 5-16 2 5-43 5-47 3 6-10 6-6 4 6-13 6-14 5 6-15 6-17Jonathan JackNo ratings yet
- Physics Sheet 3Document5 pagesPhysics Sheet 3MariamNo ratings yet
- 2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFDocument10 pages2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFAZTonseNo ratings yet
- Phys 699Document25 pagesPhys 699joseftrihandokoNo ratings yet
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocument26 pages2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25No ratings yet
- CP S HW CH 4Document8 pagesCP S HW CH 4nurhasanahNo ratings yet
- PHYF 115 Tutorial 5Document2 pagesPHYF 115 Tutorial 5Azri RahimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBacillus SubtilisNo ratings yet
- EM ModelDocument4 pagesEM ModelArunGopal PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- 2a Dynamics MCNDocument17 pages2a Dynamics MCNSnowy JiangNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2Document7 pagesPractice Test 2Maria YurlovaNo ratings yet
- Exam Review 3Document24 pagesExam Review 3api-223793512No ratings yet
- PHYF105 Tutorial Questions S3y0809edDocument17 pagesPHYF105 Tutorial Questions S3y0809edfillyana01No ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument55 pagesForces and MotionTreeicicles100% (3)
- Unit 3 FR Practice ANswersDocument4 pagesUnit 3 FR Practice ANswersXinyiNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document6 pagesCH 05Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- 2018 June Test PrepquestionsDocument14 pages2018 June Test PrepquestionsSiinozuko MasentseNo ratings yet
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDocument9 pagesPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNo ratings yet
- DynDocument7 pagesDynRyan LumNo ratings yet
- General Physics WorksheetDocument6 pagesGeneral Physics WorksheetDanielNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Linear DynamicsDocument11 pagesLinear DynamicsInfrion MatiqueonNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws PDFDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws PDFIntanrepuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 ForceDocument80 pages3.1 ForceMuhd AfifNo ratings yet
- Final Exam W07Document5 pagesFinal Exam W07Malik ANo ratings yet
- Practice Physics TestDocument7 pagesPractice Physics Testthey12No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentAishley MatharooNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Exemplar Chapter 5Document9 pages11 Physics Exemplar Chapter 5Raghav RathiNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy AsDocument4 pagesWork Power Energy Asdhruvrawat0409No ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Physics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Document12 pagesPhysics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Alexis Julia CanariaNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument26 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankdiemdac39kgkw100% (25)
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics StudentDocument13 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics StudentMark PaulNo ratings yet
- All AnswersDocument22 pagesAll AnswersNadiatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Uploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesUploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFRolando TorresNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (21 Feb 2007) - 1Document1 pagePHYSICS (21 Feb 2007) - 1Kierthianaa BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Practica Del Capítulo 6pDocument5 pagesEjercicios de Practica Del Capítulo 6pAbdul singhNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1Document4 pagesAssignment#1Anoosha ArshadNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument7 pagesForce & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Phy094 Tutorial 9 QDocument2 pagesPhy094 Tutorial 9 Qhafiz_yusoff1620No ratings yet
- Class Problems Chap 7 Physics 210 - Test BankDocument3 pagesClass Problems Chap 7 Physics 210 - Test BankKarim TabajaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Classical PhysicsDocument2 pagesPractice Questions For Classical PhysicsRaghavNo ratings yet
- ForumDocument10 pagesForumfestus wikannandaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic LectureDocument99 pagesDynamic LecturePob ParatNo ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy MCQs TestDocument26 pagesWork Power and Energy MCQs Testrizal123100% (1)
- Predicting Clinically Promising Therapeutic Hypotheses Using Tensor FactorizationDocument12 pagesPredicting Clinically Promising Therapeutic Hypotheses Using Tensor FactorizationKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- The Cook & Him - New & Old FavoritesDocument100 pagesThe Cook & Him - New & Old FavoritesKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- 2001 02775Document25 pages2001 02775Karl GemayelNo ratings yet
- 2022 12 07 22283238v1 FullDocument55 pages2022 12 07 22283238v1 FullKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- Starcraf With RLDocument22 pagesStarcraf With RLKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- Journal Pcbi 1002284-2Document11 pagesJournal Pcbi 1002284-2Karl GemayelNo ratings yet
- 2001 02574Document24 pages2001 02574Karl GemayelNo ratings yet
- HMM and Applications in Personalized Health DataDocument79 pagesHMM and Applications in Personalized Health DataKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0Document40 pagesLecture 0Karl GemayelNo ratings yet
- Computer Practical: Gibbs Sampling Model Answers: Model Code in PythonDocument3 pagesComputer Practical: Gibbs Sampling Model Answers: Model Code in PythonKarl GemayelNo ratings yet
- CP 4Document4 pagesCP 4justdlsNo ratings yet