Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Te 3000 Assignment 2
Uploaded by
PrasitOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Te 3000 Assignment 2
Uploaded by
PrasitCopyright:
Available Formats
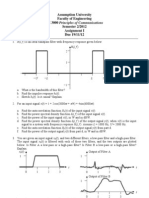
Assumption University Faculty of Engineering TE 3000 Principles of Communications Semester 2/2012 Assignment II Due 03/12/12
1. Digital communications is basically about transmitting 0 and 1. However, random noise and interference along the path may alter the signal and cause fault detections at the receiver (detected as 0 when 1 was sent, or detected as 1 when 0 was sent). Suppose the Bit Error Rate (BER), defined as the probability that the received bit is different from the transmitted bit, is equal to 0.1. If 0 is detected at the receiver, determine the probability that it is correct (i.e., 0 was sent) when: a. Probability of transmitting 0 is equal to Probability of transmitting 1 = 0.5 b. Probability of transmitting 0 = 0.1 Probability of transmitting 1 = 0.9
2. Referring to problem 1, to reduce the chance of error, we send 00000 instead of 0 and 11111 instead of 1, and the receiver of a message uses majority decoding (e.g., 10110 is decoded as 1). If the message 110 is sent as 11111 11111 00000, what is the probability that it will be correctly decoded by the receiver?
cxy 2 3. Given a joint probability density function; f ( x, y ) 0 a. Find the appropriate value of c. b. Find P(X<1,Y<1). c. Find P(1<Y<2.5). d. Find E[XY] 0 x3 0 y2 else
4. In an Electric Circuit class, the total score of students has normal distribution with mean equal to 60 and a standard deviation of 10. If the instructor wants only 5% of the class to get A, what is the lowest score for grade A? Note: Table of probability associated with Gaussian distribution can be found on the course website.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- EE2603 - Electronics Circuit Analysis - Assignment - 2/2012: ID No. Name: Sec. 61Document1 pageEE2603 - Electronics Circuit Analysis - Assignment - 2/2012: ID No. Name: Sec. 61PrasitNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Assignment 5Document1 pageAssignment 5PrasitNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Feedback AmplifiersDocument20 pagesFeedback AmplifiersPrasitNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Voltage RegulatorsDocument18 pagesVoltage RegulatorsPrasitNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Oscillator CircuitsDocument14 pagesOscillator CircuitsPrasit100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Linear Digital ICsDocument22 pagesLinear Digital ICsPrasit100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Op. Amp. Instrumentation CircuitsDocument15 pagesOp. Amp. Instrumentation CircuitsPrasitNo ratings yet
- Class A Power AmplifiersDocument13 pagesClass A Power AmplifiersPrasitNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- VCO, PLL Principles and ApplicationsDocument9 pagesVCO, PLL Principles and ApplicationsPrasitNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cascade and Cascode ConfigurationsDocument21 pagesCascade and Cascode ConfigurationsPrasit50% (2)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Class B Power AmplifiersDocument8 pagesClass B Power AmplifiersPrasitNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Op. Amp. Voltage AmplifiersDocument6 pagesOp. Amp. Voltage AmplifiersPrasitNo ratings yet
- Te 3000 Assignment 2Document1 pageTe 3000 Assignment 2PrasitNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Operational AmplifiersDocument18 pagesOperational AmplifiersPrasitNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- FET Amplifier Circuits AnalysisDocument15 pagesFET Amplifier Circuits AnalysisPrasitNo ratings yet
- Analysis of BJT CircuitsDocument14 pagesAnalysis of BJT CircuitsPrasitNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- CMOS, Current Source, Differential AmplifierDocument21 pagesCMOS, Current Source, Differential AmplifierPrasitNo ratings yet
- TE 3000 Principles of Communications - Assignment IVDocument1 pageTE 3000 Principles of Communications - Assignment IVPrasitNo ratings yet
- Te 3000 Assignment 1Document1 pageTe 3000 Assignment 1PrasitNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- TE 3000 Principles of Communications - Assignment IVDocument1 pageTE 3000 Principles of Communications - Assignment IVPrasitNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)Document35 pagesAmplitude Modulation (AM)PrasitNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Te 3000 Assignment 1Document1 pageTe 3000 Assignment 1PrasitNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lecture 10 - Discrete-Time Fourier Series - MITDocument15 pagesLecture 10 - Discrete-Time Fourier Series - MITPrasitNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)