Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorials MECH2308 Tutorial 10 2012 13
Tutorials MECH2308 Tutorial 10 2012 13
Uploaded by
sdo-30Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorials MECH2308 Tutorial 10 2012 13
Tutorials MECH2308 Tutorial 10 2012 13
Uploaded by
sdo-30Copyright:
Available Formats
MECH2308 Question One
Tutorial #10
Dec 2012
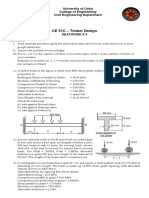
A timber beam is loaded and supported as shown in Figure. At section A-A of the beam, determine the shearing stresses on horizontal planes that pass through points a, b, and c of the cross section.
Question Two
A timber beam 4 m long is simply supported at its ends and carries a uniformly distributed load w of 8 kN/m over its entire length. If the beam has the cross section shown in Figure below, determine (a) The maximum horizontal shearing stress in the glued joints between the web and flanges of the beam. (b) The maximum horizontal shearing stress in the beam.
Question Three
A 5-m long simply supported timber beam carries two concentrated loads, as shown in fig. Determine: a) The reactions on both supports (RA and RD), b) The moment of inertia about the z-axis, c) The magnitude of the shear stress in the beam at point H in section a-a (), d) The maximum horizontal shear stress that occurs in the beam ( .), e) The bending stress that occurs in the beam at the neutral axis ().
MECH2308 Question Four
Tutorial #10
Dec 2012
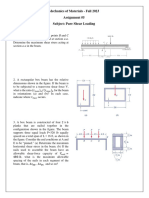
The beam shown in Figure a below is composed of three pieces of timber that are glued together as shown in Figure b below. Determine (a) The maximum horizontal shearing stress in the glued joints. (b) The maximum horizontal shearing stress in the wood. (c) The maximum tensile and compressive flexural stresses in the beam.
Question Five
A timber beam is simply supported and carries a uniformly distributed load of 4 kN/m over the full length of the beam. If the beam has the cross section shown in Figure and a span of 6 m, determine (a) The horizontal shearing stress in the glued joint 50 mm below the top of the beam and 1 m from the left support (b) The horizontal shearing stress in the glued joint 50 mm above the bottom of the beam and m from the left support. (c) The maximum horizontal shearing stress in the beam. (d) The maximum tensile flexural stress in the beam.
You might also like
- 01.structural Analysis Question (Qwah)Document26 pages01.structural Analysis Question (Qwah)linkesh balajeeNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Strength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument37 pagesStrength of Materials - Bending Stress in Beam - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen88% (26)
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- 2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedDocument12 pages2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedXprts Review100% (1)
- Bending StressDocument9 pagesBending StressUjjal Kalita 19355No ratings yet
- CE Board Problems in Steel DesignDocument10 pagesCE Board Problems in Steel DesignHomer Batalao75% (4)
- ProblemDocument3 pagesProblemChrisneil DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Subscribe To: (Helpful For Junior Engineer exams-WRD/ZP/PWD/ WCD/SSC)Document9 pagesSubscribe To: (Helpful For Junior Engineer exams-WRD/ZP/PWD/ WCD/SSC)civil techNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 4 For Topic 4Document3 pagesSeatwork 4 For Topic 4Jasper Jim LanajaNo ratings yet
- Btech Ce 8 Sem Prestressed Concrete 2011Document8 pagesBtech Ce 8 Sem Prestressed Concrete 2011Soudip patiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 V2Document3 pagesProblem Set 2 V2RalphNo ratings yet
- 2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsDocument6 pages2021 Theme 1 - Homework ProblemsMartin MugoniNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Im MechDocument16 pagesProblem Set Im MechRomel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Mechanicsofsolids Dec 2010Document10 pagesMechanicsofsolids Dec 2010simalaraviNo ratings yet
- Tutor Marked Assignment: BtwreDocument41 pagesTutor Marked Assignment: BtwrePranita JoshiNo ratings yet
- Railway Question Bank - MechanicalDocument181 pagesRailway Question Bank - Mechanicaluday bhaskar rajuNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 QuestionDocument2 pagesQuiz1 QuestionIsabella Womsiwor0% (1)
- ME202Document2 pagesME202nitinsparksNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials ProblemsDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials Problemsfaizal4yaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #5Document2 pagesAssignment #5mmdhmz875No ratings yet
- CE-303 Strength of Materials DEC 2014 PDFDocument2 pagesCE-303 Strength of Materials DEC 2014 PDFNeelam BhimwaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- IES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper IDocument15 pagesIES OBJ Civil Engineering 2007 Paper Iravi maharajNo ratings yet
- ES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Document3 pagesES 13 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Second Departmental Examination Samplex September 28, 2017 (6:00-8:00 PM) First Semester 2017-2018Carl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- StressDocument5 pagesStressmessel2013No ratings yet
- Structure Analysis - I Rce403Document3 pagesStructure Analysis - I Rce403SreNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)Document4 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- Foundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNDocument12 pagesFoundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNLata SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reg No.: - NameDocument3 pagesReg No.: - NameSijuKalladaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pure Bending PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment Pure Bending PDFFazir AzlanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument9 pagesMechanics of SolidsSrikanth GogineniNo ratings yet
- 55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IDocument16 pages55685698obj CivilEngineering 2005paper IAMIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- F 350 Mpa F 480 Mpa: Exam PractiseDocument4 pagesF 350 Mpa F 480 Mpa: Exam PractisePalesa TshetlanyaneNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 pagesMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Stress Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesStress Practice ProblemsSayantan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- M2 PDFDocument3 pagesM2 PDFVamsi GongallaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsharnishtanna21285No ratings yet
- HW#3Document9 pagesHW#3felipe GNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Beams: Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesStresses in Beams: Strength of MaterialsDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- FMEM MCQsDocument162 pagesFMEM MCQsjawaliyaabhishek1312No ratings yet
- T 06Document8 pagesT 06baskoroediNo ratings yet
- Mos 07062012Document2 pagesMos 07062012Bhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument8 pagesMechanics of SolidsKhaista RahmanNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument7 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: R15 R15 R15 R15Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: R15 R15 R15 R15mahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- Beam - Stresses - P and SDocument27 pagesBeam - Stresses - P and SDianne Rose M. MadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- (Ensc 13) Problem Set 4 - Stresses in BeamsDocument2 pages(Ensc 13) Problem Set 4 - Stresses in Beamslucas100% (1)
- QLM of SOMDocument4 pagesQLM of SOMatulkumargaur26No ratings yet
- M. Tech Degree ExaminationDocument3 pagesM. Tech Degree ExaminationvnkatNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Flexión Mecánica de Materiales: Ing. Miguel Arlenzo Durán Sarmiento, M.EngDocument6 pagesEjercicios Flexión Mecánica de Materiales: Ing. Miguel Arlenzo Durán Sarmiento, M.EngOscar Yesid Monsalve CelisNo ratings yet
- TEST (2) .Prestressed Conc RFCD (3) ..Date: 9/12/2020 Semester 8 A) B)Document2 pagesTEST (2) .Prestressed Conc RFCD (3) ..Date: 9/12/2020 Semester 8 A) B)Abdirazak Sama WadeNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set04Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set04rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Flexure Formula Stresses in BeamsDocument18 pagesFlexure Formula Stresses in BeamsAthena YoungNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural MechanicsDocument8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering CIVL2201 Structural Mechanicssky willaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument8 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFprashanthreddy26No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Lattice MaterialsFrom EverandDynamics of Lattice MaterialsA. Srikantha PhaniNo ratings yet