Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC-DC Part 6 Double
Uploaded by
Defne AktemizCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DC-DC Part 6 Double
Uploaded by
Defne AktemizCopyright:
Available Formats
Prof. S.
Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 1]
Output Voltage Ripple, Parasitic Effects
6.1 Output voltage ripple (Buck) 6.2 Parasitic effects 6.2.1 Diode recovery 6.2.2 Internal delay of switching 6.2.3 Stray and leakage inductances Clamp Diode snubber (clamp) Switch snubbers
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 2]
Output voltage ripple
S Vin control D L IL IC C R IR
IL
Iav t
IR
Iav
DC
Assumption: Low output ripple voltage
t IC Capacitor Current AC t
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 3]
IC
t1
IL 2
Ts
Ripple
IL
t2
VC
Vc
Q VC = ; C
Q = IL dt;
t1
t2
Q =
IL Ts 1 ; 2 2 2
Q =
IL Ts 8
VC =
IL 1 8C fs
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 4]
IL = Vo t off / L
IL =
Vo VD Doff Ts = o off L Lfs
VoDoff 1 VD = o off 2 CLfs 8fs 8CLfs
Ripple
VC =
The effect of fs
I =
VoDoff Lfs
VC = IL 8fsC
L; fs can be traded for same I C;fs can be traded for same I& VC if fs is increased for given L, C
VC =
VoDoff
2 8LCfs
VC goes down -40 db/dec (second order)
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 5]
S Vin control D
L IL
Example
IC C R IR
IL = 1A C = 47 F
Ts = 10 S ESR = 10 m
Find the output voltage ripple V
VC =
1A 10 S = 25 mV 8 47F
VESR = 10 m 1A = 10 mV
zApproximate
(upper limit) of total ripple)
V = VC + VESR = 25 mV + 10 mV = 35 mV
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 6]
Application of Simulation
10meg R4 D1 Dbreak V1 {Vin} L1 {L1} L2 {L1*(n*n)} out_gnd C1 220u IC = 6 RL {Load} out
drain
0
V1 = 0 V2 = 15 TD = 0 TR = 0.01u TF = 0.01u PW = 10u PER = 20u
gate V2
S1
+ +
Sbreak
K K1 K_Linear COUPLING = 1 L1 = l1 L2 = l2
PARAM ET ERS:
n = 0.5 Vin = 12 L1 = 300u Load = 10
Modify circuit to include ESR=100m Find ripple at output
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 7]
Diodes Recovery Implications
L Vin Vx C Vo R
Reverse current at switch turn on
zSoft
and hard recovery
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 8]
Stages in diode recovery
Lstray Lstray ESR Lstray
Diode voltage
VD
t VO VDmax
Lstray Lstray ESR
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 9]
Turn off of transistor
Lmain Lstray
Lmain Lstray Co Vo ESR
Lstray
Lstray Lstray
V DS VO t
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 10]
Diode forward recovery
I
+VC
I
t VD VPK VF t
clamp
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 11]
Parasitic effects: Internal delay
To turn on
RL
RL
RG CGS Vgs LS
(real) Vgs
Vgs
V'gs
Depend on Q
Q=
LS Cgs RL + R G
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 12]
Clamps
limiting maximum voltage
Vin
Vo
Vin
VO
Vds
Ipk
Llkg Cdss
Llkg Cdss
V DS VO t
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 13]
Solutions
Vin n:1 VO Vin n:1 VO
Llkg Cdss
Very fast diode Rc Cc
Llkg
Vz > Vin + Vo = Vin + nVo
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 14]
Simple Example
Vin
A
Vin
Clamp B is better from the point of view of efficiency.
VC ( A ) = Vin + Vo
But ...
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 15]
Parasitic inductance
Vin L1
Energy of L1 L2 L3 L4 will cause high spike on C (FET). The FET is not protected!
C L2 L3 L4
Rule:
Connect clamps and snubbers directly to the elements to be protected
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 16]
To protect FET
Vin Line
D LD
Line
Still:
RG LS S
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 17]
Designing the Snubber Components
Vin Rc Cc Llkg
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 18]
Snubber
VCc
Vav
Ts
+
' Vo
L lkg Ip CC R C VCc
Parasitic energy Ipav
VCc Cc
Rc
VCc > Vo
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 19]
Leakage discharge
Ipk
Ip
dI dt
Ip av Rc = VCc av Rc Cc = T > Ts
tp
dIp VCc av Vo ' = dt L lkg
tp =
L lkg Ipk VCc av Vo '
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 20]
Leakage average current
Ip av = Ipk t p fs 2
Procedure 1. Select VCc av 2. Calculate Ip av 3. Select R c = VCc av Ip av
4. Select Cc T > Ts 5. Trim in-circuit
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 21]
Simulation Exercise
10meg R4 D1 Dbreak V1 {Vin} drain L1 {L1} L2 {L1*(n*n)} out_gnd C1 220u IC = 6 RL {Load} out
0
V1 = 0 V2 = 15 TD = 0 TR = 0.01u TF = 0.01u PW = 10u PER = 20u
gate V2
S1
+ +
Sbreak
K K1 K_Linear COUPLING = 1 L1 = l1 L2 = l2
PARAM ET ERS:
n = 0.5 Vin = 12 L1 = 300u Load = 10
Add 1uH leakage to Flyback converter. Design a clamp and check it by simulation.
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 22]
Diode Snubber (clamp)
Vo
CD
Lstray
Lstray
Diode Snubber
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 23]
Snubber waveforms
VD
CS RS VO
no snubber
bad snubber
Vo
CD Lstray
VD
good snubber
CS is very l arg e VO
Cs > CD V 2CS 2
Energy lost to snubber
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 24]
Snubber design
Design - use simulation in circuit tuning Needed information Ipk ( Reverse ) Lstray
CS R S Lstray Ipk VO
L stray Ipk 2
moves to Cs Vo + V
R s damping
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 25]
Switch Snubbers
control
VGS
t
VS
VS
IS
Jd Pswitching
t
Switching losses due to overlap Pd linear with fS !
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 26]
Snubber types
Snubbers = control of
dV snubbers dt dI snubbers dt
dV dI or dt dt
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 27]
Snubber types
Passive (dissipative) snubber Energy lost to heat Non-dissipative (lossless) snubber Energy recovered Passive Snubbers by passive network Active snubbers by auxiliary active devices
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 28]
Switching overlap
control
VGS
t
VS dI dt dV dt
t
Jp
IS
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 29]
Switch Snubber
Vo
dV
dt (at turn off) can be slow down by adding external snubber capacitor C
Vo
At turn off
Cdss
C
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 30]
dV/dt
dV I = dt C + Cdss Cdss - output capacitance of FET I = 1 Amp C + Cdss= 1nF
dV 1 103 = 9 = 6 = 1 kV S dt 10 10
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 31]
Capacitor losses
C
2
Vo
Problem at turn on !
CVO EC = (J ) 2
CV Pd = O fs 2
Example : VO = 400 V C = 1 nF fs = 100 kHz Pd = 10 9 16 10 4 105 = 8 W 2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 32]
Solution
VO CS RS
VO
Snubbing
CS
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 33]
Reset
VO CS RS
RDSon
If Rds on < Rs most energy will be lost to Rs Heat Selection of Cs Selection of Rs to ensure reset
T=
1 << t on R sC s
t on 4R sCs
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 34]
CV 2 2
Losses
Cdss
2 Cdss Vmax fs lost to heat 2
Linear with fs ! Switching losses (overlap) also linear with fs !
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 35]
Lossless snubbing (simple example)
Q1
C1 C2
VC 2 VC 2
t
Q2
delay
t
IL
C1 , C2 of transistor plus external (if any)
VDS1
t
VDS2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters
[6- 36]
Dead time requirement
Q1
t
Q2
delay
t
IL
VDS1
t
VDS2
You might also like
- 10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument69 pages10ESL37 - Analog Electronics Lab ManualVinita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsFrom EverandElectrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Passive DevicesDocument72 pagesChapter 7 Passive DevicessvijiNo ratings yet
- Oscillator Design Amp Computer Simulation Randall W RheaDocument318 pagesOscillator Design Amp Computer Simulation Randall W Rheachanghye2000No ratings yet
- Vcos in Ads 699Document19 pagesVcos in Ads 699Amit JhaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsFrom EverandHigh Voltage Direct Current Transmission: Converters, Systems and DC GridsNo ratings yet
- Sequential Logic Flip Flops TimingDocument7 pagesSequential Logic Flip Flops TimingHarshal AmbatkarNo ratings yet
- Noise Sources of MOSFETDocument11 pagesNoise Sources of MOSFETDerunNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory and Design of Power Factor Correction Power SuppliesDocument51 pagesCircuit Theory and Design of Power Factor Correction Power Supplies양영주No ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply CalculationsDocument4 pagesSwitching Power Supply CalculationsEdilson TavaresNo ratings yet
- SIwave Training 2016 - Signal and Power Integrity Analysis For Complex PCBs and IC PackagesDocument153 pagesSIwave Training 2016 - Signal and Power Integrity Analysis For Complex PCBs and IC Packagesrey_hadesNo ratings yet
- 5635.under The Hood of Flyback SMPS DesignsDocument41 pages5635.under The Hood of Flyback SMPS DesignsAntochi CiprianNo ratings yet
- Eecs242 Lect3 RxarchDocument34 pagesEecs242 Lect3 Rxarchp3erezNo ratings yet
- FM - PM Demodulation - The Phase Lock LoopDocument5 pagesFM - PM Demodulation - The Phase Lock LoopSunit Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- Quadrature RC Oscillators The Van Der Pol Approach by João Carlos Ferreira de Almeida Casaleiro, Luís Augusto Bica Gomes Oliveira, Igor M. FilanovskyDocument166 pagesQuadrature RC Oscillators The Van Der Pol Approach by João Carlos Ferreira de Almeida Casaleiro, Luís Augusto Bica Gomes Oliveira, Igor M. Filanovskypedro pancoatl100% (1)
- Feedback CircuitsDocument47 pagesFeedback CircuitsPatrick SerandonNo ratings yet
- 5 Current Mode Control ModelingDocument12 pages5 Current Mode Control ModelingzmrbillNo ratings yet
- Precision Curvature-Compensated CMOS Bandgap ReferenceDocument10 pagesPrecision Curvature-Compensated CMOS Bandgap ReferenceAnonymous TPVfFif6TONo ratings yet
- Electron Devices and Circuits (EDC)Document7 pagesElectron Devices and Circuits (EDC)Sudalai Madan100% (1)
- Spice Parameter CalculatorDocument14 pagesSpice Parameter Calculatorhamid_kh_56No ratings yet
- Review Test Submission - ACK5 - 2016 Fall - ELEN 5324 - 48F.Document3 pagesReview Test Submission - ACK5 - 2016 Fall - ELEN 5324 - 48F.DarshanRavalNo ratings yet
- Inductor Loss Calcs VishayDocument12 pagesInductor Loss Calcs VishayealbinNo ratings yet
- 25510-A New Calculation For Designing Multi Layer Planar Spiral Inductors PDFDocument4 pages25510-A New Calculation For Designing Multi Layer Planar Spiral Inductors PDFkiband1No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices LectureDocument78 pagesPower Electronics Devices LectureM Waqar ZahidNo ratings yet
- 模拟CMOS集成电路设计(拉扎维 Razavi)答案Document307 pages模拟CMOS集成电路设计(拉扎维 Razavi)答案就爱吃饭团No ratings yet
- Spice Convergence Troubleshooting (BEST)Document18 pagesSpice Convergence Troubleshooting (BEST)Alexandre PennaNo ratings yet
- 123145619Document4 pages123145619hal0g3nNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Control of A Gas Pressure Reduction SystemDocument339 pagesModelling and Control of A Gas Pressure Reduction SystemErick Renzo Hidalgo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Top-Down Digital VLSI Design: From Architectures to Gate-Level Circuits and FPGAsFrom EverandTop-Down Digital VLSI Design: From Architectures to Gate-Level Circuits and FPGAsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Switched-Capacitor Common-Mode Feedback CircuitDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Switched-Capacitor Common-Mode Feedback CircuitDebopam Banerjee100% (1)
- LTspice ManualDocument206 pagesLTspice ManualGhiles Khelil100% (1)
- A High Performance Reference BGR Circuit With Improved Input Offset Voltage of Op-AmpDocument7 pagesA High Performance Reference BGR Circuit With Improved Input Offset Voltage of Op-AmpPriyanka SirohiNo ratings yet
- Ece Ade Manual 500 CopiesDocument79 pagesEce Ade Manual 500 CopiesRajkumarNo ratings yet
- 0471317780Document21 pages0471317780haribabu448No ratings yet
- Class Ab Output BufferDocument4 pagesClass Ab Output BufferrivercamNo ratings yet
- A Review of Recent MOSFET VTH Extraction MethodsDocument14 pagesA Review of Recent MOSFET VTH Extraction Methodshpnx9420No ratings yet
- CMOS Comparator Architectures ComparisonDocument4 pagesCMOS Comparator Architectures Comparisonj4everNo ratings yet
- State Space Averaging Model of Boost ConvDocument60 pagesState Space Averaging Model of Boost ConvBharti Thakur100% (1)
- Resistive Circuits: Chapter 3 in Dorf and SvobodaDocument47 pagesResistive Circuits: Chapter 3 in Dorf and Svobodaananzo3biNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Passive Elements With ASITICDocument20 pagesModeling of Passive Elements With ASITICKyusang ParkNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersFrom EverandHigh Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- SMPSRM DDocument73 pagesSMPSRM DtemplpaNo ratings yet
- ECEN 214 - Electrical Circuit Theory Fall 2017: Smiller@tamu - EduDocument4 pagesECEN 214 - Electrical Circuit Theory Fall 2017: Smiller@tamu - EduAllie JuneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Switched-Inductor Regulators With Design Insight and Intuition (Power IC Design)Document119 pagesChapter 7. Switched-Inductor Regulators With Design Insight and Intuition (Power IC Design)Minh Hai RungNo ratings yet
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksFrom EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksNo ratings yet
- A CMOS Bandgap Reference Circuit With Sub-1V OperationDocument5 pagesA CMOS Bandgap Reference Circuit With Sub-1V Operationbooky_mookyNo ratings yet
- A New Low Voltage, High PSRR, Cmos Bandgap Voltage ReferenceDocument4 pagesA New Low Voltage, High PSRR, Cmos Bandgap Voltage ReferenceBodhayan PrasadNo ratings yet
- 665report - Design of CMOS Ring VCO and Quadrature LC VCO For 8 Phases GenerationDocument17 pages665report - Design of CMOS Ring VCO and Quadrature LC VCO For 8 Phases GenerationapplebeeNo ratings yet
- STM32F4-Discovery Keil TrainingDocument32 pagesSTM32F4-Discovery Keil TrainingDefne AktemizNo ratings yet
- USB HID 01163aDocument26 pagesUSB HID 01163aGustavo Circelli100% (1)
- (Altium Tutorial) PCB Symbol Naming ConventionDocument7 pages(Altium Tutorial) PCB Symbol Naming ConventionDefne AktemizNo ratings yet
- Rittel+Webber "Dilemmas in A General Theory of Planning"Document15 pagesRittel+Webber "Dilemmas in A General Theory of Planning"Kenya WheelerNo ratings yet
- Timber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsDocument24 pagesTimber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsOmul Fara NumeNo ratings yet
- Final Annotated BibiliographyDocument4 pagesFinal Annotated Bibiliographyapi-491166748No ratings yet
- Week 4 Gen EconDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Gen EconGenner RazNo ratings yet
- Winkens Et Al 2009Document8 pagesWinkens Et Al 2009Marta SanchezNo ratings yet
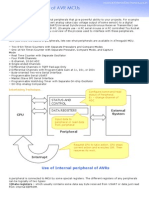
- Internal Peripherals of Avr McusDocument2 pagesInternal Peripherals of Avr McusKuldeep JashanNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument31 pagesStaining TechniquesKhadija JaraNo ratings yet
- Oral Medication PharmacologyDocument4 pagesOral Medication PharmacologyElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Ahu, Chiller, Fcu Technical Bid TabulationDocument15 pagesAhu, Chiller, Fcu Technical Bid TabulationJohn Henry AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Fjords Blue Web ENG PDFDocument20 pagesFjords Blue Web ENG PDFMoldovan MirceaNo ratings yet
- 2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFDocument430 pages2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFBrianCook73% (11)
- Lean Management AssignmentDocument14 pagesLean Management AssignmentElorm Oben-Torkornoo100% (1)
- People v. Lagarto, 326 SCRA 693 (2000)Document43 pagesPeople v. Lagarto, 326 SCRA 693 (2000)GioNo ratings yet
- AIOUDocument2 pagesAIOUHoorabwaseemNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermocoupleDocument3 pagesLaws of ThermocoupleMourougapragash SubramanianNo ratings yet
- 1571-1635319494618-Unit 04 Leadership and ManagementDocument48 pages1571-1635319494618-Unit 04 Leadership and ManagementdevindiNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis FoundationsDocument39 pagesBusiness Analysis FoundationsPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications TechnicianDocument4 pagesTelecommunications Technicianapi-78381064No ratings yet
- Inventory Storage and Retrieval System PatentDocument15 pagesInventory Storage and Retrieval System PatentdevanasokaNo ratings yet
- Abbreviation Meaning Notes: Cibo ("With Food")Document4 pagesAbbreviation Meaning Notes: Cibo ("With Food")TantriNo ratings yet
- Serv7107 V05N01 TXT7Document32 pagesServ7107 V05N01 TXT7azry_alqadry100% (6)
- United Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesDocument4 pagesUnited Airlines Case Study: Using Marketing to Address External ChallengesSakshiGuptaNo ratings yet
- Maths SolutionDocument10 pagesMaths SolutionAbhay KumarNo ratings yet
- More Than Moore: by M. Mitchell WaldropDocument4 pagesMore Than Moore: by M. Mitchell WaldropJuanjo ThepresisNo ratings yet
- A61C00100 Communication and Employee Engagement by Mary Welsh 2Document19 pagesA61C00100 Communication and Employee Engagement by Mary Welsh 2Moeshfieq WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Delhi (The Capital of India) : Ebook by Ssac InstituteDocument27 pagesDelhi (The Capital of India) : Ebook by Ssac InstituteAnanjay ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed - Assessment and Evaluation of Learning Part 1-4Document8 pagesProf. Ed - Assessment and Evaluation of Learning Part 1-4Marisol Altobar PalatinoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabDocument9 pagesOrganic Chem Diels-Alder Reaction LabPryanka BalleyNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Application FormDocument13 pagesAppendix 1 Application FormSharifahrodiah SemaunNo ratings yet
- Class Opening Preparations Status ReportDocument3 pagesClass Opening Preparations Status ReportMaria Theresa Buscato86% (7)
- Inspection and Acceptance Report: Stock No. Unit Description QuantityDocument6 pagesInspection and Acceptance Report: Stock No. Unit Description QuantityAnj LeeNo ratings yet