Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Control Model
Uploaded by
Chi Hin Ho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesThe document discusses several strategic business models including generic competitive strategies, Porter's five forces model, Porter's value chain, and the business control model. It analyzes the restaurant industry using Porter's five forces model and finds that buyer bargaining power and the threat of substitutes are medium to high while supplier bargaining power and threat of new entry are lower. Rivalry in the industry is deemed high.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several strategic business models including generic competitive strategies, Porter's five forces model, Porter's value chain, and the business control model. It analyzes the restaurant industry using Porter's five forces model and finds that buyer bargaining power and the threat of substitutes are medium to high while supplier bargaining power and threat of new entry are lower. Rivalry in the industry is deemed high.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesBusiness Control Model
Uploaded by
Chi Hin HoThe document discusses several strategic business models including generic competitive strategies, Porter's five forces model, Porter's value chain, and the business control model. It analyzes the restaurant industry using Porter's five forces model and finds that buyer bargaining power and the threat of substitutes are medium to high while supplier bargaining power and threat of new entry are lower. Rivalry in the industry is deemed high.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Generic Competitive Strategies Model
Generic Competitive Strategies
Can a firm adopt cost leadership and differentiation strategies simultaneously? Research by Greg Dess, Peter Davis and Rod White, suggests this is possible. Examples can be found of businesses which have been able to jointly follow overall low cost and high quality differentiation strategy.
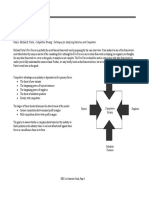
Porter's Five Forces Model
Buyer's Bargaining Power is high since:
Buyers have many restaurant choices Buyer switching costs are low Threat of backward integration is high Buyer is price sensitive Product is undifferentiated Substitutes are available
Supplier's Bargaining Power is low since:
There are many supplying sources Switching costs are low Threat of forward integration is low Buyer is price sensitive Purchase large volumes of standardized products
Threat of New Entry is Medium since:
Profitability requires economies of scale Brand names are well-known Location is an issue Consumer switching costs are low Proprietary technology is not an issue Government policy is not an issue
Threat of Substitutes is medium-high since:
Consumer switching costs are low Substitute product is cheaper than industry product
Intensity of Rivalry is high since:
Competitors are numerous Industry growth is slow Fixed costs are high Brand loyalty is insignificant Consumer switching costs are low Exit barriers are high
Porter's Value Chain
The Value System
Critical Success Factors Analysis
Business Control Model
You might also like
- Porter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4Document28 pagesPorter's Five Forces: HBS Case Interview Guide, Page 4mariaNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- Supply Chain Risk ManagementDocument45 pagesSupply Chain Risk ManagementSabir AliNo ratings yet
- Porter - S Six Forces ModelDocument37 pagesPorter - S Six Forces ModelSaad Naeem100% (1)
- Porter's Five Force AnalysisDocument24 pagesPorter's Five Force AnalysisAman Oza R100% (1)
- Porter 5 F ModelDocument7 pagesPorter 5 F Modelsaurabhtiwari2102No ratings yet
- Strategic Frameworks - Ready Reckoner PDFDocument20 pagesStrategic Frameworks - Ready Reckoner PDFShishir SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- 5 Forces OverviewDocument1 page5 Forces OverviewRohail AmjadNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces Model Is An Analysis Tool That Uses Five Industry Forces ToDocument4 pagesPorter's Five Forces Model Is An Analysis Tool That Uses Five Industry Forces ToAanchal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Customers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsDocument32 pagesCustomers: - Suppliers - CompetitorsanashussainNo ratings yet
- How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy: Your Presenters: Omair Arif Vaseer Shahzeb KhalilDocument30 pagesHow Competitive Forces Shape Strategy: Your Presenters: Omair Arif Vaseer Shahzeb KhalilOmair ArifNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Industry AnalysisDocument83 pagesUnit3 Industry AnalysisAbhishek AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Competitive Structure of IndustriesDocument28 pagesCompetitive Structure of IndustriesRavi Sharma100% (1)
- Porters Five Forces - TKIMDocument13 pagesPorters Five Forces - TKIMHuhyhuthut HutNo ratings yet
- Unit II Competitve AdvantageDocument147 pagesUnit II Competitve Advantagejul123456No ratings yet
- Generic Strategies: Market & Resource Based Strategic OptionsDocument23 pagesGeneric Strategies: Market & Resource Based Strategic OptionsDavid HermanNo ratings yet
- Five Forces ModelDocument11 pagesFive Forces ModelNicole ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- MB403 Unit 17 Generic StrategiesDocument19 pagesMB403 Unit 17 Generic StrategiesArneet SarnaNo ratings yet
- 5 PortarDocument37 pages5 Portartanmoy2000No ratings yet
- 5 ForcesDocument2 pages5 ForcesNakulParuthiNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryDocument2 pagesPorter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryJohn FaustorillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To All Five Strategies Competitive Advantages How To Achieve? Key Success Advantages and Pitfalls ExamplesDocument35 pagesIntroduction To All Five Strategies Competitive Advantages How To Achieve? Key Success Advantages and Pitfalls ExamplesSaurabh ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Poters Five ForcesDocument27 pagesPoters Five ForcesRachana ShettyNo ratings yet
- Strategy NotesDocument22 pagesStrategy NotesNoah AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Generic StrategiesDocument37 pagesGeneric StrategiesSneha KarpeNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy Module 3Document41 pagesBusiness Strategy Module 3arun prabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Competitor Analysis1Document15 pagesCompetitor Analysis1malatheshNo ratings yet
- Porters 5 Force ModelDocument18 pagesPorters 5 Force Modelnike_4008aNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Business-Level StrategyDocument40 pagesChapter 5: Business-Level StrategyNadeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Business Unit Strategic AlternativesDocument53 pagesSession 4 Business Unit Strategic AlternativesNarayana Reddy100% (1)
- Evergreening Generic StrategiesDocument35 pagesEvergreening Generic StrategiesAbhinandanNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?Document21 pagesThe Five Generic Competitive Strategies - : Which One To Employ?RajatNo ratings yet
- What Is An Industry?Document16 pagesWhat Is An Industry?North East University Business ClubNo ratings yet
- Gaining Comptv AdvDocument24 pagesGaining Comptv Advprakrit23No ratings yet
- Strategic Management in The Multinational Company: Content and FormulationDocument18 pagesStrategic Management in The Multinational Company: Content and FormulationGvz HndraNo ratings yet
- Product Policy of An Organization and Selection of A Profitable ProductDocument16 pagesProduct Policy of An Organization and Selection of A Profitable ProductarunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 Product Policy of An Organization and Selection of Profitable ProductsDocument16 pagesLecture 03 Product Policy of An Organization and Selection of Profitable ProductsVimal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Competitive AdvantageDocument41 pagesCompetitive AdvantageDr.Niraj RBL SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Sourcing: Dr. Kunal GhoshDocument72 pagesStrategic Sourcing: Dr. Kunal GhoshPankaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Siom GLS: Strategic Sourcing & Material Management Datta Kenjale 9881128282Document53 pagesSiom GLS: Strategic Sourcing & Material Management Datta Kenjale 9881128282Power IsoNo ratings yet
- STRM 05Document44 pagesSTRM 05Professor Dr. Md. Atiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 5 Forces & 7 SDocument22 pages5 Forces & 7 SLeesa RathiNo ratings yet
- References Notes Module 2 Corporate StrategyDocument27 pagesReferences Notes Module 2 Corporate StrategyPurna Chandra MohantyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Strategy and Competitive AdvantageDocument76 pagesModule 5 - Strategy and Competitive AdvantagehyraldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Porter, Industry AnalysisDocument6 pagesChapter 8 - Porter, Industry AnalysisNathalie ChahrourNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy: Knowledge ObjectivesDocument18 pagesBusiness Strategy: Knowledge ObjectivesNando GontaniNo ratings yet
- Competition: Smriti Bajaj SahniDocument17 pagesCompetition: Smriti Bajaj SahniAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Formulating Long-Term Objectives and Grand StrategiesDocument40 pagesFormulating Long-Term Objectives and Grand StrategiesGandhesNo ratings yet
- Topic-3 Generic Competitive Strategies 29.8.19Document26 pagesTopic-3 Generic Competitive Strategies 29.8.19AARTI PAREWANo ratings yet
- Generic Startegies: Name of InstitutionDocument21 pagesGeneric Startegies: Name of InstitutionNikita SangalNo ratings yet
- 4890 CHPT 5, The Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument46 pages4890 CHPT 5, The Five Generic Competitive Strategiesniki399yNo ratings yet
- The Changing Outsourcing Paradigm From Service To Strategic Partnership - A Sponsor ViewDocument39 pagesThe Changing Outsourcing Paradigm From Service To Strategic Partnership - A Sponsor ViewrainwatercloudsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 SMDocument58 pagesLecture 2 SMadil azmiNo ratings yet
- Generic StrategiesDocument36 pagesGeneric StrategiesEmbuhmas BroNo ratings yet
- Long Term StrategyDocument30 pagesLong Term StrategyEka DarmadiNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces in Market CompetitionDocument4 pagesPorter's Five Forces in Market CompetitionMd. Ziawr RahmanNo ratings yet
- Business Level StarategiesDocument91 pagesBusiness Level StarategiesKashvi ShahNo ratings yet
- Business-Level Strategy: Hassan Abbas - Bs AnfDocument21 pagesBusiness-Level Strategy: Hassan Abbas - Bs AnfMahik (Father Name:Mukesh Kumar)No ratings yet
- Winning Behavior (Review and Analysis of Bacon and Pugh's Book)From EverandWinning Behavior (Review and Analysis of Bacon and Pugh's Book)No ratings yet