Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Chapter 3 Updated
Tutorial Chapter 3 Updated
Uploaded by
Jeffrey TehCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Chapter 3 Updated
Tutorial Chapter 3 Updated
Uploaded by
Jeffrey TehCopyright:
Available Formats
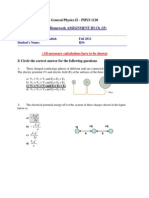
BAHAGIAN MATRIKULASI KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA TUTORIAL 3 (ELECTROSTATIC) 1.
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are 3 m apart, and their total charge is 20 C, determine the magnitud of the charges. a. If one repels the other with a force of 0.075 N.( So the Qs are 5 and 15 C ) b. If one attracts the other with a force of 0.525N. (Q1 and Q2 will be 35 and -15 C or -35 and 15 C) Q2 Three +20-C charges are place along straight line, successive charges being 2 m apart. Calculate the force on the right end.( F = 0.225 + 0.9 = 1.125 N to the right)
2.
2m Q1 3. 4. Q2
2m Q3
F1
F2
One charge (+5 C) is placed at x = 0 and a second charge (+ 7 C) at x = 100 cm. Where can a third change be placed and experience zero net force due to the other two? An infinite thin sheet of charge has a uniform surface charge density of 7.2 nC/m2. Charge configurations of this type create uniform electric field on each side of the sheet. Determine the electric field created by this sheet of charge.(E = 4.07 x10 2 Vm 1 ). The electric strength of air is about 3.0 x 106 N/C. If the electric field exceeds this value, sparking will occur. What is the largest charge a 0.50-cm-radius metal sphere can hold if sparking is not occur in the air surrounding it?( Q = 8.34 nC ). A uniform electric field of magnitude 250 N/C makes an angle of 350 with normal to a circular aperture of radius 65 cm. If the aperture lies entirely in the electric field, what is the electric flux through the aperture?( = 270 N m2 /C) A particle of charge 22.4 mC and mass 57.2 mg is initially held at rest in a constant electric field of 133 V/m. If the particle is released and accelerates through a distance of 14.9 m, determine a. the change in potential energy.( U = - 44.4J) b. the change in electrical potential.( V = -1.98 kV) c. its final speed.( v = 1.25 x103 m/s ) A pendulum with a bob of mass 10 g is charged q. The electric force, F between q and q1 enables the pendulum bob standstill with an angle of 300 as shown in the diagram below.
5.
6.
7.
8.
If q1 has a charge of +1.0x10-6C and distance of 5 cm from the bob, q, determine the charge of q? (q = 1.57x10-3C)
300 F r = 5cm 9. A point charge Q1 is at a distance of 6 m with another point charge, Q2. Q1 and Q2 has values +3.0x10-1C and -4.0x10-1C respectively. Calculate: a) electric field, E in the middle of the two charges.( E1 and E2 are in the same direction, the resultant vector E = 7x108 N/C with positive x-axis direction.) b) electric potential, V at point in the middle of the two charges. Explain the difference between answer a) and b).( V =- 3 x 108 V) A uniform electric field is established by connecting the plates of a parallel-parallel plate capacitor to a 12-V battery. a) If the plates are separated by 0.75 cm, what is the magnitude of the electric field in the capacitor?( E = 1600 V/m) b) A charge of +6.24x10-6C moves from the positive plate to the negative plate. Find the change in electric potential energy for this charge. ( In electrical system we shall assume the gravity can be ignored, unless specifically instructed otherwise.). ( U = -7.5x10-5 J) The electrons in a TV picture tube are accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 25kV. What is the speed of the electrons after they have been accelerated by this potential difference?( v = 9.4x107 m/s)
q1
10.
11.
BAHAGIAN MATRIKULASI KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA ANSWERS 1. a. Q1 + Q2 = 20 C Since the force is repulsive, F = TUTORIAL
kQ1Q2 r2
9.0 x109 xQ1Q 2 0.075 = 32 Q1Q2 = 75 C2 Substituting for Q2 = 20 Q1, Q1(20 Q1) = 75 Q12 -20Q1 + 75 = 0 So the Qs are 5 and 15 C b. The force is attractive, so one of the charge is negative. 9 x109 Q1Q 2 The equation will be 0.525 = 32 2 Q1Q2 = 525 C Substituting for Q2 = 20 Q1, Q1(20 Q1) = 525 Solving quadratic equation, Q12 -20Q1 + 525 = 0 So Q1 and Q2 will be 35 and -15 C or -35 and 15 C.
2. F1 + F2 = F QQ 9 x10 9 x ( 20 x10 6 ) 2 F1 = k 1 2 3 = = 0.225 N r 42 F2 =
9 x10 9 x ( 20 x10 6 ) 2 = 0.9 N 22
F = 0.225 + 0.9 = 1.125 N to the right 3. We assume that appropriate location for our test charge is at position x as shown below.
100 - x x F1 q F2 q2 = 7 C
q1 = 5C
If the test charge q is negative, q1 and q2 will attract q in opposite directions; if it is positive, q1 and q2 will repel q in opposite directions. In either case, the condition for q to experience no net force is that F1 = F2, kq1 q 2 kq1 q 2 = 2 x (1 x) 2 2x2 +10x -5 = 0
b b 2 4ac 2a = 0.46m @ 0.055m x12 =
Since x must lie between the two charges, the answer is 0.46 m. 4. Sketch an infinite sheet of charge. E= 20
= 7.2nCm 2 8.85 x10 12 Fm 1
= 4.07 x10 Vm 1
2
5.
E=
Q 40 r 2
r = 5 x10 -3 m E = 3.0 x106 N /C Q = 8.34 nC 6. Area, A = r2 Electric flux, = E r2 cos = (250 N/C) (0.65m)2 cos (350) = 270 N m2 /C 7. 4
a. b. c.
W = Fd = q E d U = - W = -(22.4 x10-3)(133) (14.9) = - 44.4J V = U/q = - 44.4 / 0.0224 = -1.98 kV K = - U = mv2 v = [ -2(U)/m] = [ -2 (44.4) / 57.2 x10-6]1/2 = 1.25 x103 m/s
8.
Sketch free body diagram on q
300 W
F W
tan 30 =
F ; W
F = W tan30 = (10 x10-3 )(9.8)tan 30 = 5.66x10-3 F=k 5.66x10 =
-3
qq 1 r2
(5x10 2 ) 2
9 x10 9 x1x10 6 q
9.
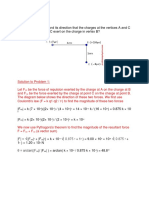
a)
E2 Q1 +3x10-1C E1 Q2 -4.0x10-1C
q r2 3x10 1 2 E1 = 9x109 3 = 3x108 N/C 4 x10 1 2 E2 = 9x109 3 = 4x 108 N/C
Given E = k
As E1 and E2 are in the same direction, the resultant vector E = 7x108 N/C with positive x-axis direction. b) Given V = k Resultant Both answers are different since E is an addition of vector quantity and V is an addition of scalar quantity. 10. a) Sketch a diagram as below.
q r
b) E=c) 11.
V 12 == 1600 V/m s 0.0075
U = q V = (6.24x10-6)(-12V) = -7.5x10-5 J Conservation of energy: U = K U = qV K = mv2 0 v=
2qV = m
2 x1.6 x10 19 x 25x10 3 =9.4x107 m/s 31 9.1x10
You might also like
- University Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFDocument1 pageUniversity Physics 13th Edition Solution Manual PDFMohammed Rashwan32% (19)
- 3 Zbiór Zadań Z Elektrotechniki - Aleksy Markiewicz Rozwiązania Od 3.1do3.71Document70 pages3 Zbiór Zadań Z Elektrotechniki - Aleksy Markiewicz Rozwiązania Od 3.1do3.71Michael45% (11)
- Cou LombDocument50 pagesCou LombJm RezanoNo ratings yet
- Physics II Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics II Finals ReviewerCarter SiyNo ratings yet
- HW 1 - CH 21 - Answers PDFDocument4 pagesHW 1 - CH 21 - Answers PDFmalonz030% (1)
- RadiativeDocument150 pagesRadiativejunjunhiromuNo ratings yet
- Coulomb Law Quiz Review AnswersDocument3 pagesCoulomb Law Quiz Review AnswersLina PinzónNo ratings yet
- FAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFDocument25 pagesFAP0025 Tutorial Solutions PDFRuben BenjaniNo ratings yet
- PHY193 Bab 3Document25 pagesPHY193 Bab 3Muhamad Fairul Nizam AzonanNo ratings yet
- E2 121 09-PreviewDocument14 pagesE2 121 09-PreviewTremendous JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential: Answers To QuestionsDocument26 pagesElectric Potential: Answers To QuestionsgaferoprNo ratings yet
- 23 - 26 - solutions 물리Document9 pages23 - 26 - solutions 물리전삼기No ratings yet
- Topic 2Document9 pagesTopic 2Bebo KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Chapter 23Document5 pagesPhysics Questions Chapter 23hamadaxx2000100% (1)
- W V W QV Q: 6 4 Ba Ba Ba BaDocument4 pagesW V W QV Q: 6 4 Ba Ba Ba BaDr. Halim AhamadNo ratings yet
- Respuestas de TallerDocument5 pagesRespuestas de TallerSergio Andres Molina MendietaNo ratings yet
- 10d-Electrostatics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSDocument15 pages10d-Electrostatics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSzeustamNo ratings yet
- Part Test 10Document79 pagesPart Test 10Srinivasarao SrinuNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (Part 1-Student Copy)Document40 pagesElectrostatics (Part 1-Student Copy)CasioEnervon100% (1)
- Module 5 - Modern PhysicsDocument23 pagesModule 5 - Modern PhysicsANGELO NINO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Potential Energy & Electric PotentialDocument6 pagesPotential Energy & Electric Potentialroamabdul1986100% (1)
- The E Field and Voltage-SolutionsDocument6 pagesThe E Field and Voltage-SolutionsRosalinaNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 1 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesTest Paper 1 ElectrostaticsPratik SharmaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsapi-283216587No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - ElectrostaticsDocument33 pagesUnit 3 - Electrostaticsshinichi_kesian6117No ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 2Document15 pagesPhysics Assignment 2Vines 747No ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Electric Potential: ProblemDocument9 pagesChapter 25 Electric Potential: ProblemMd SiamNo ratings yet
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Document7 pages3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument23 pagesNcert Solutions Class12 Physics Electric Charges and FieldsRaja KarmaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics HotDocument10 pagesElectrostatics HotShane LaraNo ratings yet
- JTKDocument26 pagesJTKThe GeruaaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Previous Year Solved Questions On Electrostatics PDFDocument10 pagesJEE Main Previous Year Solved Questions On Electrostatics PDFsumitsagar2405No ratings yet
- Solved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014Document21 pagesSolved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014believer149No ratings yet
- 07 08 II ms1Document5 pages07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesHomework 1 SolutionsmohdaficationNo ratings yet
- Phy DOC-20240417-WA0011.Document9 pagesPhy DOC-20240417-WA0011.neeharika.maringantiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxDocument17 pagesTopic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxSmk Abdul Rahim Dua100% (1)
- Ch22 SSM-1Document31 pagesCh22 SSM-1alyxs_1No ratings yet
- PHYSICS Test DemoDocument20 pagesPHYSICS Test Demomohits822No ratings yet
- Problem and Solution Electric FieldDocument10 pagesProblem and Solution Electric FieldSansen Diamante Colipano Jr.No ratings yet
- 2.short Answer Type IDocument3 pages2.short Answer Type IJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Problem and Solution Electric FieldDocument10 pagesProblem and Solution Electric FieldSansen Diamante Colipano Jr.No ratings yet
- UNIT EdittedDocument76 pagesUNIT EdittedNatalieCmFNo ratings yet
- Exam 2003 AnswersDocument10 pagesExam 2003 AnswersShootingStarPhotonsNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and EnergyDocument6 pagesElectric Potential and Energykw2533No ratings yet
- Tutorial 01 Electrostatics t2 2012 2013Document6 pagesTutorial 01 Electrostatics t2 2012 2013胡宇晟No ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law2Document8 pagesCoulomb's Law2Francisco BarreraNo ratings yet
- Homework HelpDocument7 pagesHomework HelpRodney Lucas50% (2)
- ch25 PDFDocument21 pagesch25 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Document20 pagesGrade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Priyanka KanaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields (Ws 2)Document2 pagesElectric Charges and Fields (Ws 2)samsung tabletNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedDocument98 pagesChapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument28 pagesElectrostaticssonaliswain2345No ratings yet
- Review Physics 3Document24 pagesReview Physics 3Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- Capacitors Solved Sheet For IITDocument8 pagesCapacitors Solved Sheet For IITSourabh DhavalaNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Engineering Medical Physics Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 pagesCBSE 12 Engineering Medical Physics Electric Charges and FieldsReena JainNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Ch11-Sound Waves PDFDocument5 pagesCh11-Sound Waves PDFJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- Heat Physics SPMDocument33 pagesHeat Physics SPMJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Electrostatics: Understanding Electrical Charges of Its Characters and PhenomenaDocument47 pagesChapter 3 - Electrostatics: Understanding Electrical Charges of Its Characters and PhenomenaJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionDocument40 pagesNuclear ReactionJeffrey Teh50% (2)
- APA StyleDocument7 pagesAPA StyleJeffrey TehNo ratings yet
- 04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - Ch9)Document95 pages04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - Ch9)Shobit JainNo ratings yet
- Electrothermal Processes 243Document74 pagesElectrothermal Processes 243Eduardo Elí Garcia JimenezNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument98 pagesPhysicsFGGC MINJIBIR100% (1)
- Takaaki Musha - Explanation of Dynamical Biefeld-Brown Effect From The Standpoint of ZPF FieldDocument6 pagesTakaaki Musha - Explanation of Dynamical Biefeld-Brown Effect From The Standpoint of ZPF FieldRtpomNo ratings yet
- M° (VH$ (DKMZ: Phys IcsDocument10 pagesM° (VH$ (DKMZ: Phys IcsLakshy Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- PacitoDocument66 pagesPacitonikadnisNo ratings yet
- Board Questions Chapter 1Document15 pagesBoard Questions Chapter 1nehapriyadharshini cbeiarchNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Muscle Response Testing MRTDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To Muscle Response Testing MRTJuan Aguilar HernándezNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test - Electric Potential PDFDocument1 pageChapter Test - Electric Potential PDFJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields All DerivationsDocument9 pagesElectric Charges and Fields All DerivationsFlame kaiserNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical MeasurementsDocument9 pagesBasic Electrical MeasurementsSyamsul Bahri HsNo ratings yet
- Phs 1201 Assignment 01 2021Document2 pagesPhs 1201 Assignment 01 2021Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Serway PSE Quick ch25Document21 pagesSerway PSE Quick ch25Ar Yan0% (1)
- P2B Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument13 pagesP2B Electric Forces and Electric FieldscyruselilNo ratings yet
- Questions Model PDFDocument3 pagesQuestions Model PDFfacebook userNo ratings yet
- David K. Cheng - Field and Wave ElectromagneticsDocument515 pagesDavid K. Cheng - Field and Wave Electromagneticsnikee7285% (26)
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument5 pagesElectric Charges and FieldEunbyeolNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 16 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture2 16 PDFjeez janiNo ratings yet
- Emtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabusDocument1 pageEmtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabussubramanyamNo ratings yet
- Charges and Fields 2020Document5 pagesCharges and Fields 2020reynandcpcNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Field 2 Lec3Document7 pagesElectrostatic Field 2 Lec3Sudesh Fernando Vayanga SubasinghaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Electric Field On An Insulator String Using The Finite Elements MethodDocument4 pagesCalculation of The Electric Field On An Insulator String Using The Finite Elements Methodostojic007No ratings yet
- 13 - ElectrostaticsDocument8 pages13 - Electrostaticsp_k_soni_iit_physics78% (9)
- Phys12 SM 07 6Document7 pagesPhys12 SM 07 6Adi SinghNo ratings yet
- Nature of ElectricityDocument11 pagesNature of ElectricityJohn Christian HensonNo ratings yet
- Chap 01 Electric Charges and Field (Notes)Document23 pagesChap 01 Electric Charges and Field (Notes)Uves AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and WavesDocument776 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and WavesM Rokhmat Isnaini50% (2)