Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GRND LVL Conc of Unburned Flammable Gas Joe Wong Checked
Uploaded by
ankur20610 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
Grnd Lvl Conc of Unburned Flammable Gas Joe Wong Checked
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageGRND LVL Conc of Unburned Flammable Gas Joe Wong Checked
Uploaded by
ankur2061Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
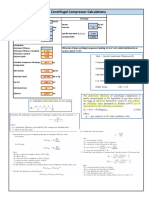
Subject : Ground-Level Concentration of Unburned Flammable Gas
Author : Ankur Srivastava (Chemical Engineer) ankur_2061@hotmail.com
Checked : JoeWong webwormcpt.wwcpt@gmail.com
Reference : Section 15.11, Handbook of Chemical Engineering Calculations, 3rd Edition, Nicholas P. Chopey
WebBlog : Chemical & Process Technology Subscribe FREE News Letter Subscribe FREE CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Ground-Level Concentration of Unburned Flammable Gas
Momentum Plume Rise (Plume rise due to gas exit velocity), H
Maximum Ground-Level Concentration
where: Inputs
H = Plume rise due to gas exit velocity, m Mass flow of gas release through flare, Q 90720 kg/h
d = flare tip diameter, m Height of flare stack, H 61 m
V
ex
= Exit velocity from flare tip, m/s Diameter of flare tip, d 0.46 m
U = Wind Speed, m/s Exit velocity from flare tip, V
ex
83.8 m/s
Wind Speed, U 3.1 m/s
Effective Flare Stack Height, H' Molecular weight of the gas 54
Calculations
where: Mass flow of gas release, Q 25200.0 g/s
H' = effective flare stack height, m Momentum plume rise, H 37.3 m
H = flare stack height, m Effective flare stack height, H' 98.3 m
H = Plume rise due to gas exit velocity, m Max. ground level concentration, C 0.193 g/m
3
193 mg/m
3
Maximum Ground Level Concentration, C Max. ground level concentration, C in ppm 87.6 ppm
where:
C = max. ground level concentration, g/m
3
Q = Mass flow of gas release, g/s
U = wind speed, m/s
H' = effective flare stack height, m
Converting mg/m
3
to ppm
where:
MW = molecular weight of the gas
Disclaimer : The information and methods included within this spreadsheet are presented for common sharing and
intended to be used by technically skilled persons at their own discretion. I do not warrant the suitability or accuracy of
these methods.
U
V d
H
ex
= A
3
H H H A + = '
2
'
23 . 0
H U
Q
C
=
|
.
|
\
|
=
MW
m mg ppm
45 . 24
/
3
You might also like
- Mine VentilationDocument37 pagesMine VentilationKemal Cengiz100% (3)
- Aspen Flare System Analyzer: Getting Started GuideDocument57 pagesAspen Flare System Analyzer: Getting Started GuideHaris ShahidNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis in Reciprocating CompressorsDocument11 pagesVibration Analysis in Reciprocating Compressorsakamalapuri388No ratings yet
- Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosions (Bleve) Jes VenartDocument17 pagesBoiling Liquid Expanding Vapour Explosions (Bleve) Jes Venartgambito2000No ratings yet
- Instrument Process Datasheet ChecklistDocument1 pageInstrument Process Datasheet Checklistankur2061No ratings yet
- P&ID Check ListDocument3 pagesP&ID Check Listankur2061No ratings yet
- 4528.07.R380.02 ShellDocument26 pages4528.07.R380.02 ShellAnil B YadavNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Calculations: Suction Discharge Input ParametersDocument1 pageCentrifugal Compressor Calculations: Suction Discharge Input Parametersankur20610% (1)
- Process Modeling Using HYSYS NGL Fractionation TrainDocument18 pagesProcess Modeling Using HYSYS NGL Fractionation TrainNasroNo ratings yet
- Pilot Valve SizingDocument4 pagesPilot Valve SizingJason ThomasNo ratings yet
- Reboiler Selection ChartDocument1 pageReboiler Selection Chartankur2061No ratings yet
- Dispersion ModellingDocument4 pagesDispersion ModellingSigma HSENo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor SealsDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Compressor SealsHadi ShahsavanNo ratings yet
- Spray - Chapter 4 - Advanced TopicsDocument73 pagesSpray - Chapter 4 - Advanced TopicsEslam ShiblNo ratings yet
- Draft in ChimneyDocument9 pagesDraft in ChimneyMunaf TamboliNo ratings yet
- Time Dependent Gas Leak Outflow Through HoleDocument14 pagesTime Dependent Gas Leak Outflow Through Holeankur2061No ratings yet
- Group C: Benefits and ConsequencesDocument16 pagesGroup C: Benefits and ConsequencesMohamad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Instrument Process Datasheet (IPDS)Document3 pagesInstrument Process Datasheet (IPDS)Vraja KisoriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Plant Start Up & Shut DownDocument16 pagesChapter 6 - Plant Start Up & Shut DownDharshica MohanNo ratings yet
- Atrium Natural Smoke CalculationsDocument5 pagesAtrium Natural Smoke CalculationsRamiAl-fuqahaNo ratings yet
- Phast: Tutorial ManualDocument42 pagesPhast: Tutorial ManualNitesh KirnakeNo ratings yet
- Process Calculation - Purge Gas CalculationDocument1 pageProcess Calculation - Purge Gas CalculationmakamahamisuNo ratings yet
- Impact of Emergency Shutdown Devices On Relief System Sizing and Design PDFDocument21 pagesImpact of Emergency Shutdown Devices On Relief System Sizing and Design PDFB rgNo ratings yet
- Equipment Process Data Sheet ChecklistDocument1 pageEquipment Process Data Sheet Checklistankur2061100% (1)
- Burner Management System PresentationDocument63 pagesBurner Management System Presentationankur2061100% (1)
- Design of Hoppers Using Spreadsheet: Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research January 2010Document7 pagesDesign of Hoppers Using Spreadsheet: Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research January 2010ankur2061No ratings yet
- Hibernia Study (Flare)Document178 pagesHibernia Study (Flare)bmgarisNo ratings yet
- Hysys TascDocument10 pagesHysys TascMariano PodestáNo ratings yet
- Flare Modeling ParametersDocument25 pagesFlare Modeling Parametersf3byz100% (1)
- Design of LPG Refigeration System: 1. Copper TubesDocument20 pagesDesign of LPG Refigeration System: 1. Copper TubesJeevan Landge PatilNo ratings yet
- Flare Modeling ParametersDocument26 pagesFlare Modeling ParametersHarryBouterNo ratings yet
- Workbook For Chemical Reactor Relief System SizingDocument123 pagesWorkbook For Chemical Reactor Relief System SizingRicardo BecNo ratings yet
- Vessel Analytical Calculation For:: InputsDocument2 pagesVessel Analytical Calculation For:: InputsmakamahamisuNo ratings yet
- Choice of Runaway Reaction Scenarios For Vent Sizing Based Onpseudo Adiabatic Calorimetric TechniquesDocument48 pagesChoice of Runaway Reaction Scenarios For Vent Sizing Based Onpseudo Adiabatic Calorimetric TechniquesgiovanniNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Depressuring PDFDocument16 pagesDynamic Depressuring PDFAsimNo ratings yet
- Basic Surge Control System: FCV CoolerDocument2 pagesBasic Surge Control System: FCV Coolerankur2061No ratings yet
- Basicflowmeasurement 150428100633 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument50 pagesBasicflowmeasurement 150428100633 Conversion Gate02 PDFankur2061No ratings yet
- Training CaseDocument15 pagesTraining CaseThái Xuân QuangNo ratings yet
- Comparison DGF and IGF UnitsDocument1 pageComparison DGF and IGF Unitsankur2061No ratings yet
- Acid Dew PointDocument1 pageAcid Dew Pointankur2061No ratings yet
- Flare Sweep GasDocument5 pagesFlare Sweep GasChem.EnggNo ratings yet
- Consider Bottom Venting For Reactive LiquidDocument10 pagesConsider Bottom Venting For Reactive LiquidAndri SaputraNo ratings yet
- Manual Flare Sim ExproDocument69 pagesManual Flare Sim ExproJuan Pablo AlonsoNo ratings yet
- OilStabOptimization PDFDocument30 pagesOilStabOptimization PDFNgoc Le LeNo ratings yet
- Calculating Two-Phase Pressure Drop: Flow TypeDocument8 pagesCalculating Two-Phase Pressure Drop: Flow TyperondonjjNo ratings yet
- Getting Start Hysys UnisimDocument38 pagesGetting Start Hysys UnisimBassem BalghouthiNo ratings yet
- PSSCV ZixxingDocument2 pagesPSSCV ZixxingShashi Kant KumarNo ratings yet
- PFD Check ListDocument2 pagesPFD Check Listankur2061No ratings yet
- Pipenet Vision Training Manual Standard: Chapter 4 Page 1 of 36 REVISION 2.1, SEP 2010Document36 pagesPipenet Vision Training Manual Standard: Chapter 4 Page 1 of 36 REVISION 2.1, SEP 2010ToyinNo ratings yet
- Trans Chapter6 PDFDocument106 pagesTrans Chapter6 PDFsammar_10No ratings yet
- Materials: Drying in TraysDocument10 pagesMaterials: Drying in TraysMira FazziraNo ratings yet
- Slug Flow Analysis ProcedureDocument1 pageSlug Flow Analysis ProcedureNeeraj NaikNo ratings yet
- Inprocess-BP Lingen Project ArticleDocument3 pagesInprocess-BP Lingen Project Articlejrz85No ratings yet
- Tube Rupture. Dynamic SimulationDocument5 pagesTube Rupture. Dynamic SimulationAbbasNo ratings yet
- HP New Analysis For FlaresDocument0 pagesHP New Analysis For Flareskataria200784No ratings yet
- Calculation of Relief Rate Due To External Heat Input For Dense Phase FluidsDocument3 pagesCalculation of Relief Rate Due To External Heat Input For Dense Phase FluidsphantanthanhNo ratings yet
- Pipenet PresentationDocument22 pagesPipenet Presentationpurwanto_tfits100% (1)
- Effect of Gas Lock in Transient Flow in HDPEDocument1 pageEffect of Gas Lock in Transient Flow in HDPEBhupendra PalNo ratings yet
- Case Study Vent SizingDocument5 pagesCase Study Vent SizingLluís Vidales SerresNo ratings yet
- Vent To Flare 1683883352Document31 pagesVent To Flare 1683883352saheem_783617392No ratings yet
- Application BriefsDocument149 pagesApplication BriefsJorge Luis HernándezNo ratings yet
- User's GuideDocument30 pagesUser's GuideAnonymous Wd2KONNo ratings yet
- OLGA 7-NotesDocument10 pagesOLGA 7-NotesraminabkNo ratings yet
- HP-LP Flare KO Drum SizingDocument2 pagesHP-LP Flare KO Drum SizingmadithakNo ratings yet
- Ipa-Water SeparationDocument8 pagesIpa-Water SeparationkashifwarsiNo ratings yet
- 3832-assomadi-PU-X-2-MODEL GAUSS Untuk DISPERSI Pencemar Udara PDFDocument40 pages3832-assomadi-PU-X-2-MODEL GAUSS Untuk DISPERSI Pencemar Udara PDFAfi LANo ratings yet
- XLXDocument14 pagesXLXVương Đình NamNo ratings yet
- Energies: Physical and Chemical Properties of Waste From PET Bottles Washing As A Component of Solid FuelsDocument17 pagesEnergies: Physical and Chemical Properties of Waste From PET Bottles Washing As A Component of Solid FuelsCQ SHONo ratings yet
- Recip RISK Rating Chart 2015Document9 pagesRecip RISK Rating Chart 2015romoexNo ratings yet
- CourseNotes HeatExchangers2008Document76 pagesCourseNotes HeatExchangers2008Jorge Giovanny Vásquez CárdenasNo ratings yet
- A Loop Thermosyphon For Asphalt Tank HeatingDocument6 pagesA Loop Thermosyphon For Asphalt Tank Heatingankur2061No ratings yet
- Natural Convection Heat Transfer From Vertical HelDocument9 pagesNatural Convection Heat Transfer From Vertical Helsachins1318No ratings yet
- Glycolysis PET WasteDocument13 pagesGlycolysis PET Wasteankur2061No ratings yet
- Protectoseal Emergency Vent Application Worksheet: Service ConditionsDocument1 pageProtectoseal Emergency Vent Application Worksheet: Service Conditionsankur2061No ratings yet
- High Purity Oxygen ( 99.5%) Production Using Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption (VPSA)Document2 pagesHigh Purity Oxygen ( 99.5%) Production Using Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption (VPSA)ankur2061No ratings yet
- Tank Steam Heating Overall HTC Heavy FODocument2 pagesTank Steam Heating Overall HTC Heavy FOankur2061No ratings yet
- General Guiidelines For Precommissioning and Commissioning A Chemical Process PlantDocument2 pagesGeneral Guiidelines For Precommissioning and Commissioning A Chemical Process Plantankur2061100% (1)
- Hyperfocal Distance CalculatorDocument28 pagesHyperfocal Distance Calculatorankur2061No ratings yet
- Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion (BLEVE) Fireball Diameter & DurationDocument2 pagesBoiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion (BLEVE) Fireball Diameter & Durationankur2061No ratings yet
- LECTURE 06 Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationDocument10 pagesLECTURE 06 Equipment Sizing and Capital Cost EstimationSomayeh SarabadanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of C6 Plus HCs in Natural GasDocument6 pagesCharacterization of C6 Plus HCs in Natural Gasankur2061No ratings yet
- PFD Check ListDocument2 pagesPFD Check Listankur2061No ratings yet
- Boiloff Gas Calcs For LNG TanksDocument1 pageBoiloff Gas Calcs For LNG Tanksankur2061No ratings yet
- General Guiidelines For Precommissioning and Commissioning A Chemical Process PlantDocument2 pagesGeneral Guiidelines For Precommissioning and Commissioning A Chemical Process Plantankur2061100% (1)
- PFD Check ListDocument2 pagesPFD Check Listankur2061No ratings yet
- Chapter2 ToxicologyDocument4 pagesChapter2 ToxicologyS JNo ratings yet
- Fermenter Design: Mahesh BuleDocument82 pagesFermenter Design: Mahesh BuleSagar DhuriNo ratings yet
- Machine Reliability in Parallel Operations: Re (%) 100 PF Liability PDocument4 pagesMachine Reliability in Parallel Operations: Re (%) 100 PF Liability Pankur2061No ratings yet