Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pages From New Math Book - Part2-4
Uploaded by
Nhocticaro NhocOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pages From New Math Book - Part2-4
Uploaded by
Nhocticaro NhocCopyright:
Available Formats
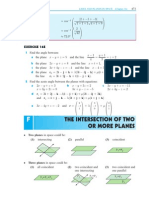
LINES AND PLANES IN SPACE (Chapter 16)
475
None of the planes are parallel. ) the line of intersection of any two is parallel to the third plane. (diag (8)) Case (2) If m 6= 1 there is a unique solution. (m 1)z = 9 m2 ) (m + 1)z = m2 9 m2 9 ) z= m+1
From row 2, 2y z = 0 ) y = 1 2z = From row 1, x = 3y + z =
m2 9 2(m + 1)
9 m2 3(m2 9) 2(m2 9) + = 2(m + 1) 2(m + 1) 2(m + 1)
The three planes meet at a unique point (diag (6)) 9 m2 m2 9 m2 9 , , provided m 6= 1. 2(m + 1) 2(m + 1) m + 1 b Comparing with a, 2 m = 1 and 9 m2 = 8 ) m = 1 8 8 8 ) the three planes meet at the point 4 , 4 , 2 , i.e., (2, 2, 4).
Example 24
a b Find the intersection of the planes: Hence solve: x + y + 2z = 2 2x + y z = 4 xyz =5 a The augmented matrix 1 2 1 1 x + y + 2z = 2 2x + y z = 4 Give a geometric interpretation of your result. 2 1 2 4 1 0 1 1 2 5 2 0
The system is consistent with infinite solutions. Let z = t so y = 5t, x = 2 + 3t, t 2 R are the solutions, ) the two planes meet in the line x = 2 + 3t, y = 5t, z = t, t 2 R : ! Note: This line passes through (2, 0, 0) has direction vector b
3 5 1
The solutions of the first 2 equations are x = 2 + 3t, y = 5t, z = t ffrom ag Substitution into the third equation gives 2 + 3t + 5t t = 5 ) 7t = 3 ) t= 3 7 15 3 ) x = 23 , y = , z = 7 7 7 15 3 ) the three planes meet at the unique point 23 7 , 7 , 7 .
476
LINES AND PLANES IN SPACE (Chapter 16)
EXERCISE 16F
1 a1 x + b1 y + c1 z = d1 a2 x + b2 y + c2 z = d2 ? b Under what conditions will the planes in a be: i parallel ii coincident? c Solve the following using elementary row operations and interpret each system of equations geometrically: i x 3y + 2z = 8 ii 2x + y + z = 5 iii x + 2y 3z = 6 3x 9y + 2z = 4 xy+z = 3 3x + 6y 9z = 18 a How many solutions are possible when solving simultaneously:
2 Discuss the possible solutions of the following systems where k is a real number. Interpret the solutions geometrically: a x + 2y z = 6 b x y + 3z = 8 2x + 4y + kz = 12 2x 2y + 6z = k 3 For the eight possible geometric solutions of three planes in space, comment on the possible solutions in each case. For example,
Pz=Px=Pc
has infinitely many solutions where x, y and z are expressed in terms of two parameters s and t.
4 Solve the following systems using elementary row operations and in each case state the geometric meaning of your solution: a x + y z = 5 b x y + 2z = 1 c x + 2y z = 8 x y + 2z = 11 2x + y z = 8 2x y z = 5 4x + y 5z = 18 5x 2y + 5z = 11 3x 4y z = 2 d xy+z = 8 2x 2y + 2z = 11 x + 3y z = 2 e x + y 2z = 1 xy+z = 4 3x + 3y 6z = 3 f xyz = 5 x+y+z = 1 5x y + 2z = 17
5 Solve the system of equations
x y + 3z = 1 2x 3y z = 3 3x 5y 5z = k where k takes all real values. State the geometrical meaning of the different solutions.
6 Find all values of m for which x + 2y + mz = 1 2x + y z = 3 mx 2y + z = 1 has a unique solution. In the cases where there is no unique solution, solve the system. Give geometrical meanings to all possible solutions. Illustrate each case. 7 Find if and where the following planes meet: P1 : r1 = 2i j + (3i + k) + (i + j k) P2 : r2 = 3i j + 3k + r(2i k) + s(i + j) P3 : r3 =
2 1 2
! +t
1 1 0
! u
0 1 2
LINES AND PLANES IN SPACE (Chapter 16)
477
REVIEW SET 16A (2-D)
1 Find a the vector equation b the parametric equations 4 of the line that passes through (6, 3) with direction 3 .
2 Find the vector equation of the line which cuts the y-axis at (0, 8) and has direction 5i + 4j. x 18 7 = + t . Find m. 3 (3, m) lies on the line with vector equation y 2 4 4 Find the velocity vector of an object that is moving in the direction 3i j with a speed of 20 km h1 . 5 A particle at P(x(t), y(t)) moves such that x(t) = 4 + 8t and y (t) = 3 + 6t, where t > 0 is the time in seconds. The distance units are metres. Find the: a initial position of P b position of P after 4 seconds c speed of P d velocity vector of P. p 6 A yacht is sailing at a constant speed of 5 10 km h1 in the direction i 3j. Initially it is at point (6, 10). A beacon is at (0, 0) at the centre of a tiny atoll. a Find in terms of i and j : i the initial position vector of the yacht ii the direction vector of the yacht iii the position vector of the yacht at any time t hours, t > 0. b Find the time when the yacht is closest to the beacon. c If there is a reef of radius 8 km around the atoll, will the yacht hit the reef? 1 7 Submarine X23 is at (2, 4). It fires a torpedo with velocity vector 3 at exactly 1 2:17 pm. Submarine Y18 is at (11, 3). It fires a torpedo with velocity vector a at 2:19 pm to intercept the torpedo from X23. a b c d Find x1 (t) and y1 (t) for the torpedo fired from submarine X23. Find x2 (t) and y2 (t) for the torpedo fired from submarine Y18. At what time does the interception occur? What was the direction and speed of the interception torpedo?
8 Trapezoid (trapezium) KLMN is formed by the lines: x 2 5 x 33 11 line 1 (KL) is = + p ; line 2 (ML) is = + q ; y 19 2 y 5 16 x 3 4 x 43 5 = + r ; line 4 (MN) is = + s line 3 (NK) is y 7 10 y 9 2 where p, q, r and s are scalars. a b c d Which two lines are parallel? Why? Which lines are perpendicular? Why? Use vector methods to find the coordinates of K, L, M and N. Calculate the area of trapezium KLMN.
You might also like
- Maths-2B Previous Question Papers (Intermediate Education, Andhra Pradesh)Document10 pagesMaths-2B Previous Question Papers (Intermediate Education, Andhra Pradesh)Edara Rajesh Kumar82% (34)
- 10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFDocument15 pages10 04 Angle Between Two Curves PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-3Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-3Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- 2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Document5 pages2413, Practice Exam 3, FA14Matthew LuNo ratings yet
- m7 REVIEW PDFDocument6 pagesm7 REVIEW PDFSkyezine Via Kit FoxNo ratings yet
- Holdays ExerciseDocument3 pagesHoldays ExerciseFraterne BiraboneyeNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus Sample ExamDocument5 pagesMultivariable Calculus Sample ExamFaithBoaz21No ratings yet
- Text 1b emDocument13 pagesText 1b emkrishNo ratings yet
- Two Marks QuestionsDocument12 pagesTwo Marks QuestionsSsNo ratings yet
- Teknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009Document25 pagesTeknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009adeksam72No ratings yet
- Linear AlgebraDocument6 pagesLinear AlgebraPeterNo ratings yet
- Teacher 20081012 1758Document4 pagesTeacher 20081012 1758Lulu LiuNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1BDocument2 pagesMathematics 1Bgouthamyadav701No ratings yet
- Neta Calculus of VariaionSolnDocument107 pagesNeta Calculus of VariaionSolnsticker592No ratings yet
- Blue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question PaperDocument14 pagesBlue Print: Class Xii Maths: Model Question Paperapi-243565143No ratings yet
- Revision Mathematics TDocument5 pagesRevision Mathematics TZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Add MathsDocument40 pagesAdd MathsJoseph TingNo ratings yet
- FinalReviewSem1 (2010)Document11 pagesFinalReviewSem1 (2010)Benjamin NgNo ratings yet
- DTP 1 2 3Document6 pagesDTP 1 2 3Anonymous rePT5rCrNo ratings yet
- Revision Maths Paper 1Document31 pagesRevision Maths Paper 1JILEDAR PAL100% (1)
- Add Maths SPMDocument21 pagesAdd Maths SPMPusat Tuisyen Siswa MudaNo ratings yet
- 17 Exercise Set FeDocument3 pages17 Exercise Set FeMarione Thea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CLASS - XII-MATHS Diff&Appl of DiffDocument11 pagesCLASS - XII-MATHS Diff&Appl of DiffNICKNo ratings yet
- 9th Third Term PDFDocument9 pages9th Third Term PDFaktsanthamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Math DifferentiationDocument9 pagesForm 4 Add Math DifferentiationYouwer WeiNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument27 pagesMathsprabhamathsNo ratings yet
- Add Maths DifferentiationDocument44 pagesAdd Maths DifferentiationShakynna ParasinNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Parametrics, Vectors, Polar S16Document8 pagesREVIEW Parametrics, Vectors, Polar S16Shruthik AlleNo ratings yet
- Review For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Document16 pagesReview For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Ian StantonNo ratings yet
- TN Board Class 12 Questions and Answers Maths 2019Document24 pagesTN Board Class 12 Questions and Answers Maths 2019Hema SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Math 40s Standards Test - Trigonometry I QUESTIONSDocument17 pagesPre-Calculus Math 40s Standards Test - Trigonometry I QUESTIONShmdniltfiNo ratings yet
- Third Perp 2023Document4 pagesThird Perp 2023Omar MohamedNo ratings yet
- Math HL Revision PackDocument21 pagesMath HL Revision Packpoocamaccotta100% (4)
- 1b Important QuestionDocument4 pages1b Important QuestionÇháråñ ÇhèrryNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam of Math100 (All Lecture Sections, Fall 2008) : A B A BDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam of Math100 (All Lecture Sections, Fall 2008) : A B A Bsfluk2No ratings yet
- Differentiation Worksheet 1Document2 pagesDifferentiation Worksheet 1DanelNo ratings yet
- Math S6Document8 pagesMath S6sugi mugiNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII HOTS Three Dimensional Geometry Chapter 11Document3 pagesCBSE XII HOTS Three Dimensional Geometry Chapter 11Om Prakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Calculus Multivariable 6Th Edition Hughes Hallett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesEbook Calculus Multivariable 6Th Edition Hughes Hallett Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbeatrixkhuyen9rm100% (8)
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDocument55 pagesMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88No ratings yet
- Hci JC 2Document7 pagesHci JC 2Hang VuongNo ratings yet
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Document39 pagesApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Final ExamDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra Final ExamDaniel TarantinoNo ratings yet
- Section-A Note:-: R R F R RDocument2 pagesSection-A Note:-: R R F R RHoney AliNo ratings yet
- Series Dps Code No. 00/3 DKSM Ua-00@3: XF - KRDocument4 pagesSeries Dps Code No. 00/3 DKSM Ua-00@3: XF - KRdeepakagarwal114_894No ratings yet
- Vedantu Telugu Jee Channel Kiran Sir Maths: Paper: JR - Inter Ipe Predicted Paper DT: 04-03-2024Document2 pagesVedantu Telugu Jee Channel Kiran Sir Maths: Paper: JR - Inter Ipe Predicted Paper DT: 04-03-2024kc802220No ratings yet
- 3004 MKJ 10th STD MATHS Quarterly Model Question Paper-01 DOOZY STUDYDocument4 pages3004 MKJ 10th STD MATHS Quarterly Model Question Paper-01 DOOZY STUDYpurshotthaman dNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - ExercisesDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - ExercisesVillamorchard0% (2)
- ECE 602 Solution To Homework Assignment 4Document7 pagesECE 602 Solution To Homework Assignment 4souleyman hassanNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2012 Complete Solved Paper Question Paper and SolutionDocument29 pagesAIEEE 2012 Complete Solved Paper Question Paper and SolutionManish PilaniaNo ratings yet
- Parametric WorksheetDocument3 pagesParametric Worksheetarghya_bi108No ratings yet
- Question Bank: ७०८ सदाशिव पेठ, कुमठेकर मार्ग, पुणे ४११०३० संपकग क्रमांक (020) 2447 6938 E-mailDocument31 pagesQuestion Bank: ७०८ सदाशिव पेठ, कुमठेकर मार्ग, पुणे ४११०३० संपकग क्रमांक (020) 2447 6938 E-mailPrayasNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pelajar Add Math f4Document6 pagesAssignment Pelajar Add Math f4Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-15Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-15Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-11Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-11Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- No. of Phone Calls Frequency: Descriptive Statistics (Chapter 17)Document1 pageNo. of Phone Calls Frequency: Descriptive Statistics (Chapter 17)Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-7Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-7Nhocticaro Nhoc0% (1)
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-14Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-14Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-12Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-12Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-9Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-9Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-10Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-10Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-4Document3 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-4Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16) : IB - HL-2edDocument2 pagesLines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16) : IB - HL-2edNhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-8Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-8Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Review Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Document4 pagesReview Set 16B (3-D) : Lines and Planes in Space (Chapter 16)Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-2Document2 pagesPages From New Math Book - Part2-2Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet
- Pages From New Math Book - Part2-22Document1 pagePages From New Math Book - Part2-22Nhocticaro NhocNo ratings yet