Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Test 1: Elasticity March 16, 2004
3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Test 1: Elasticity March 16, 2004
Uploaded by
Joanna TaylorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Test 1: Elasticity March 16, 2004
3.22 Mechanical Properties of Materials Test 1: Elasticity March 16, 2004
Uploaded by
Joanna TaylorCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
22 Mechanical properties of Materials Test 1: Elasticity March 16, 2004
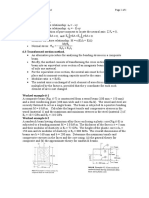
1. A material has cubic symmetry, with E1 = 62.8 GPa, G12 = 28.4 GPa and 12 = 0.36. (a) Find the strain tensor (corresponding to the x1-x2-x3 axes) for the following applied stress state: 20 10 5 = 10 50 5 MPa 5 5 30 (10 points) (b) If a new stress state, with a normal stress of 100 MPa is applied along the x1 axis, which is rotated 45 about the x3 axis, what is the normal strain in (10 points) the x1 direction? x2 =100 MPa
45 x1
x3
2. (10 points) (a) Why is the stiffness tensor symmetric? (b) Why does Poissons ratio approach 1/2 for a rubber? (c) Why does the Youngs modulus of a ceramic decrease with increasing temperature while that of a rubber increases?
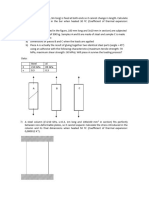
3. An old thermostat has a switch made of a bimetallic bar, with aluminum and nickel. Both layers in the bar have the same thickness, t = 100 m, and the bar has a length l = 100 mm. At 20C, the bar is straight and stress-free. Calculate the horizontal deflection of the bar for a 2C increase in temperature. What is the maximum stress in the bimetallic layers (calculate for both layers)? (10points) Aluminum: E = 69 GPa, = 0.34, = 23 x 10-6/C Nickel: E = 207 GPa, = 0.36, = 13 x 10-6/C =?
l=100mm
You might also like
- Composite Materials (Collection of Previous Final Exam) 110863Document8 pagesComposite Materials (Collection of Previous Final Exam) 110863habba3No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ansuman SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Transformed SectionDocument1 pageChapter 6 Transformed SectionFernando LopezNo ratings yet
- MOS Unit 1-Model QuestionsDocument11 pagesMOS Unit 1-Model QuestionsBhuvan RockNo ratings yet
- Lista 3Document7 pagesLista 3Rodolfo Souza MartinsNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Home TestDocument4 pagesGrade 11 Home Testsantharamsree07No ratings yet
- QuizDocument4 pagesQuizapi-253978194No ratings yet
- Coursework ContinuumSolidMechanics EJM March2021Document6 pagesCoursework ContinuumSolidMechanics EJM March2021Siddharth MahalaNo ratings yet
- (Questionpaperz - In) UPSEE Previous Paper 2005Document39 pages(Questionpaperz - In) UPSEE Previous Paper 2005Pushpendra ShawNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Paper 1Document2 pagesElasticity Paper 1Shivam DuttaNo ratings yet
- EEE118 Problem SheetsDocument6 pagesEEE118 Problem Sheetsالأردني JordanianNo ratings yet
- Exercise 26:: ∆ l=1 mω l AY m, A Y ∆ l ∝ωDocument21 pagesExercise 26:: ∆ l=1 mω l AY m, A Y ∆ l ∝ωAbhishek PathakNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoDocument7 pages2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoConstanza de la FuenteNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress StrainDocument8 pagesSimple Stress StrainJames Ortega33% (3)
- 8 Phy 08-04-19 (Slot-1) PCDocument6 pages8 Phy 08-04-19 (Slot-1) PCrineeth22745No ratings yet
- PartDocument9 pagesPartMahendranath Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- Mmems 2 UDocument163 pagesMmems 2 UHardeshkumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Practice Questions 2Document4 pagesSolutions of Practice Questions 2Sayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- Mech. Properties of SolidsDocument15 pagesMech. Properties of SolidsRakesh SNo ratings yet
- 20110926HW1Document2 pages20110926HW1David SimonNo ratings yet
- MD 5BDocument73 pagesMD 5Bctvd93100% (1)
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinite Element Analysiskumbharashish37No ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesStrength of Materialsgayatri_vyas1No ratings yet
- Me2254 - Strength of Materials 2008 PDFDocument4 pagesMe2254 - Strength of Materials 2008 PDFAndrew CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 98 - Model 2019Document10 pagesPractice Test 98 - Model 2019HimayaNo ratings yet
- HW1 - Conditions - Olevsky - Mech - Beh - Mater PDFDocument2 pagesHW1 - Conditions - Olevsky - Mech - Beh - Mater PDFwangbutt123No ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument2 pagesAssignment IISaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- NEET Exam 2005 Original Question Paper and Answer Key Click HereDocument39 pagesNEET Exam 2005 Original Question Paper and Answer Key Click HereBalaji ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- UPSEE - Full Paper - 2009Document40 pagesUPSEE - Full Paper - 2009Abhishek Kumar100% (2)
- Som Ese 2021Document7 pagesSom Ese 2021Gaurav ManeNo ratings yet
- Met201 QPDocument3 pagesMet201 QPJanit JijiNo ratings yet
- Test Exams PDFDocument7 pagesTest Exams PDFShaheer Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- JPICE Quiz BeeDocument12 pagesJPICE Quiz BeemateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Option.) : (All Questions Have Exactly One Correct Answer. You Are To Indicate The CorrectDocument11 pagesOption.) : (All Questions Have Exactly One Correct Answer. You Are To Indicate The Correctdebabrata_nagNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineeringalex mcraeNo ratings yet
- Ib Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2Document5 pagesIb Tutorial 4 (12 13) Sem 2omarnasriNo ratings yet
- January 29 - EveningDocument12 pagesJanuary 29 - Eveningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoKkNo ratings yet
- Answer The Stresses Are 69.92 Mpa and - 38.67 Mpa and The Neutral Axis Is 38.6 MM From The Tensile EdgeDocument3 pagesAnswer The Stresses Are 69.92 Mpa and - 38.67 Mpa and The Neutral Axis Is 38.6 MM From The Tensile Edgelayiro2No ratings yet
- AMT Ht16-Exam PDFDocument9 pagesAMT Ht16-Exam PDFaamersid2882No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Question PapersDocument10 pagesMechanics of Solids Question PapersNandu Sreekumar SNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set04Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set04rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument18 pagesPhysicsjonhc934No ratings yet
- Stresses in Beams AdvancedDocument10 pagesStresses in Beams Advanceddeathes0% (1)
- Reg No.: - NameDocument3 pagesReg No.: - NameSijuKalladaNo ratings yet
- Ae 35 Solid MechanicsDocument4 pagesAe 35 Solid MechanicsRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- 322 F22 PS9 - UpdatedDocument4 pages322 F22 PS9 - UpdatedlokeshNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323No ratings yet
- Toe QuestDocument4 pagesToe Questrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 15may Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument18 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 15may Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsSarojini MallickNo ratings yet
- UPCPMT Sample Paper-1 (CPMT - Paper-2 - 2001)Document18 pagesUPCPMT Sample Paper-1 (CPMT - Paper-2 - 2001)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDocument10 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NamegalehNo ratings yet
- 0109 Physics Paper With Ans EveningDocument5 pages0109 Physics Paper With Ans EveningK DHANALAKSHMI K DHANALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- Engg Final ExamDocument9 pagesEngg Final ExamTanner LeakosNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials July 2013Document0 pagesMechanics of Materials July 2013Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- EMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPDocument4 pagesEMT 3102 SUPP Solids & Structural Mechanics 1 SUPPGausss TjNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)