Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pulmonary Circulation Is The Portion of The: Cardiovascular System Deoxygenated Blood Lungs Systemic Circulation
Uploaded by
Rose Ann AlerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pulmonary Circulation Is The Portion of The: Cardiovascular System Deoxygenated Blood Lungs Systemic Circulation
Uploaded by
Rose Ann AlerCopyright:
Available Formats
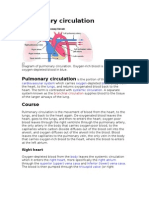
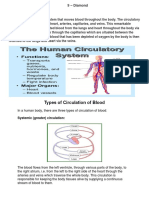
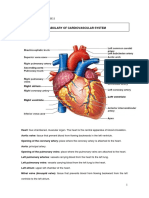
Pulmonary circulation is the portion of the cardiovascular system which carries deoxygenated bloodaway from the heart, to the
lungs, and returns oxygenated (oxygen-rich) blood back to the heart. The term pulmonary circulation is readily paired and contrasted with the systemic circulation. A separate system known as the bronchial circulation supplies blood to the tissue of the larger airways of the lung.
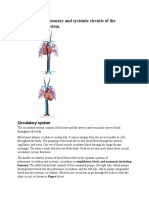
Systemic circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to thebody, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Systemic circulation refers to the part of the circulatory system in which the blood leaves the heart, services the body's cells, and then reenters the heart. Blood leaves through the left ventricle to the aorta, the body's largest artery. The aorta leads to smaller arteries, arterioles, and finally capillaries. Waste and carbon dioxide diffuse out of the cell into the blood, and oxygen in the blood diffuses into the cell. Blood then moves to venious capillaries, and then the venae cavae: the lower inferior vena cava and the upper superior vena cava, through which the blood re-enters the heart at the right atrium.
You might also like
- Fetal CirculationDocument6 pagesFetal Circulationkc-orense-1005No ratings yet
- Systamic Circulation, Pulmonary CirculationDocument2 pagesSystamic Circulation, Pulmonary CirculationAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- The Systemic CirculationDocument1 pageThe Systemic CirculationGrayson JamesNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CirculationDocument5 pagesPulmonary CirculationGPearce204No ratings yet
- Compare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCompare The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits of The Cardiovascular Systememanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- General.: Blood CirculationDocument3 pagesGeneral.: Blood CirculationJessica MichaelNo ratings yet
- Circulation of the Heart - Pulmonary & Systemic CircuitsDocument3 pagesCirculation of the Heart - Pulmonary & Systemic CircuitsAhmed AdelNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System OverviewDocument6 pagesCirculatory System OverviewMaria Christina CaceresNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument4 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocument5 pagesTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNo ratings yet
- Course of circulation through the human heartDocument4 pagesCourse of circulation through the human heartvishal pundirNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystembluewindNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory Systemkashaf bhuttaNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- ... Types of Circulation..Document2 pages... Types of Circulation..VISHWA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Double Circulatory System ExplainedDocument4 pagesDouble Circulatory System Explainedseema chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Medical Science Part 2Document21 pagesMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkNo ratings yet
- Branching Blood VesselsDocument2 pagesBranching Blood VesselsMarjia TulyNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesThe Circulatory Systemİlyas KumNo ratings yet
- PPT-GRADE 9- BLOOD CIRCULATIONDocument7 pagesPPT-GRADE 9- BLOOD CIRCULATIONEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Fungsi Dari CardiovascularDocument2 pagesFungsi Dari CardiovascularNurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1.4 Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesLearning Task 1.4 Reading ComprehensionAndrei Marie SamillanoNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument17 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationRisavina Dorothy CondorNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaDocument3 pagesParts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System GuideDocument10 pagesCirculatory System GuidenaviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument37 pagesLesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemCarla BuzetaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory 1Document2 pagesCirculatory 1Allana Louisse AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- The Blood Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Blood Circulatory SystemListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System OverviewDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System OverviewJohnferson S. BornalesNo ratings yet
- Three Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDocument4 pagesThree Circulatory Systems Working TogetherSteven OwenNo ratings yet
- MypdfDocument1 pageMypdfAidan TangNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SummaryDocument3 pagesCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorNo ratings yet
- GIDB4288666-Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesGIDB4288666-Circulatory System Notessky moonNo ratings yet
- Circulation of BloodDocument2 pagesCirculation of BloodSam LaiNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartTasha CallangNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNo ratings yet
- About The Circulatry System 001Document46 pagesAbout The Circulatry System 001gaboelgaNo ratings yet
- What Is in Our Blood & What Is The Structure of The Heart - EditedDocument1 pageWhat Is in Our Blood & What Is The Structure of The Heart - EditedConnorNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument71 pagesCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiNo ratings yet
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDocument11 pagesMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27No ratings yet
- The Function of The HeartDocument14 pagesThe Function of The HeartAaron FooNo ratings yet
- Mammalian CirculationDocument1 pageMammalian CirculationSathis VenkitasamyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System NotesDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System NotesMeleen ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDocument10 pagesSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemDainara ReyesNo ratings yet
- The 2 Types of Circulatory CircuitsDocument2 pagesThe 2 Types of Circulatory CircuitsLëz NérNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Kurgaš Ema Softić ErnaDocument10 pagesCardiovascular System: Kurgaš Ema Softić ErnaEma KurgasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemSakshi NijhawanNo ratings yet
- Iv. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesIv. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- The MyocardiumDocument8 pagesThe MyocardiumKyrene San Pedro RosalesNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Document7 pagesVocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Agustín Bravo Arreyes100% (2)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- SanggunianDocument3 pagesSanggunianRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument1 pageAccomplishment ReportRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: Edit University of The Philippines, Manila Malate, ManilaDocument16 pagesSynopsis: Edit University of The Philippines, Manila Malate, ManilaRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Subject and ContentDocument35 pagesSubject and ContentAlejandro Jard DacioNo ratings yet
- Program ShortDocument3 pagesProgram ShortRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study On Offering Bachelor PDFDocument6 pagesA Feasibility Study On Offering Bachelor PDFRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State College speech evaluation criteriaDocument3 pagesCamarines Norte State College speech evaluation criteriaRose Ann Aler100% (2)
- Document Analysis: Key Insights and TakeawaysDocument1 pageDocument Analysis: Key Insights and TakeawaysRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- SanggunianDocument3 pagesSanggunianRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Rubrics P.DDocument2 pagesRubrics P.DRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- AIMDocument6 pagesAIMRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing TOSDocument8 pagesCreative Writing TOSRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing TOSDocument8 pagesCreative Writing TOSRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- AimDocument6 pagesAimRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- QwertyDocument1 pageQwertyRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Dewey, J. (1938) - Experience and Education. Toronto: Collier-Macmillan Canada LTDDocument1 pageDewey, J. (1938) - Experience and Education. Toronto: Collier-Macmillan Canada LTDRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Teaching Bikol Literature in the K-12 ProgramDocument1 pageTeaching Bikol Literature in the K-12 ProgramRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument15 pagesBullyingRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Filipino 1Document1 pageActivity Sheets Filipino 1Rose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument15 pagesBullyingRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- AverroesDocument9 pagesAverroesRose Ann Aler100% (1)
- Cefpodoxime Protexil Azithromycin Dihydrate Cefpodoxime Protexil Azithromycin Dihydrate 40mg Per 5ML 200mg Per 5ML 40mg Per 5ML 200mg Per 5MLDocument1 pageCefpodoxime Protexil Azithromycin Dihydrate Cefpodoxime Protexil Azithromycin Dihydrate 40mg Per 5ML 200mg Per 5ML 40mg Per 5ML 200mg Per 5MLRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- AverroesDocument9 pagesAverroesRose Ann Aler100% (1)
- Phenomenology and ExistentialismDocument14 pagesPhenomenology and ExistentialismRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Thinking About The Way Children Use LanguageDocument5 pagesThinking About The Way Children Use LanguageRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument15 pagesBullyingRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- AVICENNA HandoutsDocument3 pagesAVICENNA HandoutsRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- BullyingDocument15 pagesBullyingRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Gift ChequeDocument2 pagesGift ChequeRose Ann AlerNo ratings yet
- Child Protection PolicyDocument21 pagesChild Protection PolicyPaul Michael Camania JaramilloNo ratings yet