Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future Simple - Organizing Verbs
Future Simple - Organizing Verbs
Uploaded by
Σταμάτης ΊσερηςOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Future Simple - Organizing Verbs
Future Simple - Organizing Verbs
Uploaded by
Σταμάτης ΊσερηςCopyright:
Available Formats
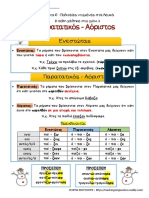
Future Simple + Past Simple Tense
(an attempt to organize the verbs on the basis of similar verb endings)
REGULAR VERBS
PRESENT
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
PAST SIMPLE
PRESENT
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
*
PAST SIMPLE
PRESENT: -
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
PAST SIMPLE: -
PRESENT: -
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
PAST SIMPLE: -
PRESENT: -
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
PAST SIMPLE: -
PRESENT: -
EXCEPTION:
FUTURE SIMPLE: -
PAST SIMPLE: -
IRREGULAR VERBS
PRESENT
PRESENT
FUTURE SIMPLE
FUTURE SIMPLE
NOTE: there's a big difference between Simple Tenses and Continuous Tenses.
The Continuous Future Tense describes action that will go on happening forever and ever, or for a long time in the
future. It is formed by simply adding in front of the verb in the Present tense (eg. - //
).
The Simple Future Tense describes action that will happen once or at a very specific time in the future. For the
majority of the verbs (called regular'), the Simple Future is formed by adding the ending - at the end of the stem of
the verb as you know it from the Present tense. his new addition might affect the last letter (-s) of the stem in a
number of ways:
a) a consonant might disappear (e.g. - = - // - = -),
b) a consonant may turn into an altogether new letter, one of those compound consonants (, ) that still preserve the
sound -s- in them (e.g. - // ),
c) the vowel -- in the group of verbs that end in turns into -- (e.g. , ).
By replacing the ending - at the end of the stem of the verb with the ending - and by moving the stress to the
previous syllable, you get the Simple Past tense. This tense describes action that took place once in the past (e.g.
- ).
You might also like
- χρονοι αγγλικωνDocument6 pagesχρονοι αγγλικωνFay Xristaki67% (3)
- Β΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFDocument60 pagesΒ΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFJenny KartNo ratings yet
- Bescherelle Des Verbes Grecs 1C Conjugation of Modern Greek Verbs (201 Pages)Document202 pagesBescherelle Des Verbes Grecs 1C Conjugation of Modern Greek Verbs (201 Pages)alainaberemani100% (3)
- ΕΝΕΡΓΗΤΙΚΗ ΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)Document4 pagesΕΝΕΡΓΗΤΙΚΗ ΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)loumbidion100% (1)
- Athenaze Cap 10Document22 pagesAthenaze Cap 10Carlos WagnerNo ratings yet
- GD7 Term2 1 Δελφινοκοριτσο GD12 Term2 1 Αρνηση GD4 Term2 1 Μαγια Κυκλαμινο Σεφερης Ελυτης ΡιτσοςDocument21 pagesGD7 Term2 1 Δελφινοκοριτσο GD12 Term2 1 Αρνηση GD4 Term2 1 Μαγια Κυκλαμινο Σεφερης Ελυτης ΡιτσοςDominick RoesstorffNo ratings yet
- ΕΝΕΡΓΗΤΙΚΗ ΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)Document4 pagesΕΝΕΡΓΗΤΙΚΗ ΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)Ελένη ΠέτρουNo ratings yet
- ΟΡΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΕΝΕΣΤΩΤΑ ΜΕΛΛΟΝΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΠΑΡΑΤΑΤΙΚΟΥ ΜΕΣΗΣ ΦΩΝΗΣDocument2 pagesΟΡΙΣΤΙΚΗ ΕΝΕΣΤΩΤΑ ΜΕΛΛΟΝΤΑ ΚΑΙ ΠΑΡΑΤΑΤΙΚΟΥ ΜΕΣΗΣ ΦΩΝΗΣΟΛΥΜΠΙΑ50% (2)
- ΣΧΗΜΑΤΙΜΟΣ ΜΕΣΗΣ ΦΩΝΗΣ ΒΑΡΥΤΟΝΩΝ ΡΗΜΑΤΩΝDocument3 pagesΣΧΗΜΑΤΙΜΟΣ ΜΕΣΗΣ ΦΩΝΗΣ ΒΑΡΥΤΟΝΩΝ ΡΗΜΑΤΩΝCaterina VenizelouNo ratings yet
- ΕΠΑΝΑΛΗΨΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΚΗΣDocument3 pagesΕΠΑΝΑΛΗΨΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΚΗΣfeggaroskoni1008No ratings yet
- Παρατηρήσεις στα ρήματα της α.ε. κανόνες τονισμού των ρημάτωνDocument7 pagesΠαρατηρήσεις στα ρήματα της α.ε. κανόνες τονισμού των ρημάτωνjohnwalker180981No ratings yet
- Verb Τenses in EnglishDocument6 pagesVerb Τenses in EnglishKostas papNo ratings yet
- 5η ΕΝΟΤΗΤΑ ΑΣΦΑΛΩΣ ΚΥΚΛΟΦΟΡΩDocument4 pages5η ΕΝΟΤΗΤΑ ΑΣΦΑΛΩΣ ΚΥΚΛΟΦΟΡΩRena SkribiaNo ratings yet
- Verb PraesensDocument4 pagesVerb PraesensΓεωργία ΣιάκουNo ratings yet
- ВГ 2-8 ПРОМЕНЛИВО ЯDocument10 pagesВГ 2-8 ПРОМЕНЛИВО ЯMlippyNo ratings yet
- БЪЛГАРСКИ ПРОМЕНЛИВО ЯDocument10 pagesБЪЛГАРСКИ ПРОМЕНЛИВО ЯMlippyNo ratings yet
- Β΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFDocument60 pagesΒ΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFAnonymous u5UR82100% (1)
- Β΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFDocument60 pagesΒ΄ τεύχος Γλώσσας Γ Δημοτικού PDFAnonymous u5UR82No ratings yet
- ΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΚΗ Nο 1Document4 pagesΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΙΚΗ Nο 1KrystaPapaioannouNo ratings yet
- FICHA 8. El MitoDocument14 pagesFICHA 8. El Mitotroia78No ratings yet
- Γραμματικά φαινόμενα 9ης ενότηταςDocument4 pagesΓραμματικά φαινόμενα 9ης ενότηταςharlemcore13No ratings yet
- Ε ΓΛΩΣΣΑ ΕΝ1 Ρήματα σε -ίζω και άρωDocument2 pagesΕ ΓΛΩΣΣΑ ΕΝ1 Ρήματα σε -ίζω και άρωbiscuitNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηΧρύσα ΧαραλαμπίδηNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηΜαρία ΞανθινίδουNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις-αρχαίων Λυκειο 1Document17 pagesAσκήσεις-αρχαίων Λυκειο 1ΠαναγιώταΔημητροπούλουNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις-Αρχαίων α΄ Λυκείου-ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις-Αρχαίων α΄ Λυκείου-Επανάληψηang.tanidou100% (3)
- Aσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηΚωνσταντίνος ΤσίπραςNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηΜαρία ΞανθινίδουNo ratings yet
- Aσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηDocument17 pagesAσκήσεις Αρχαίων ΕπανάληψηΧρύσα ΧαραλαμπίδηNo ratings yet
- ΓΛΩΣΣΑ ΣΤ' ΔΗΜΟΤΙΚΟΥDocument47 pagesΓΛΩΣΣΑ ΣΤ' ΔΗΜΟΤΙΚΟΥlionik22No ratings yet
- Η πόλη χάθηκε στο χιόνι 1Document2 pagesΗ πόλη χάθηκε στο χιόνι 1K0stasNo ratings yet
- ArxaiaDocument3 pagesArxaiaXristina BartzouNo ratings yet
- Βασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςDocument3 pagesΒασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςLin Galini100% (1)
- Geround VS InfDocument6 pagesGeround VS InfNota ProussNo ratings yet
- Βασικοι κανονες γραμματικηςDocument6 pagesΒασικοι κανονες γραμματικηςEvaggelia Flaskh100% (1)
- γενικες ασκησεις συντακτικουDocument46 pagesγενικες ασκησεις συντακτικουfeggaroskoni1008100% (1)
- Langue Grec (Le) Bescherelle Des Verbes Grecs 2C (107 Pages)Document107 pagesLangue Grec (Le) Bescherelle Des Verbes Grecs 2C (107 Pages)alainaberemani100% (3)
- Arxaia ΠΑΡΑΤΗΡΗΣΕΙΣ ΣΤΑ ΡΗΜΑΤΑDocument3 pagesArxaia ΠΑΡΑΤΗΡΗΣΕΙΣ ΣΤΑ ΡΗΜΑΤΑannadikenNo ratings yet
- Pronomi Diretti & Stare+gerundioDocument3 pagesPronomi Diretti & Stare+gerundiodimitra.apostolopoulouNo ratings yet
- παρατατικός αόριστος μφDocument7 pagesπαρατατικός αόριστος μφνεκταρια δαμορακηNo ratings yet
- ΡηματαDocument2 pagesΡηματαSophia KyriakouNo ratings yet
- Theorie Deutsch ein Hit ΓερμανικαDocument7 pagesTheorie Deutsch ein Hit ΓερμανικαIoanna KamplioniNo ratings yet
- ΜΑΘΗΜΑ21Document167 pagesΜΑΘΗΜΑ21Agrinio CultureNo ratings yet
- Stamm WurzDocument1 pageStamm Wurznaaj74No ratings yet
- ΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)Document6 pagesΥΠΟΤΑΚΤΙΚΗ (ΘΕΩΡΙΑ- ΑΣΚΗΣΕΙΣ)Photini SiamariNo ratings yet
- ΑΟΡΙΣΤΟΣ ΒDocument4 pagesΑΟΡΙΣΤΟΣ ΒaikateriniandritsouNo ratings yet
- Aktivni GlagoliDocument7 pagesAktivni GlagolitanjanizNo ratings yet
- βασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςDocument5 pagesβασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςPk20017No ratings yet
- Parakeimenos TheoriaDocument3 pagesParakeimenos TheoriaDenise Pelekouda-OikonomouNo ratings yet
- Parakeimenos TheoriaDocument3 pagesParakeimenos TheoriaDenise Pelekouda-OikonomouNo ratings yet
- Parakeimenos TheoriaDocument3 pagesParakeimenos TheoriaDionysia PelekoudaNo ratings yet
- Parakeimenos TheoriaDocument3 pagesParakeimenos TheoriaDionysia PelekoudaNo ratings yet
- Βασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςDocument5 pagesΒασικοί κανόνες ορθογραφίαςNicola Pissas100% (1)
- ΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΑΠΟ ΟΛΑ!!!Document14 pagesΤΕΛΕΙΟ ΑΠΟ ΟΛΑ!!!joan_thNo ratings yet
- 1-3 μάθημα ελληνικώνDocument9 pages1-3 μάθημα ελληνικών8b6hjzhqwtNo ratings yet
- Основна Граматика Grčkog JezikaDocument153 pagesОсновна Граматика Grčkog JezikaPredrag VelickovNo ratings yet
- Μάθετε Ρωσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνFrom EverandΜάθετε Ρωσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνNo ratings yet
- Μάθετε Λευκορωσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνFrom EverandΜάθετε Λευκορωσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνNo ratings yet
- Μάθετε Περσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνFrom EverandΜάθετε Περσικά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνNo ratings yet
- Μάθετε Εβραϊκά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνFrom EverandΜάθετε Εβραϊκά - Γρήγορα / Εύκολα / Αποτελεσματικά: Λεξιλόγια 2000 Bασικών ΛέξεωνNo ratings yet