Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
Uploaded by
Nicole Marin-ChingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP
Uploaded by
Nicole Marin-ChingCopyright:
Available Formats
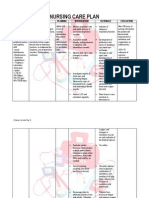
NURSING CARE PLAN (N.C.P.) Name: Paula Nicole Anne R.
Marin Assessment Subjective: Medyo giniginaw ako kaya ako nakakumot. Pero wala naman akong lagnat as verbalized by the patient Nursing Diagnosis Risk for peripheral neurovascular dysfunction related to interruption of blood flow as manifested by pallor and delayed capillary refill of 4 seconds, chills Etiology Planning Fracture Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will exhibit no signs and symptoms of neurovascular compromise Interventions Monitor v/s Year/Section: BSN 4-4 Rationale Systemic perfusion will be impaired if circulating blood volume is inadequate Increasing circumference of injured extremity may suggest general tissue swelling/edema but may reflect hemorrhage. Note: A 1-in increase in an adult thigh can equal approximately 1 unit of sequestered blood. Facilitates monitoring of circulatory status of extremity Evaluation
Compression of various end capillary bed (decreased capillary refill)
Objective: (+) pallor (+) delayed capillary refill of 4 seconds (+) chills
Assess entire length of injured extremity for swelling/edema formation. Measure injured extremity and compare with uninjured extremity. Note appearance/sprea d of hematoma. Provide immobilization to joints above and below the fractured site, leaving enough room to assess pulses Palpate peripheral pulses and identify changes in equity or character of pulses distal to injury Monitor extremity involved for rapid capillary refill, skin color, warmth, and sensation
Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
Increased intracompartmental pressure (pain upon movement)
Decreased or absent pulses may indicate vascular injury that requires immediate intervention Circulatory impairment may result in delayed refill greater than 5 seconds. Arterial compromise may occur when skin is
Compression of arterioles :
Compressed arterial flow (pallor and chills)
Monitor for changes in neurovascular integrity every 12 hours as warranted.
Evaluate complaints of pain that are abnormal for the type of injury sustained, pain with passive muscle stretching, or decreases in muscle movement distal to injury.
Assess skin around tibial pin for redness or pressure points, or for complaints of burning
cool-cold and white, and venous compromise may occur with cyanosis. Sudden ischemic signs may be caused with joint dislocation resulting from injury to adjacent arterial structures Paresthesias, numbness, tingling, or diffused pain may occur when nerves have been damaged or when circulation is impaired, and may require intervention Hemorrhage and/or edema within the muscle fascia can impair blood flow and cause compartmental syndrome that will require emergency intervention to restore circulation. Compartmental syndrome can result in permanent dysfunction and deformity within 2448 hours and irreversible damage may occur after 6 hours without intervention Pressure can result to ischemia and tissue breakdown. Burning pain may indicate pressure areas.
Position injured site in proper alignment Avoid flexion of fractured extremity
Instruct patient in signs/ symptoms to notify nurse/ physician: increased pain, decreased sensation or movement, or changes in temperature or color of injured part Instruct patient/family in correct positioning techniques, and methods to use to obtain relief from pressure
Circulation may be compromised if correct alignment is not maintained May result in decreased venous circulation and increase potential for neurovascular compromise Provides knowledge and allows for patient involvement in care. Provides method for prompt detection of potential complications to facilitate prompt intervention. Provides knowledge and helps to avoid venous pooling and potential pressure ulcerations
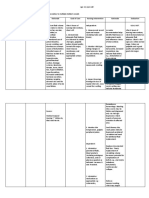
NURSING CARE PLAN (N.C.P.) Name: Paula Nicole Anne R. Marin Assessment Subjective: Ang hirap kasi limitado lang yung galaw ko. Mahirap gumalaw. Nursing Diagnosis Impaired physical mobility related to fracture as manifested by reluctance to move at will because of external fixator Etiology Fracture Planning Within 6 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will maintain optimal mobility and function of injured areas. Interventions Evaluate degree of immobility that has resulted from injury and patients perception of his limitations Rationale After trauma, patients perception of limitations may be out of proportion with their physical levels of activities and may require further information to dispel false concepts Decreases potential for further injury and impairment in alignment while stabilizing the injured area Prevents formation of pressure areas and improves circulation Prevents muscle atrophy, increases blood flow, improves joint mobility, and helps prevent reabsorption of calcium resulting from disuse Traction apparatus may be cumbersome and heavy and may require increased personnel to Year/Section: BSN 4-4 Evaluation
Limited range of motion
Pain
Objective: (+) exfix at right leg (+) open fracture, complete nondisplaced inferior pole patella @ L leg (+) open fracture, complete segmental displaced tibia @ R leg (+) reluctance to move at will
Reluctance to move injured part
Loss of function
Maintain bedrest and move injured limbs gently, supporting areas above and below the fracture Reposition patient every 2 hours and prn Assist patient with range of motion exercises of all extremities as warranted
Ensure that adequate numbers of personnel are present for repositioning
Evaluate integrity of traction apparatus and set-up
Observe for redness, tenderness, pain, or swelling to the calf
avoid injury to the patient or the nurses Traction provides for a pulling force on the long axis of a fractured bone to facilitate proper alignment and healing May indicate thrombophebitis
NURSING CARE PLAN (N.C.P.) Name: Paula Nicole Anne R. Marin Assessment Subjective: Isang lingo na akong hindi dumudumi. Nursing Diagnosis Constipation related to decreased activity as manifested by inability to pass stool for a week Etiology maintenance of tone in the intestinal and abdominal muscles requires regular exercise Planning Within 16 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will have normal bowel function with no complications to fluid status Interventions Assess bowel habits of patients; normal routines, frequency of stools, use of cathartics Administer laxatives or stool softeners as ordered. Tap water enemas should be avoided Rationale Provides baseline from which to plan interventions Year/Section: BSN 4-4 Evaluation
Objective: No stool output
Decreased activity
intestinal muscles become slackened, intestinal motility slows down Slow intestinal motility
constipation
Instruct patients in massaging abdomen along transverse and descending colon each day Instruct patient/family in appropriate use of laxatives, stool softeners, and enemas
Caution must be used in selection of pharmacologic agent so as not to further ass to fluid volume overload. Water in the enemas can be absorbed and increased overload Massage may assist to stimulate peristalsis
Overuse of purgative may increase fluid and electrolyte loss, create laxative dependence, and damage intestinal mucosa
You might also like
- USMLE Step 1 NBME Top Concepts 2021Document475 pagesUSMLE Step 1 NBME Top Concepts 2021dalia khamoNo ratings yet
- 8 Sample Care Plans For ACDFDocument11 pages8 Sample Care Plans For ACDFacasulla98No ratings yet
- NCP OsteoporosisDocument5 pagesNCP OsteoporosisAnonymous gAwcPNVRNo ratings yet
- Our Patient Pictured Here With His Daughter : Case StudyDocument1 pageOur Patient Pictured Here With His Daughter : Case StudyNicole Marin-Ching0% (1)
- Agent JohnsonDocument1 pageAgent JohnsonJulio Cesar PerezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageImpaired Gas ExchangeLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- Burns - Skin Integrity, ImpairedDocument2 pagesBurns - Skin Integrity, Impairedmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- A Nursing Care Plan VaDocument3 pagesA Nursing Care Plan VaArianne Paola QuindoyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAndrea BroccoliNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- NCP DepressionDocument2 pagesNCP Depressionhollymadison80% (5)
- NCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Document3 pagesNCP (Riskforimpairedskinintegrity)Ma Kaye Gelizabeth Corpuz-DauloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis For CholecystectomyMiguel VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageRisk For Aspirationmmcgee01No ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- CHD With NCPDocument10 pagesCHD With NCPJohanna Kirsten F. DaguioNo ratings yet
- NCP Gouty ArthritisDocument21 pagesNCP Gouty ArthritisArianne Kamille Andes67% (3)
- Case Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Document8 pagesCase Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Zhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility NCPYan ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP For Impaire and RiskDocument6 pagesNCP For Impaire and RiskMyraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNo ratings yet
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute PainsAm_300% (1)
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Document2 pagesCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16No ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerancepooper123No ratings yet
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocument4 pagesAltered Renal Perfusion CRFKristel Anne Nillo ZepolNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- Assessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment NSG DX Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale EvaluationClaudineNo ratings yet
- 3 NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pages3 NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument25 pagesCase AnalysisGerly LagutingNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument2 pagesRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuNo ratings yet
- NCP MiDocument4 pagesNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999No ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- NCP H MoleDocument6 pagesNCP H MoleMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Risk For Peripheral NeurovacularDocument4 pagesRisk For Peripheral NeurovacularRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDocument4 pagesDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDocument3 pagesAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- NCP Format - Docx 2ndDocument4 pagesNCP Format - Docx 2ndGalileo AragonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan With A FractureDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan With A FractureHasanah EkaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Rationale Intervention Planning Explanation of The Problem AssessmentDocument2 pagesEvaluation Rationale Intervention Planning Explanation of The Problem Assessmentmodi100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Pain NCP BillrothDocument2 pagesPain NCP BillrotharjayNo ratings yet
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument10 pagesNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIChristine Karen Ang SuarezNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP Painsitz04No ratings yet
- HoplessnessDocument16 pagesHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Care of The Patient Undergoing Orthopedic SurgeryDocument26 pagesPreoperative Care of The Patient Undergoing Orthopedic SurgeryAbdul Gafoor CPNo ratings yet
- Prolapse Lumbar DiscDocument40 pagesProlapse Lumbar DiscAlfred BantigueNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisGeovanni Rai HermanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Bed BathDocument5 pagesLesson Notes - Bed BathNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - CBGDocument6 pagesLesson Notes - CBGNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Blood Pressure ManagementDocument4 pagesLesson Notes - Blood Pressure ManagementNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - Body MechanicsDocument69 pagesPowerpoint - Body MechanicsNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Body MechanicsDocument9 pagesLesson Notes - Body MechanicsNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Insulin PenDocument6 pagesLesson Notes - Insulin PenNicole Marin-Ching100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Is The Program of The Department of Health Created To Lessen The Death of Infants and Mother in The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesMaternal and Child Health Is The Program of The Department of Health Created To Lessen The Death of Infants and Mother in The PhilippinesNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Pulse RateDocument4 pagesLesson Notes - Pulse RateNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Gemma Bautista 4 Enya Lacsina Enya Lacsina 2Document20 pagesGemma Bautista 4 Enya Lacsina Enya Lacsina 2Nicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Hardbound 4 JomerDocument99 pagesHardbound 4 JomerNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Planning: Cecille O. Martinez RN, RM, Man, Edd (C)Document90 pagesPlanning: Cecille O. Martinez RN, RM, Man, Edd (C)Nicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument1 pagePamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Care of Indwelling or Foley CatheterDocument2 pagesCare of Indwelling or Foley CatheterNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Operating Room NurseDocument3 pagesOperating Room NurseNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Letter Sa Bon (Di Final)Document2 pagesLetter Sa Bon (Di Final)Nicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Head NurseDocument3 pagesHead NurseNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: (University of The City of Manila)Document4 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: (University of The City of Manila)Nicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Pott's DiseaseDocument34 pagesPott's DiseaseNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Letter For ResearchDocument1 pageLetter For ResearchNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Original Contribution: The SHEZ StudyDocument9 pagesOriginal Contribution: The SHEZ StudyRaúl AñariNo ratings yet
- Liver TransplantationDocument17 pagesLiver Transplantationa_m_elsheemy1931No ratings yet
- Anti Allergic DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Allergic Drugsaamer niaziNo ratings yet
- Mri of Cervical Spine: Location: COLTONDocument3 pagesMri of Cervical Spine: Location: COLTONSusana FranklinNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesSoal Latihan Bahasa InggrisFransiska TanNo ratings yet
- RH Incompatibil TY: What Is RH Incompatibility?Document15 pagesRH Incompatibil TY: What Is RH Incompatibility?Jannah Marie A. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- LeukoplakiaDocument60 pagesLeukoplakiadimasahadiantoNo ratings yet
- List of MedicinesDocument32 pagesList of Medicinescarleen_almiraNo ratings yet
- 2 - 3 - CNS TumorsDocument14 pages2 - 3 - CNS TumorsNajeebNo ratings yet
- General Nursing Assessment FormDocument2 pagesGeneral Nursing Assessment FormMarites BarnidoNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Biopsy TechniquesDocument2 pagesAAD BF Biopsy TechniquesLos MiNo ratings yet
- Berberine Containing PlantsDocument30 pagesBerberine Containing PlantsmubeenNo ratings yet
- Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTS)Document37 pagesMalaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTS)MegbaruNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Information: (Methoxsalen, USP)Document9 pagesPrescribing Information: (Methoxsalen, USP)Jeliny Bintan MaisuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Pituitary and Adrenocortical HormonesDocument10 pagesChapter 43 - Pituitary and Adrenocortical HormonesHannaNo ratings yet
- Why GILD Remdesivir Is The Only Relevant Coronavirus DrugDocument8 pagesWhy GILD Remdesivir Is The Only Relevant Coronavirus Drugjulia skripka-serry100% (2)
- Trisomies: Abnormal Number of ChromosomesDocument10 pagesTrisomies: Abnormal Number of ChromosomesNaumanNo ratings yet
- Asa Physical Status Classification System PDFDocument2 pagesAsa Physical Status Classification System PDFAnonymous 6iLtIrNo ratings yet
- Skin AssessmentDocument45 pagesSkin AssessmentAbdurehman AyeleNo ratings yet
- What Are Glycerol Suppositories?Document2 pagesWhat Are Glycerol Suppositories?Delia TuguiNo ratings yet
- Kertas Kerja PinjamanDocument18 pagesKertas Kerja PinjamanWan AzmanNo ratings yet
- Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisDocument4 pagesAcute Necrotizing Ulcerative GingivitisNeira N SakinahNo ratings yet
- Vats Yustinus Rurie WirawanDocument6 pagesVats Yustinus Rurie Wirawanrurie wirawanNo ratings yet
- Script For Gradderall XVDocument4 pagesScript For Gradderall XVapi-273399286No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Seminar 1Document1 pageAbnormal Psychology Seminar 1Daisy RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Schizo Ppt.Document78 pagesSchizo Ppt.Nimisha ChackoNo ratings yet
- Forensic Midterm MCQsDocument4 pagesForensic Midterm MCQsNikhil TyagiNo ratings yet
- 02VBL PemphigusDocument48 pages02VBL PemphigusRaniya ZainNo ratings yet