Professional Documents
Culture Documents
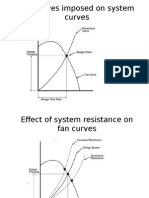
Fan Laws and Running Costs: N N Q Q
Uploaded by
forevertay2000Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fan Laws and Running Costs: N N Q Q
Uploaded by
forevertay2000Copyright:
Available Formats
CHOOSING A FAN
Page 1 of 2
Ventilation Fans - Page 1 2 3 4
Fan Laws and Running Costs
The Fan Laws are as follows: No.1 Speed / Volume N1 N2
Where; N = Q =
Q1 Q2
Fan speed (rev. per minute or r.p.m.) Volume flow rate of air (m3/s)
This means that fan speed and volume flow rate of air are directly proportional. No.2 Speed / Pressure N1 N2
Where; N = p =
2
p1 p2
Fan speed (rev. per minute or r.p.m.) Fan pressure (N/m2)
This means that as the fan speed is doubled, for example, the pressure developed is raised by a factor of 4. No.3 Speed / Power N1 N2
Where; N = P =
3
P1 P2
Fan speed (rev. per minute or r.p.m.) Fan power (Watts)
This means that as the fan speed is doubled, for example, the power required to drive the fan is raised by a factor of 8. The above three laws may be written differently to aid calculations, as follows; No.1 Speed / Volume Q2 = Q1 N2 N1
or
N2 =
N1
Q2 Q1
No.2 Speed / Pressure p2 = p1 N2 N1
2
or
N2 =
N1
p2 p1
1/2
No.3 Speed / Power
3
P2 =
P1
N2 N1
or
N2 =
N1
P2 P1
1/3
http://www.arca53.dsl.pipex.com/index_files/fans3.htm
3/18/2013
CHOOSING A FAN
Page 2 of 2
Fan Running Costs Running costs can be examined as follows; Fan power (W) = Fan pressure (N/m2 or Pa) x Air Volume flow rate (m3/s) / Efficiency
Annual running cost (/annum) =
Fan power (kW) x Hours run per annum x Electrical price per kWh
For example; if a fan runs for 2496 hours per year and delivers 0.625 m3/s against a pressure of 200 Pa, then the annual running costs can be calculated as follows; Take electricity cost at 11.2 p/kWh = 0.112 /kWh. Fan power (W) Fan power (W) Fan power (W) = = = Fan pressure (N/m2 or Pa) x Air Volume flow rate (m3/s) / Efficiency 200 x 208 Watts. 0.208 kW. 0.208 x 2496 x 0.112 0.625 / (say) 0.6
Fan power (kW) =
Annual running cost (/annum) = Annual running cost () =
58.15 per annum
Ventilation Fans - Page 1 2 3 4
http://www.arca53.dsl.pipex.com/index_files/fans3.htm
3/18/2013
You might also like
- Fans and Blowers Part I ModuleDocument26 pagesFans and Blowers Part I ModuleCharlyn Flores67% (3)
- Performance Test On Single Stage Axial Flow FanDocument3 pagesPerformance Test On Single Stage Axial Flow FanAkhil Jaiswal100% (1)
- 4 Performance of A Centrifugal FanDocument7 pages4 Performance of A Centrifugal Fanfinix33No ratings yet
- Vent Axia Vent GuideDocument23 pagesVent Axia Vent GuideblasderNo ratings yet
- Wind Power FundamentalsDocument41 pagesWind Power FundamentalsHmaedNo ratings yet
- Air Volume Calculation ProcedureDocument2 pagesAir Volume Calculation Procedurekhater ben HamedNo ratings yet
- Compressors Version 3Document4 pagesCompressors Version 3elpidiozr8229No ratings yet
- Parag Fan WriteupDocument9 pagesParag Fan Writeuprashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- 5.4 FansDocument20 pages5.4 FansbaroNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps PDFDocument54 pagesCentrifugal Pumps PDFthomastheinkyaw100% (1)
- Pressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch AbsoluteDocument8 pagesPressure Ake Int Absolute Stage Last of Pressure e Arg Disch Absolutemasih tadayonNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredDocument5 pagesStep by Step Procedure To Do Shortcut Sizing For Air Cooled Heat Exchanger and Estimate Finned Area and Power RequiredkarthickNo ratings yet
- Water Pump Impeller TheoryDocument9 pagesWater Pump Impeller TheoryspdhimanNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Wind Energy TheoryDocument6 pages2.6 Wind Energy TheoryAlaa TamimiNo ratings yet
- γ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsDocument6 pagesγ γ × ∆ × × × × P 81 - 9 2 Cp A: Selected questionsHhaabbde SybaritzNo ratings yet
- PressorsDocument8 pagesPressorsManoj MisraNo ratings yet
- Optimal Chilled Water Delta-TDocument8 pagesOptimal Chilled Water Delta-Tanup_nairNo ratings yet
- BlowerDocument5 pagesBlowerdarsh2001patelNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument19 pagesConversion of UnitsAnurag TripathyNo ratings yet
- Experiment NO.9: AIM:-To Study and Determine The Effect of A/F Ratio On The Performance of The TwoDocument6 pagesExperiment NO.9: AIM:-To Study and Determine The Effect of A/F Ratio On The Performance of The TwoAbhijeet SahuNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Lect-1Document31 pagesWind Energy Lect-1muhammad_ajmal_25No ratings yet
- Fans - Volume Flow, Pressure Head and Power Consumption vs. Air Temperature and DensityDocument11 pagesFans - Volume Flow, Pressure Head and Power Consumption vs. Air Temperature and DensitykaustavNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingDocument56 pagesAir Compressor System Compressor Fundamentals: IntercoolingAmarendra Mani TiwariNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics 5Document10 pagesAerodynamics 5Mohammed AbdoNo ratings yet
- Process Equipment Design-1Document15 pagesProcess Equipment Design-1Nikunj Thummar100% (1)
- Fan LawsDocument8 pagesFan LawsKaijie LinNo ratings yet
- Basic Motor Formulas and CalculationsDocument9 pagesBasic Motor Formulas and Calculationsmareymorsy2822100% (1)
- Fan PDFDocument28 pagesFan PDFpequenita34No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics II (Chapter 5)Kaffel100% (1)
- Performance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument6 pagesPerformance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorAji V s100% (2)
- Fan Laws - Change Speed and Pressure - ASHRAE 2000 - USADocument1 pageFan Laws - Change Speed and Pressure - ASHRAE 2000 - USAChưa Kể ChuyệnNo ratings yet
- Wind PumpDocument56 pagesWind PumpJay PortabesNo ratings yet
- Fans and Blowers LectureDocument11 pagesFans and Blowers LectureVincentNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideDocument5 pagesAir Cooled Heat Exchanger - ChE GuideAnonymous KpVxNXsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 Radial Flow FanDocument11 pagesExperiment 6 Radial Flow FanOsama RashaydaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Air Duct Pressure Loss (Circular)Document5 pagesCalculation of Air Duct Pressure Loss (Circular)Phyu Mar Thein KyawNo ratings yet
- 08 Ventilatorgrundlagen FantechnologyDocument37 pages08 Ventilatorgrundlagen FantechnologySsheshan PugazhendhiNo ratings yet
- Turbina de Viento Wind TurbineDocument7 pagesTurbina de Viento Wind TurbineAlex MendozaNo ratings yet
- Air CompressorDocument31 pagesAir CompressorEr Bali Pandhare33% (3)
- Fan Power ConsumptionDocument8 pagesFan Power Consumptionchilamkurti_sivasankararaoNo ratings yet
- Fan System InteractionDocument7 pagesFan System InteractionShanmugasundaram RaghuramanNo ratings yet
- Fans and Blowers: Learning OutcomesDocument17 pagesFans and Blowers: Learning OutcomesRyan CalicaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy and Power Calculations - FES - 2023Document3 pagesWind Energy and Power Calculations - FES - 2023Edward ChikuniNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics-Piston EnginesDocument26 pagesApplied Thermodynamics-Piston Engineslui11111No ratings yet
- Kitchen Ventilation ExampleDocument4 pagesKitchen Ventilation ExamplePretty NatyNo ratings yet
- The Affinity Laws of Centrifugal PumpsDocument5 pagesThe Affinity Laws of Centrifugal Pumpssba98No ratings yet
- Requirements of The Erp Directive On Hvac Systems. What You Need To KnowDocument9 pagesRequirements of The Erp Directive On Hvac Systems. What You Need To KnowchristianxlaNo ratings yet
- Fantastic Godbey JohnsonDocument8 pagesFantastic Godbey JohnsonOleg LevchiyNo ratings yet
- Wind ExamDocument8 pagesWind ExamwaltikraNo ratings yet
- Filosofia de ControlDocument40 pagesFilosofia de Controlejzuppelli8036No ratings yet
- Air Receiver Sizing Metric UnitsDocument4 pagesAir Receiver Sizing Metric UnitsAnonymous Od7nYs8No ratings yet
- CompAir SolenoidValvesDocument8 pagesCompAir SolenoidValvesSam JoseNo ratings yet
- Fan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Document4 pagesFan Terminology and Definitions: Technical Bulletin TBN002.2/2003Ngoc Vũ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- COP Calculation of An HVAC SystemDocument7 pagesCOP Calculation of An HVAC SystemAbhishek PangeNo ratings yet
- Commercial Building Energy Use Insix Cities in Southern ChinaDocument14 pagesCommercial Building Energy Use Insix Cities in Southern Chinaforevertay2000No ratings yet
- C Ife: MEP Coordination in Building and Industrial ProjectsDocument51 pagesC Ife: MEP Coordination in Building and Industrial Projectsfifthslip100% (1)
- 2937 Tech SpecDocument71 pages2937 Tech Specforevertay2000No ratings yet
- 4 Appendix C, SpecsDocument109 pages4 Appendix C, Specsforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Power Factor CorrectionDocument15 pagesPower Factor CorrectionRalph Jason Alvarez100% (1)
- Chiller Vs VRF 220811Document6 pagesChiller Vs VRF 220811Jebi Se100% (1)
- Three PhaseDocument17 pagesThree Phaseforevertay2000No ratings yet
- MonA1030 LugarDocument20 pagesMonA1030 Lugarforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Green Star Office v3 - Potable Water Calculator GuideDocument12 pagesGreen Star Office v3 - Potable Water Calculator Guideforevertay2000No ratings yet
- AC SpecDocument60 pagesAC SpecasdthuNo ratings yet
- COP+Greywater+Reuse+2010 v2 130103Document58 pagesCOP+Greywater+Reuse+2010 v2 130103forevertay2000No ratings yet
- Acca 5Document46 pagesAcca 5amechmar5935100% (1)
- Systematic Design of A Maximum Water Recovery Network For An Urban System Based On Pinch AnalysisDocument8 pagesSystematic Design of A Maximum Water Recovery Network For An Urban System Based On Pinch Analysisforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Fire Detection and Alarm Systems: 8.1 GeneralDocument8 pagesChapter 8 - Fire Detection and Alarm Systems: 8.1 Generalforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Rainwater Harvesting Guide For MalaysiansDocument41 pagesRainwater Harvesting Guide For MalaysiansGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Hazop Model RequirementsDocument30 pagesHazop Model RequirementsrvnesariNo ratings yet
- CB FP 2010 20Document1 pageCB FP 2010 20forevertay2000No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document16 pagesChapter 9forevertay2000No ratings yet
- Code of Practice On Sewerage and Sanitary WorksDocument56 pagesCode of Practice On Sewerage and Sanitary Worksexlife86100% (2)
- Fire Sprinkler SystemsDocument8 pagesFire Sprinkler SystemskktayNo ratings yet
- VoiceDocument27 pagesVoiceforevertay2000No ratings yet
- DryPipeSystems RevDocument24 pagesDryPipeSystems RevCostel BalasoiuNo ratings yet
- Cooling Your Home With Fans and VentilationDocument8 pagesCooling Your Home With Fans and Ventilationzubair90No ratings yet
- DuctDocument60 pagesDuctdenizkund100% (5)
- Cont 694003Document49 pagesCont 694003forevertay2000No ratings yet
- 12Document17 pages12forevertay2000No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument18 pagesDocumentforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Technical Specification El Adm 137 12Document50 pagesTechnical Specification El Adm 137 12palgvenuNo ratings yet
- 240valve Control To Major Savings)Document2 pages240valve Control To Major Savings)forevertay2000No ratings yet