Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Describe How Cells Grow
Describe How Cells Grow
Uploaded by
Michael BriscoeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Describe How Cells Grow
Describe How Cells Grow
Uploaded by
Michael BriscoeCopyright:
Available Formats
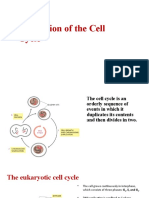
Describe How Cells Grow Can mean increase in cell size (Hypertrophy) or cell number (proliferation) Occurs during
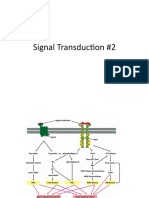
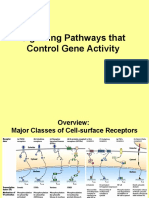
ng fetal and childhood growth, but also a feature throughout adult life Phase G1 What Happens Cell grows in size and prepares itself for DNA synthesis Monitors internal and external environment S phase DNA synthesis TRIGGERED BY S-CDKs activate proteins which unwind DNA (helicases) and initiate replication G2 Cell grows in size, duplicates organelles. Prepares for division Mitosis Condensation of duplicated chromosomes, loss of nuclear envelope, alignment of chromosomes along equator, separation to opposite poles regulated by M-CDK which also promotes breakdown of nuclear envelope Cytokinesis Cleavage of daughter cells through formation of a cellular plate Ways in which signaling molecules lead to changes in cell behavior RTK with intrinsic kinase activity directly phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues RTK are integral membrane proteins with three domains: extracellular; transmembrane; intracellular Ligand binding to a single transmembrane receptor via extracellular domain causes receptor chains to dimerise which catalyzes receptor autophosphorylation and tyrosine phosphorylation of RTK residues Increased kinase activity Signalling proteins Src/PTB (tyrosine kinases) bind to specific phosphorylated sites on receptor because of binding domains When SH2 (protein domain of Src oncoprotein) become activated, they then activate a set of genes encoding GUANINE NUCLEOTIDE EXCHANGE FACTORS. Sos gene encodes a ras-GEF, which is required for sev RTK to activate ras. Sos protein actiovates ras by acting ass Ras-GEF. Sos protein causes ras to undergo conformational change. After EXCHANGING GDP FOR GTP. Ras activates a MAP KINASE SIGNALLING MODULE. (mitogen activated protein kinase) Activated ras stimulates the enzyme Raf-protein kinase. *(map kinase kinase kinase) which phosphorylates and axtivates an enzyme MAPKK (Mek) which phosphorylates and activates Map kinase (Erk) Erk phosphorylates various proteins within the cell including gene regulatory proteins and directly influences cycling production.
You might also like
- BIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsDocument32 pagesBIOL 215 - CWRU Final Exam Learning GoalsKesharaSSNo ratings yet
- Cell Signalling 1.2 2017Document61 pagesCell Signalling 1.2 2017PutriNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Linked Receptors LectureDocument52 pagesEnzyme Linked Receptors LectureJason PastisNo ratings yet
- Effect of Growth Factors On CellsDocument6 pagesEffect of Growth Factors On Cellsv.shivakumarNo ratings yet
- Intracellular Signal TransductionDocument42 pagesIntracellular Signal TransductionYunita FatmalaNo ratings yet
- 13 Miller Chap 16 LectureDocument12 pages13 Miller Chap 16 LectureFarmasi SMKNegeri1SambiNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument30 pagesSignal Transductionpalak100% (1)
- Signaling Pathways1189Document26 pagesSignaling Pathways1189Mehedi HossainNo ratings yet
- Biosel Ke 7Document99 pagesBiosel Ke 7Rena PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Cell CommunicationDocument51 pagesMechanisms of Cell CommunicationSujanNo ratings yet
- Tendons and RehabDocument1 pageTendons and Rehablucas o'brienNo ratings yet
- DNA2life - What Does A Cell Need To Divide &surviveDocument45 pagesDNA2life - What Does A Cell Need To Divide &survivedna2lifeNo ratings yet
- G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Tyrosine Kinases: Crossroads in Cell Signaling and RegulationDocument7 pagesG-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Tyrosine Kinases: Crossroads in Cell Signaling and RegulationFlorencia FirenzeNo ratings yet
- Membraan Nucleus Voortgang GroeihormonenDocument3 pagesMembraan Nucleus Voortgang GroeihormonenMeNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction PathwaysDocument6 pagesSignal Transduction PathwaysSHREYA SENTHIL KUMAR IMS21286No ratings yet
- Cell Signaling in Space and Time:: Where Proteins Come Together and When They're ApartDocument20 pagesCell Signaling in Space and Time:: Where Proteins Come Together and When They're ApartHumbertoNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction in CellsDocument25 pagesSignal Transduction in CellsSadaf BegNo ratings yet
- Mitogen Activated Protein KinasesDocument13 pagesMitogen Activated Protein KinasesVeer BabuNo ratings yet
- Tirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Document8 pagesTirosin Kinase Receptor (RTK)Nur Afra YsNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction Lecture 2Document30 pagesSignal Transduction Lecture 2chrystalNo ratings yet
- Cell SignalingDocument28 pagesCell SignalingRosita DehiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document26 pagesLecture 5BlaNo ratings yet
- Mapk Renal Di: /ERK Signaling in Regulation of FferentiationDocument21 pagesMapk Renal Di: /ERK Signaling in Regulation of Fferentiationlinda ratna watiNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & ApoptosisDocument20 pagesThe Cell Cycle & ApoptosisSathiyaraj100% (4)
- Cell Cycle ImmunostainingDocument11 pagesCell Cycle ImmunostainingHendra Wana Nur'aminNo ratings yet
- 7 CommunicationDocument18 pages7 CommunicationUtkarsh DubeyNo ratings yet
- The Language of CellsDocument25 pagesThe Language of Cellsdry_ice123No ratings yet
- Transduction Protein Interactions Define Specificity in Signal ProteinDocument22 pagesTransduction Protein Interactions Define Specificity in Signal ProteinnitishpathaniaNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar SelDocument39 pagesKomunikasi Antar SelMOCHILNo ratings yet
- BiosignallingDocument16 pagesBiosignallingAsmaa HatemNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression 2018Document34 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression 2018nikkiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Final Exam Notes For Daly's Cell Bio Class at Purchase CollegeDocument3 pagesCell Biology Final Exam Notes For Daly's Cell Bio Class at Purchase CollegeTori RoggenNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases 2021Document44 pages1 2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases 2021Bilakovics NoemiNo ratings yet
- Fimmu 03 00130Document18 pagesFimmu 03 00130Isabella1237No ratings yet
- How To Study DNA: 1. Genetic Material 2. Expression ProductDocument57 pagesHow To Study DNA: 1. Genetic Material 2. Expression ProductLaila Istighfaroh Ella EllEllNo ratings yet
- L13 Biol 261 ERegulation 2013Document30 pagesL13 Biol 261 ERegulation 2013jdazuelosNo ratings yet
- GADD45B Growth Arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, BetaDocument6 pagesGADD45B Growth Arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, BetaHassan Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Its RegulationDocument16 pagesCell Cycle & Its RegulationElina GNo ratings yet
- Kul Biokimia Homeostasis FK 2023Document17 pagesKul Biokimia Homeostasis FK 2023soraya rahmanisaNo ratings yet
- Epigenetic Regulation in Plants: Ryza Aditya Priatama (리자 아디티아)Document30 pagesEpigenetic Regulation in Plants: Ryza Aditya Priatama (리자 아디티아)lordniklausNo ratings yet
- OncogeneDocument1 pageOncogenedrnazzNo ratings yet
- Signaling of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in The Nucleus: Sally-Anne Stephenson, Inga Mertens-Walker and Adrian HeringtonDocument25 pagesSignaling of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in The Nucleus: Sally-Anne Stephenson, Inga Mertens-Walker and Adrian HeringtonAyu SafitriNo ratings yet
- Cell SignallingDocument72 pagesCell SignallingSheerin SulthanaNo ratings yet
- Cell SignallingDocument8 pagesCell SignallingLemar NawabiNo ratings yet
- 16) Signaling Pathways That Control Gene ActivityDocument27 pages16) Signaling Pathways That Control Gene ActivityRNo ratings yet
- MBB 201 Problem Set 10Document5 pagesMBB 201 Problem Set 10Taran DhattNo ratings yet
- Regulation of The Cell Cycle For UVLeDocument31 pagesRegulation of The Cell Cycle For UVLeErika Corinne SisonNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument42 pagesSignal TransductionchinnnababuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document15 pagesLesson 6DollyNo ratings yet
- Chuong63 Tyrosine KinaseDocument19 pagesChuong63 Tyrosine KinaseLê Phuong MaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 8-2Document26 pagesUnit 8-2beboooo1483No ratings yet
- Self - Sufficiency in Growth Signals Cancer.Document21 pagesSelf - Sufficiency in Growth Signals Cancer.siddhant kushareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234Document35 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234afeeqrashidNo ratings yet
- Biologia Molecular e Celular: Signaling PathwaysDocument25 pagesBiologia Molecular e Celular: Signaling PathwaysMariana MesquitaNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes: Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory Syahril@medic - Upm.edu - MyDocument28 pagesGene Regulation in Eukaryotes: Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory Syahril@medic - Upm.edu - MySuren BobNo ratings yet
- TheMitoticCellCycle PDFDocument15 pagesTheMitoticCellCycle PDFStiven Andrade PeñaNo ratings yet
- Biology 230 - Molecules and Cells: TermsDocument12 pagesBiology 230 - Molecules and Cells: TermsAman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2saras87No ratings yet
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Countercurrent MultiplicationDocument4 pagesCountercurrent MultiplicationMichael Briscoe100% (1)
- (Nor) Is The (Murky-Side) (North of The Hamptons) of (Northwards), (Nor Your) (Oxygen) (Sloppy) inDocument1 page(Nor) Is The (Murky-Side) (North of The Hamptons) of (Northwards), (Nor Your) (Oxygen) (Sloppy) inMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet
- Common Methods of Contraception Methods With No User Failure Method Effectiveness How It Works Advantages DisadvantagesDocument5 pagesCommon Methods of Contraception Methods With No User Failure Method Effectiveness How It Works Advantages DisadvantagesMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 - Week 4 - Cell CycleDocument3 pagesPhase 1 - Week 4 - Cell CycleMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet
- Human Growth HormoneDocument2 pagesHuman Growth HormoneMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 RevisionDocument3 pagesPhase 1 RevisionMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet
- The Volume of Blood in An Average Sized Person Is Approximately 5.5LDocument2 pagesThe Volume of Blood in An Average Sized Person Is Approximately 5.5LMichael BriscoeNo ratings yet