Professional Documents
Culture Documents
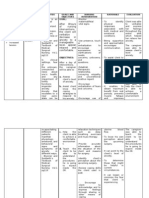
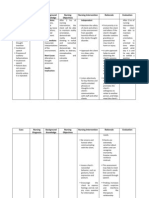
Cues / Clues Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis Psychodynam Ics (Rationale) Planning Therapeutic Approach Rationale (With Theories) Evaluation
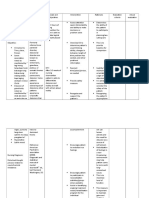
Cues / Clues Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis Psychodynam Ics (Rationale) Planning Therapeutic Approach Rationale (With Theories) Evaluation
Uploaded by
Diana TardecillaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
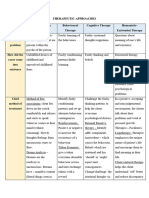
Cues / Clues Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis Psychodynam Ics (Rationale) Planning Therapeutic Approach Rationale (With Theories) Evaluation
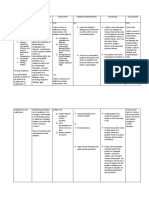
Cues / Clues Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis Psychodynam Ics (Rationale) Planning Therapeutic Approach Rationale (With Theories) Evaluation
Uploaded by
Diana TardecillaCopyright:
Available Formats
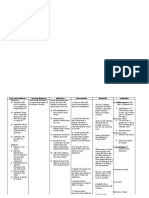
Cues / Clues
Psychiatric Nursing Diagnosis Disturbed Thought Processes related to disruption in cognitive operations and activities as evidenced by confused facial expression
Psychodynam ics (RATIONALE)
PLANNING
Therapeutic Approach
RATIONALE (with Theories)
EVALUATION
Subjective Cue: Nung nasa Taiwan ako napossess ako. Dinala ako dito ng tatay ko sa Pilipinas tapos nasaktan ko yung nanay ko nung may kausap siya sa phone , as verbalized by the patient Objective: GA: Poor personal grooming Confused facial expression Unkempt/disheveled appearance Sensory & Cognition: Conscious, oriented to time, person & place Impaired memory on personal information Poor concentration regarding specific topics
Short term outcome:
INDEPENDENT: 1. Providing general After 8 hours of nursing leads intervention, the pt will a. Approach the be able to : client in slow, calm, matter-af Demonstrate fact manner reality based b. Maintain facial thinking in expression and verbal and non behaviors that are verbal behavior consistent with Demonstrated verbal statements reduction of frequency of delusions Participate in social activities and group therapies
1. A calm approach Outcome helps to avoid Achieved: distorting the clients sensory The perceptual field patient which helps could demonstr promote disturbed ated thoughts and reality perceptions based Peplau defined thinking in Psychodynamic verbal nursing as being and non able to understand verbal ones own behavior. behavior to help The others identify felt patient difficulties and to demonstr apply principles of ated a human relations to reduction the problems that of arise at all levels frequency of experience. of delusions. The 2. Delusions cannot patient
2. Providing specific questions Avoid challenging the clients delusional system or arguing with the client.
be changed thru logic and challenging the belief of the patient, no matter how irrational. As the client may be forced to cling to it and defend it. Rogers described a variation of self as the inherent potentialities of the actualizing tendencies that can suffer the distorted expression when maladjustment occurs resulting in behavior destructive to oneself and others.
participate d in social activities such as group therapies.
3. Presenting Reality Distract the client from the delusion by engaging him in a less threatening or a
3. Dwelling to the delusional content may increase the clients anxiety, aggression and
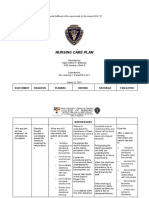
more comforting topic or activity at the first sign of anxiety and discomfort.
4. Offering praise Offer recognition as soon as the client begins to differentiate between reality based and non reality based thoughts and behaviors.
other dysfunctional behavior. Rogers revised his previous thinking concerning this incongruence. He stated the perversions of the unitary actualizing tendency. We do not come into the world estranged from ourselves, socialization is behind this alienation. 4. Positive reinforcement increases self esteem and encourage the client to identify and continue reality based thoughts and behavior. 5. Clear direct
5. Giving information Offer the client clear, simple explanations of environmental events, activities and
the behaviors of other clients as necessary,
explanations of environment events help to lessen the clients suspiciousness and fear or mistrust of the surroundings and other. This can prevent aggressive behavior.
COLLABORATIVE: 1. Continue to administer and monitor the effects of the prescribed medication CHLORPROMAZINE (Thorazine) Haloperidol Fluprenazine
CHLORPROMAZINE is classified as a low potency antipsychotic and in the past was used for the treatment of both acute and chronic psychosis, including Schizophrenia. It is still well recommended for short term management of severe anxiety and aggressive episodes.
You might also like
- Alcoholism Care PlanDocument11 pagesAlcoholism Care Planilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- DBT Visual Review Flash CardDocument14 pagesDBT Visual Review Flash CardBeyza Gül89% (9)
- Needs/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleDocument1 pageNeeds/ Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleHarold PeranduzNo ratings yet
- Schiz NCPDocument5 pagesSchiz NCPCharisse LuteroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: Short Term Goal: Short Term Goalmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Shortcut Keys A To ZDocument7 pagesAutoCAD Shortcut Keys A To Zamirkhanhbk83% (6)
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- NCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMDocument3 pagesNCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Depression PDFDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Depression PDFtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- A Historical Examination of Concrete PDFDocument324 pagesA Historical Examination of Concrete PDFMa Ria Fe100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCharles Mallari Valdez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Situational Low SelfChar Perea100% (1)
- Horkheimer, Max - Critical Theory (Continuum, 1972)Document312 pagesHorkheimer, Max - Critical Theory (Continuum, 1972)hank07No ratings yet
- S09-07 - Salvation of The SagesDocument35 pagesS09-07 - Salvation of The SagesNicolasNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Mundane MaterialsDocument140 pages3.5 Mundane MaterialsJames LewisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Cerebrovascular AccidentJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - YoungDocument15 pagesAssignment 1 - Youngejyoung928100% (2)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSIris Coronel AdamosNo ratings yet
- Light and Sound Unit Study GuideDocument11 pagesLight and Sound Unit Study GuideHCSLearningCommonsNo ratings yet
- Alzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesAlzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanMary Josette NavarraNo ratings yet
- Group NCPDocument17 pagesGroup NCPNiña Noreen Torres VallegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan CVAhermesdave175% (4)
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Document3 pagesDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezNo ratings yet
- NCP-Alzheimer's Disease (Caguimbay)Document9 pagesNCP-Alzheimer's Disease (Caguimbay)Christine Claire CaguimbayNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence & CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques for improving Your Relationships and EQ - Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Manipulation, Narcissistic Abuse, and More!From EverandEmotional Intelligence & CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Techniques for improving Your Relationships and EQ - Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Manipulation, Narcissistic Abuse, and More!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (35)
- NCP ImpairedSocial AutismDocument2 pagesNCP ImpairedSocial AutismPaul AnteNo ratings yet
- NPI WorkingDocument4 pagesNPI Workingejyoung928100% (1)
- PostgreSQL Functions by ExampleDocument41 pagesPostgreSQL Functions by ExampleNguyễn Đăng HưngNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence Mastery: The Complete Guide for Improving Your EQ, Relationships, and Social Skills to Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Manipulation, Narcissistic Abuse, and More!From EverandEmotional Intelligence Mastery: The Complete Guide for Improving Your EQ, Relationships, and Social Skills to Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Manipulation, Narcissistic Abuse, and More!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (56)
- Nursing Care Plan Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Autism Spectrum DisorderHarold Peranduz100% (5)
- Leading ChangeDocument6 pagesLeading ChangeMarcela CostaNo ratings yet
- NCP Low Self Esteem DreiDocument5 pagesNCP Low Self Esteem DreiEllenare RacionNo ratings yet
- Complicated Grief NCPDocument2 pagesComplicated Grief NCPChristine LebicoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 AssignmentDocument3 pagesModule 5 AssignmentjessiejuliacNo ratings yet
- ANGEL-NCP - CaseloadDocument7 pagesANGEL-NCP - CaseloadNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Care Plan UndifferentiatedDocument11 pagesCare Plan Undifferentiatedilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 in RLE 117Document2 pagesNCP 2 in RLE 117unkown userNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Subject NCM 117Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Subject NCM 117Ingrid Valerie BalendezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Mr. John E: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rational EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For Mr. John E: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rational EvaluationArnold Dickens JosephNo ratings yet
- NCP MentalDocument3 pagesNCP MentalColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Cues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCues Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanRenz VillalobosNo ratings yet
- NCP NCM 117 Silva Bsn-3aDocument3 pagesNCP NCM 117 Silva Bsn-3aLance SilvaNo ratings yet
- Care Plan On AlzheimerDocument4 pagesCare Plan On Alzheimeranimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Labio Psych Eval ReportDocument7 pagesLabio Psych Eval ReportDesiree Obtial LabioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesNo ratings yet
- Schizo NCPDocument18 pagesSchizo NCPRoscheen Berg TutorNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationSTA INES, ELIJAH DOMINIQUENo ratings yet
- NCP SchizDocument12 pagesNCP SchizKristine Reyes - MerleNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Basic Counselling SkillsDocument1 pageTopic 5 Basic Counselling SkillsNanthiniNaveeshaNo ratings yet
- Azarcon NCPDocument5 pagesAzarcon NCPROGEN KATE AZARCONNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Fatima MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process: SL NO Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions and Rationale Implementation EvaluationDocument13 pagesNursing Process: SL NO Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions and Rationale Implementation Evaluationilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology - THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES TableDocument3 pagesAP Psychology - THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES TableneelNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermhelloaNo ratings yet
- Margaret Newman NCPDocument4 pagesMargaret Newman NCPRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2LwhynnNo ratings yet
- Npi and ReadingDocument10 pagesNpi and ReadingCHARLEMAIGNE RECOMESNo ratings yet
- Deficient Knowledge CanalesDocument4 pagesDeficient Knowledge CanalesIzhra MargateNo ratings yet
- Basic Helping SkillsDocument2 pagesBasic Helping SkillsMaFe Villanueva AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument12 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Goal & Outcome Criteria Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Modificati On Interventi On RationaleDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan Goal & Outcome Criteria Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Modificati On Interventi On RationaleJan Dee ApuraNo ratings yet
- Communicating The Management To The PatientDocument1 pageCommunicating The Management To The PatientML MariaWengNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence Mastery: Everything You Need to Know About EQ to Achieve Your Goals and Master Your Emotions (2022 Guide for Beginners)From EverandEmotional Intelligence Mastery: Everything You Need to Know About EQ to Achieve Your Goals and Master Your Emotions (2022 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Unveiling the Power of Your Subconscious Mind: A Journey to Self-Discovery and Personal GrowthFrom EverandUnveiling the Power of Your Subconscious Mind: A Journey to Self-Discovery and Personal GrowthNo ratings yet
- Nighttime Narratives: How to Use Dreams for Personal Growth and Understand Dream Symbols and Their MeaningsFrom EverandNighttime Narratives: How to Use Dreams for Personal Growth and Understand Dream Symbols and Their MeaningsNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 - YoungDocument12 pagesPractice Questions 1 - Youngejyoung928100% (1)
- 2010Document59 pages2010ejyoung928No ratings yet
- Express Terms (Lecture Notes) - UKTDocument7 pagesExpress Terms (Lecture Notes) - UKTJeyshinaa dev kumarNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 2 COPY OF LECTURE 21st Century LitDocument10 pagesWEEK 1 2 COPY OF LECTURE 21st Century LitHazel ZabellaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Debugging Simulation ModelsDocument74 pagesPresentation Title: Debugging Simulation ModelsflyingdreamsNo ratings yet
- Cost Acctg FohDocument37 pagesCost Acctg FohRizza Christine Thereza UsbalNo ratings yet
- OADocument27 pagesOADarkKnighthere100% (1)
- Lat235 Pset 8Document5 pagesLat235 Pset 8Muhamad Arthura Arya FarrozNo ratings yet
- Sample Seminar Report PDFDocument8 pagesSample Seminar Report PDFhimavanthNo ratings yet
- The Four Confidences EbookDocument38 pagesThe Four Confidences EbookIgor PopadicNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Hip Dislocation in Children: Original StudyDocument6 pagesTraumatic Hip Dislocation in Children: Original StudyAlvin JiwonoNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Contingency Model:: An Integrated Framework To Manage The Complexity of CommunicationDocument18 pagesThe Strategic Contingency Model:: An Integrated Framework To Manage The Complexity of CommunicationHang Zi QiNo ratings yet
- EQT SIM Release Note 1.6.4Document8 pagesEQT SIM Release Note 1.6.4veerabossNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Helminth - EditedDocument58 pagesBab 6 Helminth - EditedChrisfenna MadihvolNo ratings yet
- 2020 Fact Sheet 11th Report SG On CRSVDocument2 pages2020 Fact Sheet 11th Report SG On CRSVsofiabloem100% (1)
- GyroscopesDocument27 pagesGyroscopesMadhan RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- The Poetic Process and The Poetic GeniusDocument6 pagesThe Poetic Process and The Poetic Geniusadeloptera100% (2)
- UKG Holiday WorkDocument20 pagesUKG Holiday WorktrasbaceNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Unity of MindsDocument1 pageAnalysis of Unity of MindsNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1-UCA RC June 2019 Reading Comprehension and Précis S2Document3 pages1-UCA RC June 2019 Reading Comprehension and Précis S2salma benallaNo ratings yet
- Non-Classical Models of IR (Uploaded by Snaptricks - In)Document8 pagesNon-Classical Models of IR (Uploaded by Snaptricks - In)sharan rajNo ratings yet
- DLL-Take Body MeasurementDocument5 pagesDLL-Take Body MeasurementRhea GuevarraNo ratings yet
- (Heat and Mass Transfer) Karl Sommer (Auth.), Henning Bockhorn, Dieter Mewes, Wolfgang Peukert, Hans-Joachim Warnecke (Eds.)-Micro and Macro Mixing_ Analysis, Simulation and Numerical Calculation-SpriDocument345 pages(Heat and Mass Transfer) Karl Sommer (Auth.), Henning Bockhorn, Dieter Mewes, Wolfgang Peukert, Hans-Joachim Warnecke (Eds.)-Micro and Macro Mixing_ Analysis, Simulation and Numerical Calculation-SpriGian Carlos Perea DiazNo ratings yet
- Andy WarholDocument4 pagesAndy WarholAngel Angeleri-priftis.No ratings yet