Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RMS of Common Waveforms
Uploaded by
senthilanview0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesThis document provides equations and values for the root mean square (RMS) of various common waveforms including DC, sine waves, square waves, shifted square waves, modified square waves, triangle waves, sawtooth waves, and pulse trains. It notes that the RMS of waveforms made by summing known simple waveforms is the square root of the sum of the component RMS values squared, if the components are orthogonal. It also gives a special case equation for finding the RMS when a signal has both DC and AC components.
Original Description:
RMS of Common Waveforms
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides equations and values for the root mean square (RMS) of various common waveforms including DC, sine waves, square waves, shifted square waves, modified square waves, triangle waves, sawtooth waves, and pulse trains. It notes that the RMS of waveforms made by summing known simple waveforms is the square root of the sum of the component RMS values squared, if the components are orthogonal. It also gives a special case equation for finding the RMS when a signal has both DC and AC components.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesRMS of Common Waveforms
Uploaded by
senthilanviewThis document provides equations and values for the root mean square (RMS) of various common waveforms including DC, sine waves, square waves, shifted square waves, modified square waves, triangle waves, sawtooth waves, and pulse trains. It notes that the RMS of waveforms made by summing known simple waveforms is the square root of the sum of the component RMS values squared, if the components are orthogonal. It also gives a special case equation for finding the RMS when a signal has both DC and AC components.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
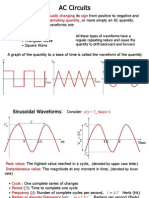
RMS of common waveforms
Waveform
Equation
RMS
DC, constant
Sine wave
Square wave
DC Shifted Square wave
Modified square wave
Triangle wave
Sawtooth wave
Pulse train
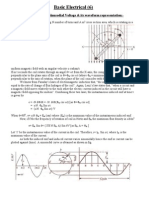
Notes: t is time f is frequency a is amplitude (peak value) D is the duty cycle or the percent(%) spent high of the period (1/f) {r} is the fractional part of r Waveforms made by summing known simple waveforms have an RMS that is the root of the sum of squares of the component RMS values, if the component waveforms are orthogonal (that is, if the average of the product of one simple waveform with another is zero for all pairs other than a waveform times itself).
A special case of this, particularly helpful in electrical engineering, is
where refers to the DC component of the signal and the AC component of the signal.
is
You might also like
- 083 Martin RotorDocument60 pages083 Martin RotormarintraianNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sinusoidal WaveformsDocument19 pagesSinusoidal WaveformsAshlee VNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Module 1Document28 pagesAC Circuits Module 1YoNo ratings yet
- Stilson-Smith - Alias-Free Digital Synthesis of Classic Analog Waveforms (BLIT)Document12 pagesStilson-Smith - Alias-Free Digital Synthesis of Classic Analog Waveforms (BLIT)HangTheBankersNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument9 pagesRoot Mean Squarebauro mikaereNo ratings yet
- Sinusodial WaveDocument7 pagesSinusodial WaveDave PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Root Mean Square: VerificationDocument11 pagesRoot Mean Square: VerificationNick JohnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4Mouath AlsebaieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Phasors 1: Sinusoidal SignalsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Phasors 1: Sinusoidal SignalsshivanshuNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit (2) Lec1Document15 pagesElectric Circuit (2) Lec1Mohamed HammadNo ratings yet
- 01 Fundtls and WaveshapingDocument29 pages01 Fundtls and WaveshapingFrancisNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument30 pagesAC FundamentalsSouhardya RoyNo ratings yet
- Pe Chapter 2 - 3Document14 pagesPe Chapter 2 - 3yiyej11346No ratings yet
- CKTS LESSON-SinusoidDocument36 pagesCKTS LESSON-SinusoidNicoNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: Continually Changing Sign Alternating QuantityDocument10 pagesAC Circuits: Continually Changing Sign Alternating QuantityMathew ClewlowNo ratings yet
- Ci It TH Circuit Theory: Electronic & Communication Engineering Danang University of TechnologyDocument43 pagesCi It TH Circuit Theory: Electronic & Communication Engineering Danang University of TechnologyDoan Thanh ThienNo ratings yet
- Form FactorDocument4 pagesForm FactortusharNo ratings yet
- Some Terminology: Power and RMS Values Motors and GeneratorsDocument2 pagesSome Terminology: Power and RMS Values Motors and GeneratorsMahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Module 2A (AC Fundamentals)Document102 pagesModule 2A (AC Fundamentals)vipin10thj.27828No ratings yet
- M3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitDocument67 pagesM3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitUDhayNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument19 pagesChapter Oneمصطفى احمد محيسنNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Electrical EnggDocument79 pagesModule 3 Electrical EnggAnand ANo ratings yet
- PAPER 2003 05 en RMS Measuring Principles in The Application of Protective Relaying and MeteringDocument22 pagesPAPER 2003 05 en RMS Measuring Principles in The Application of Protective Relaying and MeteringNirmala AllamNo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument29 pagesSingle Phase AC Circuitskali hembramNo ratings yet
- ApplicationNoteAN1108-RegulationofHarmonics 000 PDFDocument8 pagesApplicationNoteAN1108-RegulationofHarmonics 000 PDFBalan PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- Root Mean SquareDocument3 pagesRoot Mean SquaresenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Waveform: Waveform Means The Shape and Form ofDocument2 pagesWaveform: Waveform Means The Shape and Form offiraszekiNo ratings yet
- 01 Electrical Parameter Periodic WaveDocument15 pages01 Electrical Parameter Periodic WaveYash MotianiNo ratings yet
- Idresss Sir#1Document11 pagesIdresss Sir#1Dil NawazNo ratings yet
- Power Quality 4Document36 pagesPower Quality 4Angel Fel BurlatNo ratings yet
- Signals and Spectra: Dr. Ho Van Khuong Tele. Dept., HCMUT Email: ADocument38 pagesSignals and Spectra: Dr. Ho Van Khuong Tele. Dept., HCMUT Email: AmottiendayNo ratings yet
- Señales Pasabanda de CWDocument83 pagesSeñales Pasabanda de CWgermanNo ratings yet
- Harmonics AnalysisDocument4 pagesHarmonics Analysisabdulla ahmedNo ratings yet
- Module2 Besck104bDocument19 pagesModule2 Besck104bdivyaNo ratings yet
- Computation of Transient Electromagnetic Force On Power Transformer Windings by Inrush CurrentDocument8 pagesComputation of Transient Electromagnetic Force On Power Transformer Windings by Inrush CurrentDavid LopesNo ratings yet
- AC TheoryDocument10 pagesAC TheoryshrnbolonneNo ratings yet
- Waveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesDocument10 pagesWaveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical NotesDocument58 pagesBasic Electrical NotesKamal Joshi100% (2)
- Average Values & Effective ValuesDocument11 pagesAverage Values & Effective ValuesDravid NagiNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument91 pagesAC Circuitcarlverano0428No ratings yet
- Titolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: ActodcDocument72 pagesTitolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Electronic Power Conversion: ActodcEliot KhNo ratings yet
- RMSDocument11 pagesRMSRsuneelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document8 pagesLecture 7muneeralhrNo ratings yet
- Papirntobfgwuifbgbogbg BeeDocument13 pagesPapirntobfgwuifbgbogbg BeeHANZ JERICHO HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 EEDocument14 pagesLecture 9 EESwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09-IDocument14 pagesLecture 09-IzaidNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document51 pagesUnit 4karnatisharathNo ratings yet
- Reviewer FinaleDocument15 pagesReviewer FinaleJesslian Agatha RiceroNo ratings yet
- Spatial FrequencyDocument4 pagesSpatial Frequencynaivedya_mishraNo ratings yet
- Types of Square, Triangular and Sine SignalsDocument4 pagesTypes of Square, Triangular and Sine Signals492210672No ratings yet
- HFE0611 BennettDocument4 pagesHFE0611 Bennettarunkr1No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document7 pagesLecture 5Hussain NaushadNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering Lecture No: 7-10 Unit No: 1: Smith ChartDocument12 pagesMicrowave Engineering Lecture No: 7-10 Unit No: 1: Smith ChartAshutosh PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 1Document15 pagesLecture 1 1nehaNo ratings yet
- Elec 6Document2 pagesElec 6logon_saralNo ratings yet
- EECE105L 2021 Part1Document119 pagesEECE105L 2021 Part1Shreyansh GargNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2marcelineparadzaiNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Oil Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageWorking Principle of Oil Circuit BreakersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Your Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginesDocument2 pagesYour Dash Lights: Heavy-Duty EnginessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Just The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightsDocument1 pageJust The Facts: Vehicle Warning LightssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Potential Transformer DefinitionDocument1 pagePotential Transformer DefinitionsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- VT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)Document1 pageVT Error Voltage Error or Ratio Error in Potential Transformer (PT) or Voltage Transformer (VT)senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- The Dashboard WarningDocument2 pagesThe Dashboard WarningsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Figure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2Document5 pagesFigure 49: AC Method For Testing Transformer Polarities: POL H X 1 2 POL H X 1 2senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- (Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementDocument3 pages(Employee Signature) Post-Accident Drug Test Requests of - County ManagementsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding Transformer 1Document1 pageTwo Winding Transformer 1senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Two Winding TransformerDocument3 pagesTwo Winding TransformersenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Experienced Driver Ongoing TrainingDocument3 pagesExperienced Driver Ongoing TrainingsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- What Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?Document1 pageWhat Happens When A Transformer Is Subjected To DC Voltage in The Primary? What Happens in The Saturation Mode?senthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Winding Temperature Simulation SystemDocument3 pagesWinding Temperature Simulation SystemsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Marking of Bushing CtsDocument2 pagesIdentifying and Marking of Bushing CtssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Primary Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pagePrimary Duties and ResponsibilitiessenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Module4 PKDocument21 pagesModule4 PKsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Learn How To Study EffectivelyDocument1 pageLearn How To Study EffectivelysenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current TransformersDocument2 pagesCurrent TransformerssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Current Transformes:: Accuracy ClassDocument1 pageCurrent Transformes:: Accuracy ClasssenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Effect of Transient DDocument1 pageEffect of Transient DsenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- Polarity CheckDocument2 pagesPolarity ChecksenthilanviewNo ratings yet
- CT SaturationDocument2 pagesCT SaturationsenthilanviewNo ratings yet