Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy
Anatomy
Uploaded by
kristel_nicole18yahoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy
Anatomy
Uploaded by
kristel_nicole18yahoCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy & Physiology
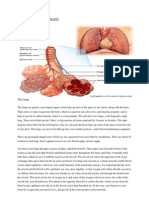
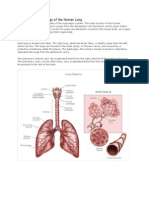
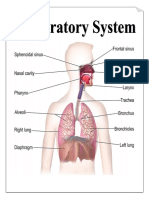
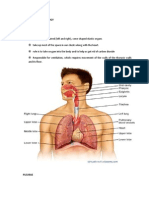
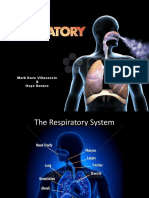
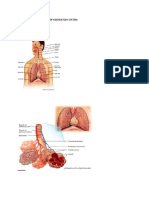
The LUNGS are paired cone-shaped organs which take up most of the space in our chests, along with the heart. Their role is to take oxygen into the body, which we need for our cells to live and function properly, and to help us get rid of carbon dioxide, which is a waste product. Each of us has two lungs, a left lung and a right lung. These are divided up into lobes, or big sections of tissue separated by fissures or dividers. The right lung has three lobes but the left lung has only two, because the heart takes up some of the space in the left side of our chest. The lungs can also be divided up into even smaller portions, called bronchopulmonary segments. These are pyramidal-shaped areas which are also separated portions from each other by membranes. There are about 10 of them in each lung. Each segment receives its own blood supply and air supply. The PLEURA is the body cavity that surrounds the lungs. And this is divided into two, the inner and outer. The pleural cavity, with its associated pleurae, aids optimal functioning of the lungs during respiration. The pleural cavity also contains PLEURAL FLUID, which allows the pleurae to side effortlessly against each other during ventilation.
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1Document1 pagePathophysiology of Spinal Cord Injury 1kristel_nicole18yaho67% (6)
- Learning Activity Sheets Grade 9 Science (Biology) First QuarterDocument18 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Grade 9 Science (Biology) First QuarterAngel88% (8)
- 3rd NCP Risk For ConstipationDocument2 pages3rd NCP Risk For Constipationkristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- PresentationDocument17 pagesPresentationLyka Ann GonzagaNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument2 pagesLungsDik DikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyBranzuela ChristineNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System.Document3 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory System.Alvin Patrick Colobong AsisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemchacameroNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument2 pagesLungsAlex MiuNo ratings yet
- Iv. Anatomy and Physiology of The Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesIv. Anatomy and Physiology of The Human Respiratory SystemJenny Vi CodenieraNo ratings yet
- The Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AliveDocument14 pagesThe Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AlivePeperoniiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemDavid DanielNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory Systemๆรำำทแร หบหฝำมฟNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Zahra Anggita PratiwiDocument36 pagesRespiratory System: Zahra Anggita PratiwizahraanggitaNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- 025735919Document3 pages025735919Vinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human LungDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human Lunghoneydine_03No ratings yet
- Body SystemDocument15 pagesBody SystemChris Timothy TurdanesNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 1 and 2Document6 pagesScience 9 Week 1 and 2Cherry Beth PagenteNo ratings yet
- F122100 Anisa Nurul HidayahDocument4 pagesF122100 Anisa Nurul HidayahAnisa Nurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Pathophy of CapDocument4 pagesPathophy of CapKatzii FranciaNo ratings yet
- Parts & Function of Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesParts & Function of Respiratory SystemLucille Ballares83% (6)
- Breathing Process PDFDocument3 pagesBreathing Process PDFDianeNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 - Module 1Document7 pagesSCIENCE 9 - Module 1cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- Core Concepts in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument50 pagesCore Concepts in Anatomy and PhysiologyMohamed Abdullah KhojaliNo ratings yet
- Q1 9 Science Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesQ1 9 Science Respiratory SystemPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 pagesVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acute Respiratory FailureDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Acute Respiratory FailureErieca Barsabal PamittanNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesVi. Anatomy and PhysiologyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Upper Respiratory TractDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Upper Respiratory TractAltea MartirezNo ratings yet
- Transparency 2Document11 pagesTransparency 2nitesh tirkeyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemBritany ReyesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsAillen AgustinNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Respiratory System For TodayDocument12 pagesOrgans of The Respiratory System For TodaySeptian PutraNo ratings yet
- Respiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory Systemegfr3yfgNo ratings yet
- Mark Dave Villasencio & Hope DuranoDocument11 pagesMark Dave Villasencio & Hope DuranoMark Dave VillasencioNo ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- LO4 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesLO4 - Respiratory SystemCHR1555No ratings yet
- Structure of The Respiratory System 2Document5 pagesStructure of The Respiratory System 2domhughes1093No ratings yet
- Why Do You Need To Breathe? - To LiveDocument5 pagesWhy Do You Need To Breathe? - To LiveJuan DavisNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Science 9 (Handouts)Document11 pagesModule 1-Science 9 (Handouts)leizl MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy of Respiratory Organs and Their FunctionsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemNesra de PeraltaNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Manusia Sistem RespirasiDocument12 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Manusia Sistem RespirasiJan ZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Second Sem Human Anatomy Notes PDFDocument34 pagesUnit - 1 Second Sem Human Anatomy Notes PDFeduardo vieiraNo ratings yet
- PDF 20231106 125606 0000Document1 pagePDF 20231106 125606 0000estradarhyestcocmlNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityDocument8 pagesRespiratory System: Nose and Nasal CavityJasper AlbuferaNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument5 pagesLungsTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 (Bil)Document6 pagesScience Week 1 (Bil)shashaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (MID)Document53 pagesScience Reviewer (MID)Francesca KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- Why Do You Need To BreatheDocument4 pagesWhy Do You Need To BreatheNur Hidayah MahaliNo ratings yet
- LUNGSDocument1 pageLUNGSVergel Jigs EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Function of The Normal LungDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Function of The Normal LungMangesh KetkarNo ratings yet
- Lungs - English ProjectDocument3 pagesLungs - English ProjectDokacodeNo ratings yet
- 34-2 Respiratory SystemDocument19 pages34-2 Respiratory Systemnancie8No ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Monday, Tuesday, Thursday & Friday: St. Pio of Pietrelcina ChapelDocument2 pagesMonday, Tuesday, Thursday & Friday: St. Pio of Pietrelcina Chapelkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects/Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility CNS-malaiseDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects/Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility CNS-malaisekristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Middle Adulthood (40 To 65 Years)Document1 pageMiddle Adulthood (40 To 65 Years)kristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Diagram I Pathogenesis of Insulin Dependent DM (Type 1) : DiagramsDocument2 pagesDiagram I Pathogenesis of Insulin Dependent DM (Type 1) : Diagramskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process: University of The East Ramon MagsaysayDocument5 pagesNursing Care Process: University of The East Ramon Magsaysaykristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Date: 04/29/14: Developed or Changed The Ranges From Her Chemistry LabDocument1 pageChemistry Date: 04/29/14: Developed or Changed The Ranges From Her Chemistry Labkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Behavior Student'S Learning Response: Conceptual FrameworkDocument5 pagesClinical Teaching Behavior Student'S Learning Response: Conceptual Frameworkkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Past Health History Medward3Document1 pagePast Health History Medward3kristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Hinds & Gattuso, 1999Document1 pageHinds & Gattuso, 1999kristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Practice: Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: ManagementDocument3 pagesEvidence-Based Practice: Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Managementkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePredisposing Factors Precipitating Factorskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Post-Cesarian Section: University of The EastDocument3 pagesCase Study: Post-Cesarian Section: University of The Eastkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan. 1st and 2nd Level AssessmentDocument7 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan. 1st and 2nd Level Assessmentkristel_nicole18yaho100% (1)
- Childlessness Is Defined As The Condition of Being Without ChildrenDocument2 pagesChildlessness Is Defined As The Condition of Being Without Childrenkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologykristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet