Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ups Types
Uploaded by
sri248Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ups Types
Uploaded by
sri248Copyright:
Available Formats
UPS:
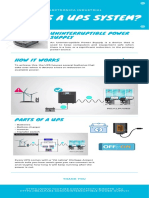
An uninterruptible power supply, also uninterruptible power source, UPS or battery/flywheel backup is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source, typically mains power, fails. A UPS differs from an auxiliary or emergency power system or standby generator in that it will provide near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying energy stored in batteries or a flywheel. The on-battery runtime of most uninterruptible power sources is relatively short (only a few minutes) but sufficient to start a standby power source or properly shut down the protected equipment. A UPS is typically used to protect hardware such as computers, data centers, telecommunication equipment or other electrical equipment where an unexpected power disruption could cause injuries, fatalities, serious business disruption or data loss. UPS units range in size from units designed to protect a single computer without a video monitor (around 200 VA rating) to large units powering entire data centers or buildings. The world's largest UPS, the 46-megawatt, Battery Electric Storage System (BESS), in Fairbanks, AK, powers the entire city and nearby rural communities during outages.
UPS TYPES:
A variety of design approaches are used to implement UPS systems, each with distinct performance characteristics. The most common design approaches are as follows: Standby Line Interactive Standby on-line hybrid Standby-Ferro Double Conversion On-Line Delta Conversion On-Line
OFF LINE/ STANDBY:
LINE INTERACTIVE:
STANDBY-FERRO DOUBLE CONVERSION ON-LINE
STANDBY ON-LINE HYBRID
DOUBLE CONVERSION ON-LINE
DELTA CONVERSION ON-LINE
APPLICATIONS:
Data Centers IT Financial Emergency Services Healthcare Leisure and Sport Government Broadcasting and Communications Power/Oil/Gas Defence Retail Education Transportation Industrial & Manufacturing
You might also like
- Uninterruptible Power SuppliesDocument21 pagesUninterruptible Power SuppliesVer BautistaNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) : Mr. Fotsing Kamgang Installation and Maintenance of Hardware and SoftwareDocument17 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) : Mr. Fotsing Kamgang Installation and Maintenance of Hardware and SoftwareAlexandre CabrelNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Standby Power Systems For BuildingsDocument153 pagesEmergency and Standby Power Systems For BuildingsMAKENGO ELIASNo ratings yet
- UPSDocument54 pagesUPSy m dNo ratings yet
- Types of UPS 2Document3 pagesTypes of UPS 2Pedro MauricioNo ratings yet
- UpsDocument27 pagesUpsmatthew02012010No ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply - WikipediaDocument82 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply - WikipediaKalimbwe TutaNo ratings yet
- Uniterruptible Power Supply SystemDocument8 pagesUniterruptible Power Supply SystemSk The AlternatorNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply and InvertersDocument10 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply and InvertersnicenezaNo ratings yet
- Uninterrupted Power Supply ArticleDocument14 pagesUninterrupted Power Supply ArticlechukwunemeNo ratings yet
- Design Construction of One Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)Document25 pagesDesign Construction of One Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)Suva nilNo ratings yet
- Mains Power Emergency Power System Standby GeneratorDocument1 pageMains Power Emergency Power System Standby GeneratorSatyender Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- Information SheetDocument2 pagesInformation SheetacademicNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1Document4 pagesInformation Sheet 1academicNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument2 pagesUninterruptible Power SupplyRanier Atienza MagcawasNo ratings yet
- Source, UPS or Battery/flywheel Backup, Is An Electrical ApparatusDocument1 pageSource, UPS or Battery/flywheel Backup, Is An Electrical ApparatusVenkatNo ratings yet
- Aisya Nadya Damarcha: Pengantar Ilmu Komputer Cs IupDocument4 pagesAisya Nadya Damarcha: Pengantar Ilmu Komputer Cs IupAisya Nadya DamarchaNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 5: Aim: TheoryDocument2 pagesExperiment: 5: Aim: TheorypiyushdalsaniaNo ratings yet
- Iot Based Ups Monitoring and Faulty Battery Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIot Based Ups Monitoring and Faulty Battery Detection SystemMAHESH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (Ups)Document7 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply (Ups)elx321 electronics system designNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument18 pagesUninterruptible Power SupplyLuz ArriagaNo ratings yet
- How Does An Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument2 pagesHow Does An Uninterruptible Power SupplyKumarappan MrmNo ratings yet
- Power ProtectionDocument17 pagesPower ProtectionParis JosephNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Draft 1Document17 pagesComputer Science Draft 1Paris JosephNo ratings yet
- Ecopowersupplies: Avoid Loss of Data and Fatalities With Uninterrupted Power Supplies.Document1 pageEcopowersupplies: Avoid Loss of Data and Fatalities With Uninterrupted Power Supplies.Tim ParkerNo ratings yet
- Practical 6: AIM: Study The Operation and Maintenance of Ups. UPSDocument2 pagesPractical 6: AIM: Study The Operation and Maintenance of Ups. UPSVasundharaNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument34 pagesWelcomeDev KumarNo ratings yet
- Solar Based Uninterrupted Power SupplyDocument8 pagesSolar Based Uninterrupted Power SupplyShubhda ChandaneNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Power Concern FactsDocument2 pages2.2.5 Power Concern FactsLisha De LeonNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Papers For IEEE T M (Revised May 2015) : Ransactions ON AgneticsDocument5 pagesPreparation of Papers For IEEE T M (Revised May 2015) : Ransactions ON Agneticshkparmar003No ratings yet
- Back-UPS: Models 250, 400, 450, 600, 900 & 1250Document40 pagesBack-UPS: Models 250, 400, 450, 600, 900 & 1250Sid RcNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)Document13 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)ThasithaNo ratings yet
- Sample - The Impact of Gadgets in Learning AmongDocument2 pagesSample - The Impact of Gadgets in Learning AmongCasinillo KahivhenNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument12 pagesUninterruptible Power SupplyJameer AsifNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet # 11: Your Reliable Guide For Power SolutionsDocument2 pagesInformation Sheet # 11: Your Reliable Guide For Power Solutionskhaledmahmoud2483No ratings yet
- COPS (Critical Operational Power Supply)Document4 pagesCOPS (Critical Operational Power Supply)wog jimNo ratings yet
- COPS (Critical Operational Power Supply)Document4 pagesCOPS (Critical Operational Power Supply)wog jimNo ratings yet
- UPS Basics: Executive SummaryDocument14 pagesUPS Basics: Executive SummarysolomonNo ratings yet
- Eaton WhitePaper Distributed Vs Centralized BypassDocument9 pagesEaton WhitePaper Distributed Vs Centralized BypassParveshi PusunNo ratings yet
- Powerware 5110 UPS Uninterruptible Power System: FeaturesDocument4 pagesPowerware 5110 UPS Uninterruptible Power System: FeaturesjulioNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply: UPS in The Data CenterDocument6 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply: UPS in The Data CenterMahMoud IBNo ratings yet
- Ups Utilization Tech PaperDocument6 pagesUps Utilization Tech PaperMonirul IslamNo ratings yet
- UPSEnterprisePlus Data SheetDocument4 pagesUPSEnterprisePlus Data SheetCarlos CelisNo ratings yet
- Surge Protector Vs UPS Vs Power StripDocument4 pagesSurge Protector Vs UPS Vs Power StripTransformerOptimusNo ratings yet
- What Is A Ups System?: Uninterruptible Power SupplyDocument1 pageWhat Is A Ups System?: Uninterruptible Power SupplyGerardo AlpizarNo ratings yet
- Building A Data CenterDocument3 pagesBuilding A Data CenterGuillermo Lopez-FloresNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 4Document3 pagesInformation Sheet 4academicNo ratings yet
- UPS Power Systems With Generator Sets: Your Reliable Guide For Power SolutionsDocument2 pagesUPS Power Systems With Generator Sets: Your Reliable Guide For Power SolutionssolomonNo ratings yet
- Jumpers in EngineeringDocument4 pagesJumpers in EngineeringprabuNo ratings yet
- UP-E - Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems: Price: $139.94Document10 pagesUP-E - Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems: Price: $139.94Saber AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Therson-Cofie Therson-Cofie ReportDocument16 pagesTherson-Cofie Therson-Cofie ReportMichael McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power Supply: A Guide To Equipment Eligible For Enhanced Capital AllowancesDocument12 pagesUninterruptible Power Supply: A Guide To Equipment Eligible For Enhanced Capital AllowancesLatha HemanthNo ratings yet
- Css 10 Lesson 2 4th QTRDocument19 pagesCss 10 Lesson 2 4th QTRMarcusNo ratings yet
- What Your IT Equipment Needs From A UPSDocument4 pagesWhat Your IT Equipment Needs From A UPSrajuanthatiNo ratings yet
- Uninterruptible Power SuppliesDocument3 pagesUninterruptible Power SuppliesJames BautistaNo ratings yet
- Guide Protection GroundDocument36 pagesGuide Protection GroundcalecaleNo ratings yet
- D S E U P S S P C: Esign of A Mart Mbedded Ninterrupted Ower Upply Ystem For Ersonal OmputersDocument20 pagesD S E U P S S P C: Esign of A Mart Mbedded Ninterrupted Ower Upply Ystem For Ersonal OmputersAli KhaniNo ratings yet
- Lizwe Engineers - UPSDocument103 pagesLizwe Engineers - UPSBenjamin MqenebeNo ratings yet