Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microorganisms Sample
Uploaded by
AizilIbrahimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microorganisms Sample
Uploaded by
AizilIbrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
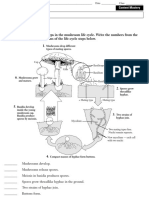
slow down bacterial growth
kill bacteria into organic fertilisers
produce antibiotics Yeast
Very tiny living things
b
bacteria and fungi break down plants / animals remains
Medicine manufacture Fertilisers manufacture
In form of plants and animals
shapes
1
sizes
2 3
colours
air
1 2
water soil
3 4
1 2 3
Not seen by naked eye
3 2
singular = bacterium
Different
Habitat
other organisms
+ dough
bread / buns
Food manufacture
5 4
USES
UNSEEN LIVING THINGS
4 5
seen through microscopes breathe
a
c
plural = viruses Tiniest microorganism
Bacteria
+ tapioca / glutinous rice
tapai
b
Yeast
Undergo life processes
b c
move grow
b c
Seen through electron microscope
bacteria
+ soya bean + wheat + water
tempe
3 2 1
Virus
A
1
d
Infect other organisms
1 2 3 4 6 5
fungi protazoa plants animals humans
+ soya bean + salt + water soya sauce vinegar + juices alcoholic drinks
Bacteria
4 3 2
cheese
D
TYPES
soy sauce
yogurt
YEAR 5 UNIT 1
B
bread rice
fully grown
white patch black patch
mouldy orange
2
MICROORGANISMS (1/2)
Protozoa
e
Euglena
3 2
3
a
singular = fungus
oranges
rotten food
papaya 1
rotten fruits
mouldy bread seen as white or black patches Food turns bad warm moist
2 1
Examples
c
2 1
C
Examples
1
Fungi
a
singular = protozoan
Habitat
2 3
trees
On food
b a
G r ow
human skin
c
largest microorganisms Examples
forest floors
Conditions
CHARACTERISTICS
2
Paramecium Ameoba Lives by
2 1 1
Habitat
5 4 3 2 1
moulds
mushrooms ponds yeast
Move
c
By
2 balloon inflated by carbon dioxide
eating other microorganisms
making own food
human body
swamps rivers lakes
hair like /whip-like structure
changing body shape
away from enemies
Yeast / ballon experiment
d c
Breathe
a b
Yeast flour water yeast Dough = mixture of
yeast cells Eating a bacteria
towards food sources and water
sugar solution + yeast
dough rises
before
after
gives out carbon dioxide and fill in spaces in dough
takes in oxygen
direct contact microscopic mi te fever sore throat sneezing muscle pain cough runny nose headache
skin rash itchy rash
Spread by
b a
Symptoms
c
Caused by
eye pain swollen eye red eye Symptoms eye itch sticky eye discharge c b a
Scabies
Conjuctivitis
Spread by Caused by
direct contact neck swelling headache fever appetite loss ai r virus itchy rashes fever cough headache appetite loss air direct contact virus rashes fever
Symptoms Spread by Flu Caused by
3 4
virus Symptoms c
conjunctivitis
to prevent chicken pox contact with mumps microorganism
towel toothbrush comb b
To isolate people with disease for certain time period
For contageous disease
a
b c
to prevent direct contact with other people
Examples
a
sore throat runny nose cough muscle pain fever rashes rash itch direct contact virus
direct contact air virus
Mumps
a
Spread by Caused by
6 c
Symptoms
c
Symptoms Spread by
Do not share personal items to prevent flies bring in microorganisms
Qurantine patients
Spread by Caused by
b a
Measles
Disease Types and Characteristics
8 1
Chicken pox
a
Caused by Rubella
a c b
Cover foods
stomach pain nausea/vomiting
Symptoms Spread by
virus
9
to prevent infection Cover wounds
10
direct
Symptoms
c
diarrhoea contact bacteria
8 7
YEAR 5 UNIT 1
Spread by Caused by
b a
Stomach upset
air
Caused by
AIDS
c a b
virus
Symptoms Spread by
bacteria virus fungus infections by fever, sweating weight loss direct contact of blood to virus
to prevent micoorganism entering air
Cover mouth/ nose when sneezing
PREVENTION OF DISEASES
5
MICROORGANISMS (2/2)
E
HARMFUL EFFECTS
I llness / Disease
Caused by
virus
from body fluid containing virus
a
a b food drink air
Cook raw food before eating to kill germs
Bacteria / virus enters body
4
through
d di re ct c o nt a c t with
sick person p er s o na l ite ms
Boil water before drinking to kill germs
c
Prevent tooth decay Wash hands Store food in freezer
a c
a b
avoid sugary food brush teeth after meals
contageous if spread easily
produce toxins that cause illness
grow / reproduce inside body
floss teeth after meals Prevent microorganisms growing
cavity
use soap
After using toilet
Before handling food
Tooth decay
Food poisoning
Food Spoilage
a b
Forms cavity in teeth
c b a
Food turns bad
2 smelly 1 rotten
c b
a
Bacteria / fungi enters food Symptoms
4 3 1 2
food Bacteria ai r drink contaminated / virus enters 1 2 3 ha nd s body d through 5 4 contaminated u t e ns i l s
Acid produced dissolves teeth's surface
Bacteria in mouth react with sugar
grow / repoduce in food
houseflies /coackroaches stomach upset
diarrhoea vomitting
nausea
You might also like
- Knowledge and Attitude On Antibiotic Use Among Residents of Banawa (Responses)Document2 pagesKnowledge and Attitude On Antibiotic Use Among Residents of Banawa (Responses)rexvillavelezNo ratings yet
- Bio Fertilizer Udyami - Org.inDocument16 pagesBio Fertilizer Udyami - Org.inAndreea DeeaNo ratings yet
- Our Environment - Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesOur Environment - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- How To Make A Good Quality Compost (Naturland)Document1 pageHow To Make A Good Quality Compost (Naturland)Quynh H NguyenNo ratings yet
- Case Studies-Bt Brinjal BT CottonDocument3 pagesCase Studies-Bt Brinjal BT Cottonarpit_nNo ratings yet
- Biopolymers From Crop Plants: R 2019 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument10 pagesBiopolymers From Crop Plants: R 2019 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedM HNo ratings yet
- Penggunaan Bacillus Thuringiensis Sebagai Bio-Insektisida: January 2002Document9 pagesPenggunaan Bacillus Thuringiensis Sebagai Bio-Insektisida: January 2002Firyaliza AlyaNo ratings yet
- Bio FertilizerDocument15 pagesBio FertilizerAamir SajjadNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument14 pagesProjectSomashekar LNo ratings yet
- Plant - Microbe Interactions (Eng) 2020Document11 pagesPlant - Microbe Interactions (Eng) 2020Dans DansNo ratings yet
- 2021 Issue 3 IPPTA Article 01Document3 pages2021 Issue 3 IPPTA Article 01jasvinder kumarNo ratings yet
- Biopestcides: Types and Applications: IJAPBC - Vol. 1 (4), Oct-Dec, 2012Document8 pagesBiopestcides: Types and Applications: IJAPBC - Vol. 1 (4), Oct-Dec, 2012Balaji RajendranNo ratings yet
- Bio-Fertilizers: Profile No.: 06 NIC Code: 24129Document14 pagesBio-Fertilizers: Profile No.: 06 NIC Code: 24129arpit85No ratings yet
- Biopesticides InfographicDocument1 pageBiopesticides InfographicBernadette L. CashNo ratings yet
- Presspb2023d4 enDocument4 pagesPresspb2023d4 eneyob yohannesNo ratings yet
- Bio-Inks For 3D Bioprinting Recent Advances and BiopirntDocument21 pagesBio-Inks For 3D Bioprinting Recent Advances and BiopirntRafael Franco GontijoNo ratings yet
- ch23 3Document1 pagech23 3quimicosorioNo ratings yet
- 2020-R-Farcas-Macroalgae - A Sustainable Source of Chemical Compounds With Biological ActivitiesDocument23 pages2020-R-Farcas-Macroalgae - A Sustainable Source of Chemical Compounds With Biological ActivitiesOscar Cabrera HerraizNo ratings yet
- Industrial Production of Bacillus Thuringiensis Based Bioinsecticide Whichway Forward 2155 6202 1000e126Document1 pageIndustrial Production of Bacillus Thuringiensis Based Bioinsecticide Whichway Forward 2155 6202 1000e126BioinformaticsNo ratings yet
- Bio FertilizerDocument11 pagesBio FertilizerHoney krishnaNo ratings yet
- BT CottonDocument8 pagesBT Cottoniqra buttNo ratings yet
- Quality Control in Business AreasDocument13 pagesQuality Control in Business Areaschukwu solomonNo ratings yet
- What Is BT Cotton?Document3 pagesWhat Is BT Cotton?sunnyminusNo ratings yet
- Spray Programme For Tomatoes and Peppers: Control 70DF Before Sowing HelpsDocument3 pagesSpray Programme For Tomatoes and Peppers: Control 70DF Before Sowing HelpsKennedy NgoseyweNo ratings yet
- gramPosOrganisms PDFDocument1 pagegramPosOrganisms PDFPurple basket100% (1)
- ScienceDocument16 pagesSciencebrabbit927No ratings yet
- Dirty Dozen 2022 Final PDFDocument1 pageDirty Dozen 2022 Final PDFMaxim Hornby StudentNo ratings yet
- BiofertilizersAnoveltoolforagriculture1 2 6 IJMRDocument10 pagesBiofertilizersAnoveltoolforagriculture1 2 6 IJMRSantosh SongalNo ratings yet
- Flyer MycormaxDocument2 pagesFlyer MycormaxŞtefan PruteanuNo ratings yet
- 300 Sample-ChapterDocument12 pages300 Sample-Chapterrajiv pathakNo ratings yet
- Hemp Herbicide Poster PDFDocument1 pageHemp Herbicide Poster PDFPintrijel LaurNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 WK6Document3 pagesScience7 Q2 WK6hannahsofiapreyesNo ratings yet
- 2022 06 15 Haccp Plan Milling ExtDocument23 pages2022 06 15 Haccp Plan Milling ExtcomfortNo ratings yet
- Chapter01 LectureDocument8 pagesChapter01 LectureTrần LinhNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Assessment of Azotobacter Rhizobium and Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria With Potential Biofertilizer ProductionDocument6 pagesEvaluation and Assessment of Azotobacter Rhizobium and Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria With Potential Biofertilizer ProductionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ecosystems PDFDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Ecosystems PDFCyndi SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Annex IDocument2 pagesAnnex Ibabji dudekulaNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter IV - Module 6 Week 6: Department of EducationDocument15 pagesScience Quarter IV - Module 6 Week 6: Department of EducationMycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Biopesticide Market Now and Where It Is Going PDFDocument4 pagesAn Analysis of The Biopesticide Market Now and Where It Is Going PDFRobertoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 03 PDFsalman672003No ratings yet
- SuperGroW Bokashi FertilizerDocument20 pagesSuperGroW Bokashi FertilizerEM® Nature FarmingNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Name: Year/ Section: Date: Score: Science 8Document9 pagesDepartment of Education: Name: Year/ Section: Date: Score: Science 8Mycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- Productionof BiopesticidesDocument9 pagesProductionof BiopesticidesPalak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 NCERT Science Book MICROORGANISMS ICROORGANISMS FRIEND RIEND AND AND FOE Chapter 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCBSE Class 8 NCERT Science Book MICROORGANISMS ICROORGANISMS FRIEND RIEND AND AND FOE Chapter 2 PDFAll Type GurujiNo ratings yet
- WA0011. CombinedDocument24 pagesWA0011. CombinedDivyanshu tripathiNo ratings yet
- Useful MicroorganismsDocument1 pageUseful MicroorganismsNeet 720No ratings yet
- Search For Most Outstanding Gulayan Sa Paaralan CoordinatorDocument6 pagesSearch For Most Outstanding Gulayan Sa Paaralan CoordinatorREYMART ROYANDOYANNo ratings yet
- Pesticide Registration Manual - Chapter 3 - BiopesticideDocument11 pagesPesticide Registration Manual - Chapter 3 - BiopesticideSudhir ReddyNo ratings yet
- Biopesticides: An Ecofriendly Approach For Pest Control: © Jbiopest. 125Document3 pagesBiopesticides: An Ecofriendly Approach For Pest Control: © Jbiopest. 125Noor afzaNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter IV - Module 6 Week 6: Department of EducationDocument14 pagesScience Quarter IV - Module 6 Week 6: Department of EducationMycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- 4.-Kenneth JhonsonDocument17 pages4.-Kenneth JhonsonRomualdo Martinez LopezNo ratings yet
- RSC - Li/chem-Soc-Rev: As Featured inDocument54 pagesRSC - Li/chem-Soc-Rev: As Featured inOtieres Cirino De CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- BLR 2020 29161 ZMNDocument7 pagesBLR 2020 29161 ZMNThe rockNo ratings yet
- Scientia Horticulturae: Patrick Du JardinDocument12 pagesScientia Horticulturae: Patrick Du JardinHector Chavez TeuberNo ratings yet
- Sura 2019 PosterDocument1 pageSura 2019 PosterSurendraraj AlagarsamyNo ratings yet
- CANNABISDocument2 pagesCANNABISVinicius S. SuraciNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument19 pagesProject ReportAkshor SonuNo ratings yet
- 14 Bacterial InoculantDocument8 pages14 Bacterial InoculantRAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Spurious BT Cottonseeds Is It The Right WayDocument3 pagesSpurious BT Cottonseeds Is It The Right WayPrasanth TalakantiNo ratings yet
- The 10 Personality DisordersDocument6 pagesThe 10 Personality DisordersCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- List of 600 Personality TraitsDocument8 pagesList of 600 Personality TraitsCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Trait Theory: Allport's 4,000 TraitsDocument3 pagesTrait Theory: Allport's 4,000 TraitsOevide SeinNo ratings yet
- Positive TraitsDocument15 pagesPositive TraitsCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Character and Personality TraitsDocument14 pagesPositive and Negative Character and Personality TraitsCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders: Causes/syc-20354463Document5 pagesPersonality Disorders: Causes/syc-20354463Ctmanis Nyer100% (1)
- Psychodynamic Perspectives On PersonalityDocument8 pagesPsychodynamic Perspectives On PersonalityCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- What Is The Trait Theory of PersonalityDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Trait Theory of PersonalityCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- The Big Five Personality TheoryDocument20 pagesThe Big Five Personality TheoryCtmanis Nyer100% (1)
- Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument4 pagesPsychoanalytic TheoryCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Trait Perspectives On PersonalityDocument10 pagesTrait Perspectives On PersonalityCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Earth Moon Sun SampleDocument2 pagesEarth Moon Sun SampleCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- PsychoanalysisDocument10 pagesPsychoanalysisCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- PsychoanalysisDocument20 pagesPsychoanalysisanon_374008477No ratings yet
- School Couns Cover LetterDocument1 pageSchool Couns Cover LetterCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioural TherapyDocument8 pagesCognitive Behavioural TherapyCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Internship Resume SampleDocument3 pagesInternship Resume SampleCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 31 Personality&Its TheoriesDocument17 pagesLesson 31 Personality&Its TheoriesHassan SalalNo ratings yet
- All Possible Symptoms of AnxietyDocument18 pagesAll Possible Symptoms of AnxietyCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 31 Personality&Its TheoriesDocument17 pagesLesson 31 Personality&Its TheoriesHassan SalalNo ratings yet
- Six Factors Necessary For Growth in Rogerian TheoryDocument1 pageSix Factors Necessary For Growth in Rogerian TheoryCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet
- Pekeliling NKRADocument43 pagesPekeliling NKRAYuliamin SahirursahNo ratings yet
- Guidance Counselor ResumeDocument2 pagesGuidance Counselor ResumeCtmanis NyerNo ratings yet