Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Doesan Optical Encoder Work?: Structure of An Absolute Encoder
How Doesan Optical Encoder Work?: Structure of An Absolute Encoder
Uploaded by
Bassy KaserOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Doesan Optical Encoder Work?: Structure of An Absolute Encoder
How Doesan Optical Encoder Work?: Structure of An Absolute Encoder
Uploaded by
Bassy KaserCopyright:
Available Formats
H OW D OES AN OPT IC AL EN C OD ER W OR K ?
Structure of an Absolute Encoder
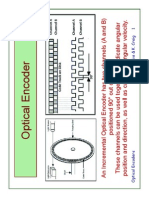
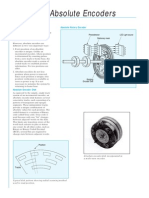
The Optical Encoders typically consist of a rotating and a stationary member. The rotor is usually a metal, glass, or a plastic disc mounted on the encoder shaft. The disc has some kind of optical pattern, which is electronically decoded to generate position information. The rotor disc in absolute optical encoder uses opaque and transparent segments arranged in a gray-code pattern. The stator has corresponding pairs of LEDs and phototransistors arranged so that the LED light shines through the transparent sections of the rotor disc and received by phototransistors on the other side. After the electronic signals are amplified and converted, they are then available for the evaluation of the position.
Opto-Array
Reticle IR-LED
Shaft
Ball bearing
Code disk
Image 1: Construction Absolute Encoder
www.posital.com
FRABA Inc. 116 Nassau Drive, Lawrenceville, NJ 08648 Phone (609) 896-1188, Fax (609) 896-1183 www.posital.com, info@posital.com
H OW D OES AN OPT IC AL EN C OD ER W OR K ?
Single-Turn In some applications the encoder shaft makes one revolution for one complete cycle of machine operation (angular rotation of a crankshaft in a punch press or rotary indexing table). Absolute single-turn encoders can provide absolute position values over a 360 range. After one turn the measuring range is completed and it starts over again. The resolution (number of position values over the 360 range) can be as high as 16 bits (216 = 65536). Multi-Turn In multi-turn applications the encoder shaft makes more than one revolutions to complete one machine cycle (e.g. most linear positioning, where the encoder shaft makes several turns to complete total travel). For these applications a multi-turn encoder will be required.
The principle of the multi-turn encoder is relatively simple: Several single turn encoders are connected using a reduction gear (see Image 2). The first stage supplies the resolution per turn; the stages behind supply the number of turns. The available number of turns is usually 12 bits (212 = 4096).
Code Discs
16 1
16 1
16 1
Image 2: Principle of the Multi-Turn
www.posital.com
FRABA Inc. 116 Nassau Drive, Lawrenceville, NJ 08648 Phone (609) 896-1188, Fax (609) 896-1183 www.posital.com, info@posital.com
You might also like
- Encoders and Resolvers PDFDocument5 pagesEncoders and Resolvers PDFMURTHY RAJNo ratings yet
- Encorder SCM70Document20 pagesEncorder SCM70MakNo ratings yet
- EncoderDocument5 pagesEncoderAndari Dian AriestianiNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoder PDFDocument8 pagesRotary Encoder PDFKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Safari - Feb 4, 2024 at 11:38 PMDocument1 pageSafari - Feb 4, 2024 at 11:38 PMsyansyncNo ratings yet
- Encoder SDocument8 pagesEncoder SpanchalabNo ratings yet
- Encoder White PaperDocument9 pagesEncoder White Papersaneie99No ratings yet
- EE17401-Measurements and Instrumentation Unit - V: Optical Encoder Type Digital TransducerDocument18 pagesEE17401-Measurements and Instrumentation Unit - V: Optical Encoder Type Digital TransduceravsNo ratings yet
- Absolute Rotary EncoderDocument7 pagesAbsolute Rotary EncoderNanda DeepaNo ratings yet
- Single-Turn Encoders Vs Multi-Turn Encoders - DynaparDocument4 pagesSingle-Turn Encoders Vs Multi-Turn Encoders - DynaparMozhdeh HeydariNo ratings yet
- Servo Encoder LabDocument8 pagesServo Encoder LabGoran MiljkovicNo ratings yet
- Solarbotics Wheel Watcher Encoder ManualDocument10 pagesSolarbotics Wheel Watcher Encoder ManualYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic EncodersDocument5 pagesMagnetic EncodersGarcia F. Marcio100% (1)
- Motion Control Feedback DeviceDocument20 pagesMotion Control Feedback DeviceZyzerull SaadNo ratings yet
- Optical Encoder and The Arduino 2012Document35 pagesOptical Encoder and The Arduino 2012Fredy Gustavo Cujia Bolaño100% (1)
- SynopsisDocument12 pagesSynopsisGopal AggarwalNo ratings yet
- What Are Rotary Encoders Used ForDocument11 pagesWhat Are Rotary Encoders Used ForjackNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: AEDT-9140 SeriesDocument9 pagesData Sheet: AEDT-9140 SeriesehuamanibNo ratings yet
- Hm8350 Mouse CiDocument3 pagesHm8350 Mouse CiSilvioNo ratings yet
- Digital Encoders: Absolute EncoderDocument5 pagesDigital Encoders: Absolute EncoderAnshu Kumar BhartiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document8 pagesWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoder Training MaterialDocument30 pagesRotary Encoder Training MaterialLuckyboybk FCNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument8 pagesCollectionvsrikala68100% (1)
- 01 EncoderDocument4 pages01 EncoderAngel ChicchonNo ratings yet
- How To Build An Omni Wheels RobotDocument10 pagesHow To Build An Omni Wheels RobotJonty ChanduNo ratings yet
- Encoder 2Document5 pagesEncoder 2mohamedsamimorsiNo ratings yet
- Digital Encoders 1.2Document6 pagesDigital Encoders 1.2controlorNo ratings yet
- Compass Repeater PDFDocument62 pagesCompass Repeater PDFBf Ipanema83% (6)
- Encoders & Resolvers:: How To Choose The Right Feedback OptionDocument5 pagesEncoders & Resolvers:: How To Choose The Right Feedback OptionAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoder - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesRotary Encoder - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSigid AriewibowoNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis CNC Plotter From DC Motors and Optical EncoDocument41 pages3 Axis CNC Plotter From DC Motors and Optical Encoryan.jane171287No ratings yet
- Whitepaper EncodersDocument4 pagesWhitepaper EncodersalexNo ratings yet
- Encoder CatalogDocument24 pagesEncoder CatalogCao Minh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Angulation Theory PDFDocument10 pagesAngulation Theory PDFAndreyNo ratings yet
- Encoder Measurements: How-To Guide: 1. Encoder and Applications OverviewDocument4 pagesEncoder Measurements: How-To Guide: 1. Encoder and Applications Overviewj.emmett.dwyer1033No ratings yet
- Optical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoDocument4 pagesOptical Encoder For Motion Control Through ArduinoMary LongNo ratings yet
- QuadDocument55 pagesQuadVgokulGokulNo ratings yet
- POV Display Project Without MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesPOV Display Project Without MicrocontrollerZia AzamNo ratings yet
- From Mech: Jump ToDocument16 pagesFrom Mech: Jump ToMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Datasheet AEAT-6600Document11 pagesDatasheet AEAT-6600ArminNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Balancing Robot)Document10 pagesCase Study (Balancing Robot)Homer Jay ManabatNo ratings yet
- EncoderDocument6 pagesEncoderHue BachNo ratings yet
- Build An LED Propeller ClockDocument4 pagesBuild An LED Propeller ClockImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 10 Wheel Encoders-1Document5 pagesLab Assignment 10 Wheel Encoders-1api-519059218No ratings yet
- Block Diagram: Body of RobotDocument11 pagesBlock Diagram: Body of RobotAbraham Rohith RoyNo ratings yet
- ME 462 - Lab 5 - Stepper Motor Light TrackerDocument2 pagesME 462 - Lab 5 - Stepper Motor Light TrackerKhabir IslamNo ratings yet
- Rotary Encoder PDFDocument12 pagesRotary Encoder PDFRahul Soren100% (1)
- Encoders For Brushless Motor Commutation HEIDENHAINDocument3 pagesEncoders For Brushless Motor Commutation HEIDENHAINCristopher EntenaNo ratings yet
- Encoder H9720Document10 pagesEncoder H9720Marco Antonio Henriquez100% (1)
- Optical EncoderDocument35 pagesOptical Encoderimmery18No ratings yet
- The Rotational Speed of The Drive Motor Control With Arduino UNO and CardDocument5 pagesThe Rotational Speed of The Drive Motor Control With Arduino UNO and CardoubahaNo ratings yet
- 1) Give Classification of Positioning Feedback Device. Explain (I) Linear Transducers (Ii) Rotary EncodersDocument5 pages1) Give Classification of Positioning Feedback Device. Explain (I) Linear Transducers (Ii) Rotary EncodersJonty PatelNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 Digital and Intelligent Sensors: Position EncodersDocument23 pagesModule - 4 Digital and Intelligent Sensors: Position EncodersJnanavi B ANo ratings yet
- Absolute Encoders Principle of OperationDocument2 pagesAbsolute Encoders Principle of OperationSakhawat Hossain RonyNo ratings yet
- Sanyo Camara Circuitos Vpc-Az1 - sm5310328Document52 pagesSanyo Camara Circuitos Vpc-Az1 - sm5310328jorge_chaparro_1No ratings yet
- FTF Aut f0234Document38 pagesFTF Aut f0234vishiwizardNo ratings yet
- Repeater Compass System With Serial Interface RS 422: Operator, Technical and Service ManualDocument62 pagesRepeater Compass System With Serial Interface RS 422: Operator, Technical and Service ManualDimon SergeevichNo ratings yet
- TachometerDocument51 pagesTachometerKiran SugandhiNo ratings yet