Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 3
Uploaded by
delhiprashantOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 3
Uploaded by
delhiprashantCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY 5346
HW Set 1 Solutions – Kimel
2
1.3 In general we take the charge density to be of the form ρ = fr⃗δ, where fr⃗ is determined by
physical constraints, such as ∫ ρd 3 x = Q.
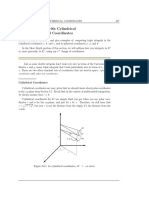
a) variables: r, θ, φ. d 3 x = dφd cos θr 2 dr
ρ = fr⃗δr − R = frδr − R = fRδr − R
∫ ρd 3 x = fR ∫ r 2 drdΩdr − R = 4πfRR 2 = Q → fR = Q
4πR 2
Q
ρr⃗ = δr − R
4πR 2
b) variables: r, φ, z. d 3 x = dφdzrdr
ρr⃗ = fr⃗δr − b = fbδr − b
∫ ρd 3 x = fb ∫ dzdφrdrδr − b = 2πfbbL = λL → fb = λ
2πb
ρr⃗ = λ δr − b
2πb
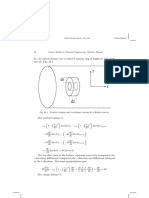
c) variables: r, φ, z. d 3 x = dφdzrdr Choose the center of the disk at the origin, and the z-axis
perpendicular to the plane of the disk
ρr⃗ = fr⃗δzθR − r = fδzθR − r
where θR − r is a step function.
∫ ρd 3 x = f ∫ δzθR − rdφdzrdr = 2π R2 f = Q → f = πRQ 2
2
Q
ρr⃗ = δzθR − r
πR 2
d) variables: r, θ, φ. d 3 x = dφd cos θr 2 dr
ρr⃗ = fr⃗δcos θθR − r = frδcos θθR − r
∫ ρd 3 x = ∫ frδcos θθR − rdφd cos θr 2 dr = ∫ 0 frrrdrdφ = 2πN ∫ 0 rdr = πR 2 N = Q
R R
where I’ve used the fact that rdrdφ is an element of area and that the charge density is uniformly
distributed over area.
Q
ρr⃗ = δcos θθR − r
πR 2 r
You might also like
- BSLTPCh2p2B9 Fluid Mech Low Density PhenomenaDocument6 pagesBSLTPCh2p2B9 Fluid Mech Low Density PhenomenaAdam LyleNo ratings yet
- Flow of A Film On The Outside of A Circular TubeDocument6 pagesFlow of A Film On The Outside of A Circular TubeShubh100% (6)
- Phys 132 - Homework 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesPhys 132 - Homework 1 SolutionsHenry JurneyNo ratings yet
- Respuesta Del Problema 8.Document5 pagesRespuesta Del Problema 8.CAMILA ARIASNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus - MTH 243, Sections 1 & 3Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus - MTH 243, Sections 1 & 3Camilo TorresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Astrophysics Tutorial 2: Polytropic Models: 1 Summary of The Equations of Stellar StructureDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Astrophysics Tutorial 2: Polytropic Models: 1 Summary of The Equations of Stellar Structureعمر الفاروق عبيديةNo ratings yet
- Problem 2C.4Document9 pagesProblem 2C.4NajwaAinayaZawaidNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Final EMTDocument33 pagesChapter3 Final EMTJohn wickNo ratings yet
- Math032 11 19 151Document6 pagesMath032 11 19 151we_spidus_2006No ratings yet
- HomwworkDocument12 pagesHomwworkESTUDIANTE JOSE DAVID MARTINEZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Static Magnetic FieldsDocument28 pagesStatic Magnetic Fieldsআল আবদুল্লাহ্ হাসানNo ratings yet
- PQ 10Document1 pagePQ 10224883061No ratings yet
- Math 23 Lecture 3.3 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates PDFDocument24 pagesMath 23 Lecture 3.3 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates PDFyeahNo ratings yet
- ME/CHE/BME 6782 Cellular Engineering: Notes For 11/2 LectureDocument20 pagesME/CHE/BME 6782 Cellular Engineering: Notes For 11/2 LecturepriyaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Cone Clutch: AdvantagesDocument6 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Cone Clutch: AdvantagesamolNo ratings yet
- Physics 416G: Solutions For Problem Set 6: Due: October 9, 2015Document4 pagesPhysics 416G: Solutions For Problem Set 6: Due: October 9, 2015DavidSuarezNo ratings yet
- Concentrated Load On A Wedge PDocument27 pagesConcentrated Load On A Wedge PNaga Manikanta TatikondaNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Integration With Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates: BasicsDocument8 pages3.6 Integration With Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates: BasicsAbdullah AltwirqiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 5Document10 pagesProblem Set No. 5Carl Malone TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Gravity and Cosmology (Lecture 3 Onwards) : 7 December 2021Document8 pagesGravity and Cosmology (Lecture 3 Onwards) : 7 December 2021Husain Mustansir ManasawalaNo ratings yet
- HW1 Phys3041Document3 pagesHW1 Phys3041Sam TseNo ratings yet
- PHD Lecture11 12Document10 pagesPHD Lecture11 12Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Examples For Green's Theorem, Cylindrical Coordinates, and Spherical CoordinatesDocument2 pagesExamples For Green's Theorem, Cylindrical Coordinates, and Spherical CoordinatesMohd ZubiNo ratings yet
- COORDENADASDocument15 pagesCOORDENADASDaiana AguirreNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 SoluttionDocument9 pagesSheet 3 SoluttionShima ElsofyNo ratings yet
- Integration in Polar CoordinatesDocument5 pagesIntegration in Polar CoordinatestressNo ratings yet
- Integration in Polar CoordinatesDocument5 pagesIntegration in Polar CoordinatestressNo ratings yet
- BSLTPCH 2 P 2 B7Document7 pagesBSLTPCH 2 P 2 B7AnjaliNo ratings yet
- River Shangu MathDocument3 pagesRiver Shangu MathMd Abid Afridi0% (1)
- Assignment 14: Green's /stoke's /gauss's TheoremsDocument4 pagesAssignment 14: Green's /stoke's /gauss's Theoremsritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Derivation of Added Mass Around A Sphere: 2.016 HydrodynamicsDocument2 pages0.1 Derivation of Added Mass Around A Sphere: 2.016 HydrodynamicsIhab OmarNo ratings yet
- Area of A Circle by Integration: R 2 R R R 0 2Document2 pagesArea of A Circle by Integration: R 2 R R R 0 2Ahmed SudanNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Ibthisham PART 2Document9 pagesCh07 Ibthisham PART 2Saqi1234No ratings yet
- Solutions To Laplace's Equation in Polar and Spherical CoordinatesDocument9 pagesSolutions To Laplace's Equation in Polar and Spherical Coordinatesatul206No ratings yet
- Math24 SolDocument2 pagesMath24 SolSharif M Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Optimising Sustainable PracticesDocument16 pagesOptimising Sustainable PracticesHasan QatatoNo ratings yet
- Formation of Bubbles-2019Document68 pagesFormation of Bubbles-201902indexchosenNo ratings yet
- Ex 7Document5 pagesEx 7Jean AraúzNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates - SolutionsDocument9 pagesDouble Integrals in Polar Coordinates - SolutionsCarolyn Cadogan100% (1)
- Ia Dyn Chapter8Document11 pagesIa Dyn Chapter8ram kumarNo ratings yet
- AY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics P01 Basic Concepts ExamplesDocument15 pagesAY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics P01 Basic Concepts ExamplesEmily ShumNo ratings yet
- Equations of Stellar Structure - 7Document7 pagesEquations of Stellar Structure - 7John BirdNo ratings yet
- Lec Week11Document5 pagesLec Week11KRITANTNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsTanisha GangradeNo ratings yet
- Kružne Ploče Opterećene Na Savijanje-Rotacina SimetrijaDocument5 pagesKružne Ploče Opterećene Na Savijanje-Rotacina SimetrijaLazić MilošNo ratings yet
- A320 Orbits 1Document23 pagesA320 Orbits 1garfacio30No ratings yet
- Sup 14 - 4Document12 pagesSup 14 - 4Ziad JreijNo ratings yet
- 12.3 Double Integrals in Polar CoordinatesDocument6 pages12.3 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinatesيا ابا صالح المهديNo ratings yet
- Soluciones A Problemas de Mecaninca CuanticaDocument7 pagesSoluciones A Problemas de Mecaninca CuanticaIván GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5: University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 126 Leclair Fall 2011Document11 pagesProblem Set 5: University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 126 Leclair Fall 2011AngelicaDominguezNo ratings yet
- Sol 5Document2 pagesSol 5Gag PafNo ratings yet
- Problem41 36Document1 pageProblem41 36IENCSNo ratings yet
- SphereDocument2 pagesSphererootkit5678No ratings yet
- SLP Presentation 1Document12 pagesSLP Presentation 1Jone jackNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 3 SuppDocument3 pagesUnit - 2 3 SuppPowell HinkNo ratings yet
- Biot Savart Laplace LawDocument12 pagesBiot Savart Laplace LawGu HonghaoNo ratings yet