Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular Impairment
Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular Impairment
Uploaded by
Yaj Oliveros PanganOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular Impairment
Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular Impairment
Uploaded by
Yaj Oliveros PanganCopyright:
Available Formats
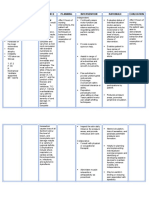
Nursing Care Plan ASSESSMENT Subjective: Hindi ko maigalaw ang aking kaliwang kamay at medyo hindi ko rin maigalaw
ang kaliwa kong paa. Objective: Left hemi paralysis Limited range of motion !O"# $unctional level: level %&re'uires help SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION (mpaired physical mobility related to neuromuscular impairment INFERENCE )euromuscular disorders affect the nerves that control the voluntary muscles. *oluntary muscles are the ones that can be controlled+ like in the arms and legs. ,he nerve cells+ also called neurons+ send the messages that control these muscles. -hen the neurons become unhealthy or die+ communication Long term .fter / months of continuous +effective and collaborative nursing interventions+ .fter / hours+ the patient verbali0e understanding situation or risk factors and individual treatment regimen and safety measures 3ncourage and facilitate early ambulation and other .2Ls when possible. .ssist with each initial change: dangling+ sitting in chair+ ambulation ,he longer the patient remains immobile the .fter / months of continuous +effective 2etermine the diagnosis that contributes to immobility ,o be informed about the PLANNING Short term INTERVENTION "onitor *1S RATIONALE ,o note changes and for baseline comparison. EVALUATION .fter / hours of nursing intervention the patient was able to verbali0e understanding situation or risk
situations that may factors and individual treatment restrict movements regimen and safety measures
greater the level of and collaborative nursing debilitation that will occur interventions+ patient was able to maintain position and function
between the nervous patient will
from another person.
system and muscles breaks down. .s a result+ the muscles weaken and waste away. ,he weakness can lead to twitching+ cramps+ aches and pains+ and joint and movement problems. Sometimes it also affects heart function and ability to breathe. "any neuromuscular diseases are genetic+ which means they run in families or there is a mutation in your
maintain position+ function and skin integrity 4erform passive or active !O" e5ercises to all e5tremities increased venous return+ prevents stiffness+ and maintains muscle strength and endurance ,urn and position every % hours or as needed. ,his optimi0es circulation to all tissues and relieves pressure. 4rovide safety measures side rails+ using pillow to support body part# ,o provide safety and reduce the risk of pressure ulcers
and skin integrity as 35ercise promotes evidenced by the absence of contractures+ footdrop+ decubitus and so forth
genes. Sometimes+ an immune system disorder can cause them. "ost of them have no cure. ,he goal of treatment is to improve symptoms+ increase mobility and lengthen life.
"assage back and bony prominences
(t provides comfort to the patient and promotes good circulation
6onsult with physical or occupational therapist as indicated
,o develop individual e5ercise therapy or program
!eference: http:11www7.us.elsevierhealth.com1"3!L()18ulanick16onstructor1inde5.cfm9plan:;<
ASSESSMENT
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
INFERENCE
PLANNING
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
Subjective: =Hindi ako mapadumi. Objective: .bdominal pain+ urgency .ltered bowel sounds Left Hemi paralysis Limited !O" 6onstipated for five days
6onstipation related to insufficient physical activity
. decrease in a person>s normal fre'uency of defecation+ accompanied by difficult or incomplete passage of stool and1or passage of e5cessively hard+ dry stool. . lack of physical activity can lead to constipation. $or e5ample+ constipation often occurs after an accident or during an illness when one must stay in bed and cannot e5ercise. Lack of
.fter ? hours+ the patient will establish or return to normal patterns of bowel functioning
2etermine stool color+ consistency+ fre'uency and amount
.ssist in identifying causative and contributing factors and appropriate interventions
.fter ? hours+ the patient was able to establish or return to normal patterns of bowel functioning as evidenced by easy passage of long+ round+ and smooth brown& shaded stool with a te5ture similar to creamy peanut butter
.uscultate bowel sounds
Aowel sounds are generally decreased in constipation
3ncourage increased fluid intake+ %<@@&;@@@ ml1day within cardiac tolerance
.ssists in improving stool consistency
3ncourage to eat high&fiber rich
,o enhance easy defecation
physical activity is thought to be one of the reasons constipation is more common in older people. "oreover+ increased physical activity is more likely to stimulate bowel motility and improve the symptoms of constipation.
foods 2ecrease gastric !ecommend avoiding gas& forming foods distress and abdominal distention 4revents skin .ssist in perianal skin condition fre'uently+ noting changes or beginning breakdown $acilitates 2iscuss use of stool softeners+ mild stimulants+ bulk& forming la5atives+ or enemas as indicated. "onitor defecation when constipation is present e5coriation and breakdown
effectiveness 6onstipation is a (dentify factors e.g.+ medications+ bed rest+ diet# that may cause or contribute to constipation. 3valuate medication profile for gastrointestinal side effects. $iber absorbs water+ which adds 6onsult dietitian to provide well& balanced diet high in fiber and bulk bulk and softness to the stool and speeds up passage through the intestines common side effect of many drugs including narcotics and antacids.
!eference: http:11www.med.umich.edu17libr1aha1umconstipation.htm
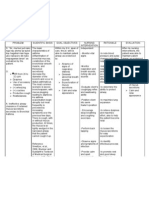
ASSESSMENT SBAC36,(*3: =ayoko kumain ng walang lasa OAC36,(*3: Dpale to pinkish conjunctiva and lips Dweak looking Dfair appetite+ selective with food
DIAGNOSIS (mpaired adjustment related to health status re'uiring change in lifestyle
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION (nability to modify lifestyle in a manner consistent with a change in status. ,he objective of nursing care for focuses on lowering and controlling the blood pressure without adverse effects and without
PLANNING Short ,erm 8oal .fter / days of nursing intervention+ there will be an increase interest and participation on the
INTERVENTION (ndependent *ital signs monitored and recorded. A4 monitored regularly .ssist the patient in identifying modifiable risk factors like diet high in sodium+ saturated fats and
RATIONALE
EVALUATION .fter / days of
$or baseline comparison
nursing interventions the goal is met through participation and demonstration of lifestyle changes
hypertensive patients demonstration of self care and will initiate lifestyle changes that will permit adaptation to present medical situation
,hese risk factors have been shown to contribute to hypertension
preferences A4&7;@1E@ mmHg
undue cost. ,o achieve these goals+ the nurse must support and teach the patient to adhere to the treatment regimen by implementing necessary lifestyle changes like avoidance of foods high in sodium and fats and taking medications as prescribed.
cholesterol (nstruct and emphasi0e necessary care and lifestyle changes that will enhance her recovery. ,his will promote trust and will on the patient to adhere to such activities that will enhance fast recover 4lan necessary care and assistance in .2Ls with the relative 3mphasi0e the importance of ade'uate rest 3mphasi0e the Hypertension 4lanning with the relative will add more cooperation of the patient ,his will lower the patientFs A4
importance of adherence to medications 4rovide an open environment encouraging communication
needs medications to maintain the A4 in its normal range 35pression of feelings concerning impaired function is dealt with realistically
!eference: http:11www.medicinenet.com1highGbloodGpressure1article.htm
DRUG STUDY
Nursing Name o Drug 8eneric )ame: "annitol Arand )ame: Classi i!a"ion "iscellaneous $luids or 2iuretics A!"ion &increase osmotic pressure of !oute and $re'uency: (* '/ 2ose: glomerular filtrate which inhibits tubular re&absorption of water and electrolytes and increases urinary output In#i!a"ions !eduction of increased intracranial pressure associated with cerebral edema !eduction of increased ocular pressure 4romotion of diuresis in the prevention and1or treatment for oliguria or anuria due to acute renal failure Si#e E e!"s 2i00iness Headache 6onvulsions Alurred vision 2iuresis 2ry mouth Loss of hearing Con"rain#i!a"ions Hypersensitivity Severe renal disease Severe dehydration 4ulmonary congestion Res$onsi%ili"ies .ssess patientFs condition before therapy and regularly thereafter to monitor drug effectiveness .ssess for possible drug induced adverse reactions. .ssess patient for possible drug induced adverse reactions. ,each patient to recogni0e and immediately report adverse
Moni"oring Parame"ers "onitor vital signs+ 6*4+ and urine specific gravity "onitor manifestations of electrolyte imbalance .ssess A4 before and during the therapy with patient lying+ standing and sitting+ orthostatic hypotension can occur rapidly.
Osmofudin %@H
7@@ cc
reactions .sses patientFs and familyFs knowledge of drug therapy
Nursing Name o Drug 8eneric )ame: 6iticholine Arand )ame: Classi i!a"ion 6)S stimulants or )eurotonics A!"ion In#i!a"ions 6*. in acute and recovery phase. Signs and symptoms of cerebral insufficiency. !ecent cranial trauma 4arkinsonFs disease 6ytidine 2iphosphate &. derivative of choline and cytidine 6holine involved in the !oute and $re'uency: (* '7% 2ose: biosynthesis of lecithin. (t is claimed to increased blood flow and o5ygen consumption. Si#e E e!"s Shock Hypersensitivity Hypotension (nsomnia Stimulates parasympathetic action and fleeting and discreet hypotension effect Con"rain#i!a"ions Hypertonia of the parasympathetic nervous system 4regnancy and lactation Res$onsi%ili"ies 3valuate patient medical history .ssess patient condition Should not be administered to patient with hypertonia of the parasympathetic nervous system 6aution that large doses could
Moni"oring Parame"ers "onitor vital signs .ssess allergic reaction like 8( disturbances
7 gm
aggravate increase in cerebral blood flow in episodes of persistent intracranial hemorrhage. ,each patient to gain benefits and not to miss any dose
Nursing Name o Drug Classi i!a"ion In#i!a"ions Si#e E e!"s Con"rain#i!a"ions Res$onsi%ili"ies
Moni"oring Parame"ers
8eneric )ame:
6ardiovascular Statins A!"ion &(nhibits H"8&6O. reductase en0yme+
,o reduce L2L cholesterol+ apolipoprotein beta and triglycerides
.bdominal pain 6onstipation $latulence (nsomnia Headache !ashes 2i00iness "uscle cramps
Hypersensitivity to any component of the preparations
.ssess nutrition: fat + protein+ carbohydratesI nutritional analysis should be completed by dietitian before treatment is initiated
"onitor creatinine phophokinase levels due to possibility of myopathyI serum cholesterol
Simvastatin Arand )ame:
.ltovast !oute and $re'uency: Oral Od 2ose:
6hildren and lactation .ctive liver disease Bne5plained persistent elevations of serum transaminases
,o increase H2L cholesterol in the treatment of hyperlipidaemias
which reduces cholesterol production
"onitor triglycerides+ cholesterol baseline and throughout treatment
6oronary heart disease
.ssess liver function tests prior to therapy and periodically thereafter 3valuate therapeutic response and adverse reactions on a regular basis
/@ mg
.ssess
knowledge or teach patient proper use
Nursing Name o Drug 8eneric )ame: (midapril Arand )ame: Classi i!a"ion In#i!a"ions 6ardiovascular drugs ,reatment of =antihypertensive A!"ion &inhibits angiotensin converting en0ymeI !oute and $re'uency: Oral O2 2ose: reduction of angiotensin (( resulting in dilation of peripheral vessels and reduction of vascular resistance hypertension Si#e E e!"s 2ry cough Headache !ash 4alpitation $atigue 2iscomfort in the throat Con"rain#i!a"ions 4atients with known hypersensitivity to angiotensin converting en0yme inhibitors or with history of angioneorotic edema 4regnancy and lactation Res$onsi%ili"ies 3stablish baselines in renal+ liver function tests before therapy 6heck for edema .sses for patient allergic reactions .dvise patient to avoid potassium+ salt substitutes ,each patient how to take Ap
Moni"oring Parame"ers "onitor blood studies "onitor bp+ orthostatic hypotension "onitor electrolytes during the firs % weeks of therapy "onitor renal studies and symptoms
*ascor
<@ mg
and normal readings for age group
Nursing Name o Drug 8eneric )ame: 6lonidine Arand )ame: A!"ion &stimulates central& !oute and $re'uency: Oral O2 2ose: alpha adrenergic receptors to inhibit sympathetic cardioaccelareators and vasoconstrictor centers Classi i!a"ion 6ardiovascular drugs =6entrally&acting drugs In#i!a"ions "anagement of all grades of hypertension with the e5ception of H4) due to phaeochromooyto ma 4rophylactic treatment of migraine or recurrent vascular treatment of Si#e E e!"s Local skin irritation 2rowsiness 2ry mouth Headache $atigue .nore5ia .n5iety Con"rain#i!a"ions Res$onsi%ili"ies Hypersensitivity to .ssess pain+ clonidine Sick sinus syndrome location+ intensity+ character+ alleviating+ aggravation factors+ baseline and fre'uency 4erform blood studies+ neorophils+ decreased platelets 4erform renal
Moni"oring Parame"ers "onitor baselines for renal+ liver function test before therapy begins "onitor A4+ standing+ sitting+ supine+ mental status+ and heart rate.
6atapres
J< mcg
migraine $or relief of cancer pain
studies .ssess Ap and apical pulse before initial dose )ote allergic reactions
NAME OF DRUG 8eneric )ame: !anitidine Arand )ame: Kantac
CLASSIFICATION 8astrointestinal 1 hepatobiliray 2rugs H% !eceptor .ntagonists
INDICATIONS Bsed in management of gastrointestinal 8(# disorders. 4rophyla5is of 8( hemorrhage from stress ulceration and in patients at risk of developing acid aspiration during general
SIDE EFFECTS Aradycardia Headache $atigue 2epression
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity History of acute porphyria Long&term therapy
NURSING RESPONSI&ILITIES Bse caution in presence of renal or hepatic impairment. .ssess for potential for interactions with other pharmacological agents patient may be taking. 3valuate results of
MONITORING PARAMETERS "onitor .S,+ .L,+ Serum creatinine+ signs and symptoms of peptic ulcer disease+ occult blood with 8( bleeding. "onitor renal function to correct dos.
Me!'anism o !oute: (.* $re'uency: ' 7% A!"ion: (nhibits histamine at H% receptor site in the gastric parietal cells+ which inhibits gastric acid
!ashes 6onstipation
2ose: <@ mg
secretion.
anesthesia.
laboratory tests+ therapeutic effectiveness.
You might also like
- Impaired Physical Mobility NCPDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility NCPMick De Leon67% (3)
- End - Life of Care PPT 1 MainDocument48 pagesEnd - Life of Care PPT 1 MainNancy Singh63% (16)
- Exp 4 chm556Document7 pagesExp 4 chm556Azli AzmanNo ratings yet
- Magarpatta City: Case StudyDocument5 pagesMagarpatta City: Case StudyKhemrajNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - NumbnessDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - NumbnessJasmin Jacob100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocument1 pageActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord Injury NCPEmmanuelRodriguez100% (1)
- History of Prostitution in India 11111Document2 pagesHistory of Prostitution in India 11111Ankit AnandNo ratings yet
- Race, Ethnicity, and Health A Public Health Reader - (Introduction The Ethnic Demographic Transition)Document10 pagesRace, Ethnicity, and Health A Public Health Reader - (Introduction The Ethnic Demographic Transition)Anonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Baby Kids KnittingDocument30 pagesBaby Kids KnittingGarath ランカスター0% (4)
- NCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)Document2 pagesNCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)yanny0350% (2)
- NCP-Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP-Impaired Physical MobilityradarsoulNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Burns - Airway Clearance, Risk For IneffectiveDocument2 pagesBurns - Airway Clearance, Risk For Ineffectivemakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Nanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Document3 pagesNanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Besael Baccol0% (1)
- Acute Pain NCPDocument6 pagesAcute Pain NCPPesky Pescante-MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Exudates in The Alveoli TBMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CVADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan CVAessevyNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- HyperkalemiaDocument5 pagesHyperkalemiaNolan Cabral50% (2)
- Acute Pain NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearancejomerdalonaNo ratings yet
- Flank Pain, Anxiety...Document7 pagesFlank Pain, Anxiety...reneighdNo ratings yet
- Objectiv ES Rationa LE: Evaluatio NDocument3 pagesObjectiv ES Rationa LE: Evaluatio NAnonymous FgT04krgym100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- NCP CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesNCP Cholelithiasiskmpg11100% (2)
- Glaucoma NCPDocument4 pagesGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMichelleNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocument3 pagesNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyKyle Stephen TancioNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (2)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- DM NCPDocument8 pagesDM NCPCaress Mae Gubaton CabudoyNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Document3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- NP Motor Vehiculr AccidentDocument16 pagesNP Motor Vehiculr AccidentAngelie Joy100% (1)
- Ncp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONDocument4 pagesNcp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONHania Polangi100% (1)
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP Painsitz04No ratings yet
- NCP For HeadacheDocument1 pageNCP For HeadacheJohn MajanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityLilet Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Skin Integritysinister17No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument23 pagesNursing Care PlanLorielle HernandezNo ratings yet
- Defient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPDocument6 pagesDefient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPjordan aguilarNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesActivity IntolerancemizzybaylonNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstraction MajDocument44 pagesIntestinal Obstraction MajHamss AhmedNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocument77 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- Actual Nursing Care Plan GT DisorderDocument3 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan GT DisordermandzkievonnieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlansMargaret SibugNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism NCP DrugstudyDocument6 pagesHyperthyroidism NCP DrugstudyTrisha Joyce MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Improving Nutritional and Fluid Volume StatusDocument4 pagesImproving Nutritional and Fluid Volume StatusEllmaaanNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- ConstipationDocument12 pagesConstipationfrechel kimNo ratings yet
- Stephanie Leone ResumeDocument1 pageStephanie Leone ResumeStephanie LeoneNo ratings yet
- ANJ - Texty Na ČítanieDocument2 pagesANJ - Texty Na ČítanieIvana ZimovaNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence and AcaDocument10 pagesEmotional Intelligence and AcaSassy BlaireNo ratings yet
- Mouth CareDocument11 pagesMouth CareKedamObulesu Kedam50% (2)
- Information Technology Employee Code of EthicsDocument2 pagesInformation Technology Employee Code of EthicsAlvy LumbaNo ratings yet
- SL01 397Document2 pagesSL01 397thiseus25No ratings yet
- Familiarization With Rational RoseDocument12 pagesFamiliarization With Rational RoseKota Venkata Jagadeesh100% (1)
- Evaluation of Recycling Reuse of Building Materials From DemolitionsDocument44 pagesEvaluation of Recycling Reuse of Building Materials From DemolitionsMynadeem RahmounNo ratings yet
- Pure Competition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument31 pagesPure Competition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinLeticia AvelynNo ratings yet
- Oregon 600 Series Settings v4 July 2015Document3 pagesOregon 600 Series Settings v4 July 2015Faisal AzizyNo ratings yet
- Alaa Elghazaly CVDocument3 pagesAlaa Elghazaly CVAlaa ElghazalyNo ratings yet
- Secondary Music 8 q2 Week1Document10 pagesSecondary Music 8 q2 Week1Nelson Jeff Jr. MagpaliNo ratings yet
- SCDT0315 PDFDocument80 pagesSCDT0315 PDFGCMediaNo ratings yet
- Health10 Q1 M2 Healthcare Providers and Fraudelent ServicesDocument23 pagesHealth10 Q1 M2 Healthcare Providers and Fraudelent Serviceswincy CubioNo ratings yet
- SBTA1502Document119 pagesSBTA1502Vishnupriya MuruganNo ratings yet
- Memorandum ReadingDocument10 pagesMemorandum ReadingJeric MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning The FingernailsDocument12 pagesCleaning The FingernailsKaren MartoniaNo ratings yet
- Channel Partner Short DataDocument30 pagesChannel Partner Short DatamanishaNo ratings yet
- Flours and Flour MixturesDocument55 pagesFlours and Flour MixturesMaydell Alberto DanacNo ratings yet
- Midterm-2017 Fuel CellsDocument2 pagesMidterm-2017 Fuel CellsAlex MarkNo ratings yet
- Strand Century Lighting 3342 6-Inch Fresnelite Spotlight Spec Sheet 6-77Document2 pagesStrand Century Lighting 3342 6-Inch Fresnelite Spotlight Spec Sheet 6-77Alan Masters100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering: A Level/IB Requirements by College For 2021 EntryDocument9 pagesChemical Engineering: A Level/IB Requirements by College For 2021 EntryJames BondNo ratings yet
- Direct Torque Control of BLDC MotorDocument10 pagesDirect Torque Control of BLDC MotorNirmal MahesNo ratings yet
- A318 Airbus: ATA 24 Electrical PowerDocument27 pagesA318 Airbus: ATA 24 Electrical PowerGiáo ViênNo ratings yet
- Dublin Bus and Bus Eireann ReviewDocument119 pagesDublin Bus and Bus Eireann ReviewJohn SirautNo ratings yet