Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indications: Drug Study Kalium Durule
Uploaded by
melissagabrielOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indications: Drug Study Kalium Durule
Uploaded by
melissagabrielCopyright:
Available Formats
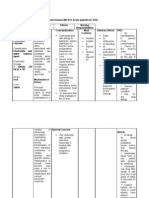
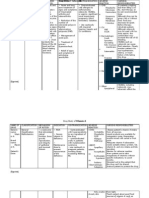
DRUG STUDY Kalium durule
Indications
Prevention and correction of potassium deficiency; when associated with alkalosis, use potassium chloride; when associated with acidosis, use potassium acetate, bicarbonate, citrate, or gluconate
Adverse effects
Dermatologic: Rash GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, GI obstruction, GI bleeding, GI ulceration or perforation Hematologic: Hyperkalemiaincreased serum K+, ECG changes (peaking of T waves, loss of P waves, depression of ST segment, prolongation of QTc interval) Local: Tissue sloughing, local necrosis, local phlebitis, and venospasm with injection
Nursing considerations Arrange for serial serum potassium levels before and during therapy.
Administer liquid form to any patient with delayed GI emptying. Administer oral drug after meals or with food and a full glass of water to decrease GI upset. Caution patient not to chew or crush tablets; have patient swallow tablet whole. Mix or dissolve oral liquids, soluble powders, and effervescent tablets completely in 38 oz of cold water, juice, or other suitable beverage, and have patient drink it slowly. Arrange for further dilution or dose reduction if GI effects are severe. Agitate prepared IV solution to prevent layering of potassium; do not add potassium to an IV bottle in the hanging position. Monitor IV injection sites regularly for necrosis, tissue sloughing, phlebitis. Monitor cardiac rhythm carefully during IV administration. Caution patient that expended wax matrix capsules will be found in the stool. Caution patient not to use salt substitutes.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- ATI Med Surg TipsDocument17 pagesATI Med Surg Tipsmike Gee100% (5)
- Drug Study - Potassium ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Potassium ChlorideBalloonsRus PHNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument31 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesiamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesDocument64 pagesStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehydration SaltDocument3 pagesOral Rehydration SaltVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Revised Drug IndexDocument76 pagesRevised Drug IndexMinette SantosNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Kalium Durule Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKalium Durule Drug StudyJustine Garcia100% (1)
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Classification Action Adverse Effect Indication Contraindicat Ion Nursing InterventionDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Classification Action Adverse Effect Indication Contraindicat Ion Nursing InterventionJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- ORS Mechanism of Action and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesORS Mechanism of Action and Nursing ConsiderationsCyric Jyn Fadul Full100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CaptoprilDocument2 pagesDrug Study - CaptoprilGlenda GalanganNo ratings yet
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionFrom EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNo ratings yet
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Kalium DuruleDocument3 pagesKalium DurulenebuchadnezzarkingheNo ratings yet
- ancog-KALIUM DURULEDocument3 pagesancog-KALIUM DURULEtpmellizaNo ratings yet
- Osmotic LaxativesDocument2 pagesOsmotic LaxativesACanNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideDocument8 pagesPotassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideJoy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lactulose Drug Mechanism, Indications, and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesLactulose Drug Mechanism, Indications, and Nursing ConsiderationsKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Oral & IV electrolyte solutions for water, electrolyte & acid-base imbalancesDocument10 pagesOral & IV electrolyte solutions for water, electrolyte & acid-base imbalancesArie Yanti YahyaNo ratings yet
- Drugs OphthaDocument3 pagesDrugs OphthaJha NhinNo ratings yet
- Slow KDocument1 pageSlow KDevon TossellNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideBorlong100% (1)
- Antipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsDocument6 pagesAntipyretics, Nonopioid AnalgesicsLeevi Paul LaviñaNo ratings yet
- Drug laxative reduces ammonia lactuloseDocument6 pagesDrug laxative reduces ammonia lactuloseRj MagalingNo ratings yet
- MetoprololDocument5 pagesMetoprololMaricon AlbercaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoNo ratings yet
- Benazepril Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesBenazepril Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDocument1 pageDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNo ratings yet
- Backup NclexDocument61 pagesBackup NclexSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib drug guideDocument10 pagesCelecoxib drug guidejessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- LP Di HDDocument7 pagesLP Di HDSyarif HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Brand Names: Generic NameDocument3 pagesBrand Names: Generic NameEzraManzanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Document7 pagesHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraNo ratings yet
- GI Osmotic Agents: Uses, Examples, DosingDocument4 pagesGI Osmotic Agents: Uses, Examples, DosingsyerlyNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocument5 pagesAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- RENAL DIALYSIS - Nutrition, Imbalanced, Less Than Body RequirementsDocument3 pagesRENAL DIALYSIS - Nutrition, Imbalanced, Less Than Body Requirementsmakyofrancis20No ratings yet
- Drug Study - CholangioDocument10 pagesDrug Study - CholangioClaireMutiaNo ratings yet