Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Protein
Properties of Protein
Uploaded by
drng48Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Protein
Properties of Protein
Uploaded by
drng48Copyright:
Available Formats
This PH which is specific to every protein is called iso-electric point .
At this PH : - the protein will not move in an electric field { i.e does not have the property of electrophoresis }. - The solubility of protein is at minimum & will be precipitated . 5. Solubility of proteins : - Every ptrotein has a specific solubility at a certain PH & certain concentration of salt . - At the isoelectric point , the solubility of protein is minimum & is easily precipitated . - High concentration of neutral salts causes precipitation of proteins .This is called salting out phenomenon . Example of salting out is the precipitation of globulin by 1/2 saturation of ammonium sulfate . - Small concentration of neutral salts help the solubility of protein . This is called salting in phenomenon . Example of salting in is the solubility of globulin in water by the help of small concentration of sodium chloride . Methods of precipitation of protein : 1. At the iso-electric point . 2. By high concentration of neutral salts , e.g : sodium chloride , ammonium sulphate ,etc 3. By organic solvents which are miscible with water , e.g : ethyl alcohol , acetone , etc 4. By salts of heavy metals , e.g : silver nitrate , lead acetate , etc 5. By strongs and heavy acids , e.g : trichloracetic acid , tanic acid , etc
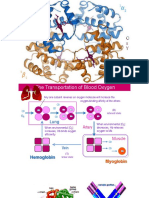
6. Buffering action of proteins : - A buffer solution is the solution which resists the change of its PH by the addition of acids or alkalies . - Proteins act as buffers because they contain many ionic groups . Some of these groups are negatively charged while the others are positively charged . Examples of the ionizable groups are the carboxyl group , amino group , thiol group of cysteine , imidazole group of histidine , etc. 7 . Electrophoresis : - It is the migration of proteins in an electric field at a certain PH . - Every protein migrates by a certain rate depending on the number of net electric charges carried by this protein at this PH . - In alkaline medium protein migrate to anode . In acid medium protein migrate to cathode . At the isoelectric point the protein is electrically stable & there is no movement at all .
You might also like
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 pagesPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal Paindrng48100% (1)
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 pagesMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (9)
- PDF PDFDocument9 pagesPDF PDFCindy Nona100% (2)
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3Document1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3drng480% (1)
- Properties of ProteinsDocument2 pagesProperties of ProteinsDrbee10No ratings yet
- Chemguide Notes For Application of ChemistryDocument48 pagesChemguide Notes For Application of ChemistryKevin Martin100% (1)
- Protein Chemistry 1Document67 pagesProtein Chemistry 1ShadowStormNo ratings yet
- Basics Biochemistry 1-Practice 3Document23 pagesBasics Biochemistry 1-Practice 3emir krlpNo ratings yet
- Acid CatalysisDocument16 pagesAcid CatalysisTayyaba SadaqNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 PostDocument9 pagesExperiment No 1 PostShaina TabjanNo ratings yet
- Hofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsDocument11 pagesHofmeister Series: Ions Franz Hofmeister ProteinsRajeshwari SridharanNo ratings yet
- ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesElectrophoresisRura DangaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of ProteinsDocument10 pagesPhysical Properties of Proteinsaditi_joshee419No ratings yet
- Bich411 Enzyme Catalysis PDFDocument7 pagesBich411 Enzyme Catalysis PDFAn TranNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument1 pageSolutionsChristin Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Share Lecture 2 - Acids, Bases, PH, BuffersDocument42 pagesShare Lecture 2 - Acids, Bases, PH, BuffersNoel ManyiseNo ratings yet
- 1.bioenergeticsDocument38 pages1.bioenergeticsberreozbayraktarNo ratings yet
- Purification of ProteinsDocument28 pagesPurification of ProteinsaasthaNo ratings yet
- Definition List Chemistry IB HLDocument3 pagesDefinition List Chemistry IB HLMichelle TingNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry of ProteinsDocument26 pagesPhysical Chemistry of ProteinsEvernim OmpacanNo ratings yet
- Study of ElectrophoresisDocument26 pagesStudy of ElectrophoresisAayushman YadavNo ratings yet
- Serum Protein ElectrophoresisDocument59 pagesSerum Protein ElectrophoresisLeo NoquilNo ratings yet
- Classification and Reactions of ProtiensDocument23 pagesClassification and Reactions of ProtiensShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Aa, Protein, Peptide, EnzymeDocument149 pagesAa, Protein, Peptide, EnzymeoparesxNo ratings yet
- METABOLISM Unit 1Document12 pagesMETABOLISM Unit 1Siddhant MazumderNo ratings yet
- Chem Note 4Document5 pagesChem Note 4Gee BandongNo ratings yet
- Proteins Properties. Types of ProteinsDocument60 pagesProteins Properties. Types of ProteinsanaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell PhysiologyDocument39 pagesBacterial Cell PhysiologyMohammad MambuayNo ratings yet
- CH 490 Exam 1 NotesDocument60 pagesCH 490 Exam 1 Notescr4zyvi3tNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument24 pagesProteins and Amino Acidsqwerty masterNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Energy and ChemistryDocument41 pagesModule 2 - Energy and ChemistryCamille F. ManlapigNo ratings yet
- ElectroDocument10 pagesElectroAbel BateriNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument85 pagesPost Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsELAINE MARIEJOY MANGAOILNo ratings yet
- Optically Inactive: 1 PointDocument16 pagesOptically Inactive: 1 PointSimon Abcede100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2Jaisy PatelNo ratings yet
- Bio-Inorganic ChemistryDocument66 pagesBio-Inorganic ChemistryPhalynxNo ratings yet
- Salting Out: 1. Last Updated Save As PDF Share Share Share Tweet Share Page IDDocument8 pagesSalting Out: 1. Last Updated Save As PDF Share Share Share Tweet Share Page IDveronicaNo ratings yet
- Salting Out: 1. Last Updated Save As PDF Share Share Share Tweet Share Page IDDocument8 pagesSalting Out: 1. Last Updated Save As PDF Share Share Share Tweet Share Page IDveronicaNo ratings yet
- Group II TBM Class: ProteinDocument53 pagesGroup II TBM Class: ProteinAziz RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- Biochem 01Document6 pagesBiochem 01hamza jassarNo ratings yet
- Heat Coagulation TestDocument8 pagesHeat Coagulation TestRawan MaherNo ratings yet
- Leg Um inDocument2 pagesLeg Um inJet Tan Eng KiatNo ratings yet
- Lab2 Precipitation of Casein at Isoelectric PointDocument29 pagesLab2 Precipitation of Casein at Isoelectric PointMeiday0% (1)
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base BalanceDocument42 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base BalanceMiss Vina100% (1)
- Unit 3 and Unit 4 EnzymologyDocument126 pagesUnit 3 and Unit 4 Enzymologysanthosh nNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes: George A. HarwellDocument29 pagesElectrolytes: George A. HarwellWho Knows100% (1)
- Electrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceDocument4 pagesElectrolyte: 1 Physiological ImportanceZiedTriki100% (1)
- Which Amino Acids Are Considered As Acidic Amino Acids and Why?Document4 pagesWhich Amino Acids Are Considered As Acidic Amino Acids and Why?Rojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- BTN-345 L2 ProteinsDocument54 pagesBTN-345 L2 ProteinsAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument76 pagesAmino AcidsContact AmsibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 - ElectrolytesDocument10 pagesLesson 14 - ElectrolytesLUZVIMINDA GORDONo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument454 pagesUntitledMegan Grace EbreoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hadi Kuncoro, S.Farm., Apt., M.Farm - Elektrolit, Non Elektrolit Dan Zwitter IonDocument16 pagesDr. Hadi Kuncoro, S.Farm., Apt., M.Farm - Elektrolit, Non Elektrolit Dan Zwitter IonCiNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation LabDocument2 pagesProtein Denaturation LabMickaela Olan0% (1)
- ProteinDocument5 pagesProteinMaria Virginia Orticio100% (1)
- CH 8 Enzyme Mech. and InhibitionDocument5 pagesCH 8 Enzyme Mech. and Inhibitioncococat015No ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument7 pagesBiochemistrymalaver528No ratings yet
- Denaturation of ProteinsDocument16 pagesDenaturation of ProteinsLineah Untalan100% (2)
- SL12102 Lecture 10 NotesDocument4 pagesSL12102 Lecture 10 NotesSafia ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument23 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsJethro LemosneroNo ratings yet
- Salt Induced Precipitation of ProteinsDocument2 pagesSalt Induced Precipitation of ProteinsMohini BajajNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Metabolism 2Document18 pagesOxidative Metabolism 2Frolian MichaelNo ratings yet
- توزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيDocument3 pagesتوزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيdrng48No ratings yet
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National PhyDocument1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phydrng48No ratings yet
- Neurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? AnswerDocument9 pagesNeurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? Answerdrng48No ratings yet
- Assessment of Development and GrowthDocument21 pagesAssessment of Development and Growthdrng48No ratings yet
- MCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural MechanismsDocument3 pagesMCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural Mechanismsdrng48No ratings yet
- Stomacolostomy 161108133919Document3 pagesStomacolostomy 161108133919drng48100% (1)
- Shenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXDocument281 pagesShenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXJeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy MCQDocument2 pagesCerebral Palsy MCQdrng4882% (11)
- Infections: (2013 - 2017)Document1 pageInfections: (2013 - 2017)drng48No ratings yet
- Table: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest PainDocument2 pagesTable: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest Paindrng48No ratings yet
- Burn RehabilitationDocument5 pagesBurn Rehabilitationdrng48No ratings yet
- 31 Da 7 CBB 2 eDocument2 pages31 Da 7 CBB 2 edrng48No ratings yet
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- Epidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1Document3 pagesEpidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1drng48No ratings yet
- Contraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania HospitalDocument20 pagesContraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospitaldrng48No ratings yet