Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Burn Rehabilitation
Uploaded by
drng48Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Burn Rehabilitation
Uploaded by
drng48Copyright:
Available Formats
Burn Rehabilitation
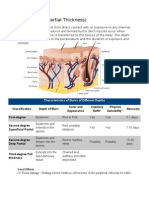
Dermis is the
highly vascularized layer or skin
epidermis is the
non-vascular layer of skin
burns are classified based on
1. causes
2. depth
3. extent or location
Four main causes (types) of burn
Thermal
Chemical
Electrical
Radiation
causes of burn: THERMAL
results from flame, steam, hot liquids or metals, extremes in temperatures
most common type of burn
causes of burn: ELECTRICAL
results from any type of voltage (pruning a tree, electrical plugs)
can cause renal failure, cardiac arrest, pulmonary arrest... depends on duration of
contact, voltage, and current
cause of burn: CHEMICAL
from cleaning agents, acids or from a combo of agents (tylex, fantastic)
chemical burns-->
- smaller as far as amount of skin that is covered
- most likely to cause full thickness burn which is the most severe
- inhalation --> burn
- it takes 24-72 hours for a chemical burn to fully develop
Cause of burn: radiation
nuclear exposure, chemotherapy can also cause a radiation burn
superficial burns
involve the upper layers of the epidermis (not vascularized layer that is about to shed)
- first degree burn
sunburn, hot fluids, minor flash injuries are considered
superficial burns
superficial burns also includes:
dry/bright red/ or pink skin that blanches under pressure
- generally do not cause edema
- no blisters are formed
- skin may exfoliate
- resolve spontaneously in 3-5 days without scarring
partial thickness burns
2nd degree burns- superficial partial thickness, deep partial thickness
superficial partial thickness burns are
-2nd degree burns
-involve the epidermis and papillary dermis
-moist, weepy, blistered skin
superficial partial thickness burns
-local erythema and edema
- blanch under pressure
-extremely painful
superficial part. thickness burns
-heal within 10-14 days with minimal to no scarring
-pigment changes are possible (hyperpigmented, freckles in that area)
- immediate capillary refill
superficial partial thickness burns can heal
without surgical intervention or hospitalization. to protect against infection, you want
to keep it dry
- deep 2nd degree
- involves the epidermis and dermis
- mottled areas of red and white eschar (dead tissue)
deep partial thickness burn
- may be painful
-capillary refill is sluggish
- prone to hypertrophic scarring (forms in knots) and contracture
deep partial thickness
deep partial thickness
may need some skin grafting
and boutonniere-dorsal fingers
full thickness burn
* third degree
- adipose tissue may be exposed
- initially may be red, quickly become mottled white, grey, or black, non blanching
full thickness burns
- appear dry, leathery
- no pain
-requires skin grafting and debridement of tissues
full thickness
- high risk for hypertrophic scarring
- more than three weeks to close
- destruction of dermis, epidermis, and subcutaneous tissues
subdermal burns
- fourth degree
- destruct fat, muscle, tendon, bone
- charred or mummified appearance
subdermal burns-
- skin is dry with minimal edema (No vascularization)
- extensive surgical intervention
subdermal burns -
amputation is often necessary
- paralysis is possible
5 functions of the skin
-protection
-conservation of fluids
-temperature regulation
-sensation
-identity
Superficial burn
Involves epidermis
Superficial partial-thickness burn
Involves epidermis, and papillary dermis
Deep partial-thickness burn
Complete destruction of epidermis and most of dermis
Full-thickness burn
Destruction of epidermis, dermis and partial damage of subcutaneous layer
Sub dermal burn
Complete destrcution of epidermis, dermis, subdermal tissue n may involve muscle
tissue, tendon or bone
A superficial burn involves what layer of skin
epidermis
What are the 2 s/s of superficial burns
-local pain
-erythema
Do superficial burns have blisters
no
Do superficial burns have scarring
no
How many days does a superficial burn normally take to heal
3-5 days
What layers of skin does a superficial partial thickness affect
-epidermis
-superficial layer of dermis
Superficial partial thickness.... color? blisters or no blisters? wet or dry?
-pink or red
-blisters
-pain
-wet
Is a persons sensation intact or absent with a superficial partial thickness burn
intact
Does a pt have hair with a superficial partial thickness burn
yes
How many days will a superficial partial thickness burn to heal
14-21
Will a superficial partial thickness burn scar
there is a possibility
What layers of skin are affected with a deep partial thickness burn
-epidermis
-most of the demris
3 s/s of deep partial thickness burn...color? skin condition? dry or wet?
-mottled
-cherry red or white
-dry
What is sensation like in a deep partial thickness burn
-can feel pressure but not pin prick because the pressure sensors are deeper so you
dont lose those
Will hair be present in a deep partial thickness burn
yes
How long will it take to heal a deep partial thickness burn
3-6 weeks
Will there be scarring in a deep partial thickness burn
yes
Layers of skin affected by a full thickness burn
-epidermis
-dermis
-subcutaneous
Full thickness burn
-What color? texture? sensation? is it dry or wet? hair or no hair? what happens
to the vessels? and what does it require
-red, black, or white
-leathery
-insensate
-dry
-no hair
-coagulated vessels because the blood is all dried up
-requires skin graft unless it is a small area
You might also like
- Brawny EdemaDocument3 pagesBrawny EdemaKris TejereroNo ratings yet
- Burn Workshop:: Splint and PositioningDocument31 pagesBurn Workshop:: Splint and Positioninganon_886804756No ratings yet
- KNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationDocument2 pagesKNGF Guideline: Cardiac RehabilitationsilkofosNo ratings yet
- Hand BurnsDocument17 pagesHand BurnsYEIMY CATHERINE BARBOSA QUIROGANo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Edema Management Techniques For Subacute Hand EdemaDocument14 pagesEffectiveness of Edema Management Techniques For Subacute Hand EdemaRiky SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Rehabilitation BMJ 2015Document8 pagesCardiac Rehabilitation BMJ 2015Sebastian ApeleoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument4 pagesCardiac RehabilitationBhaskar DhyaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument15 pagesCardiac RehabilitationammarmashalyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument2 pagesCardiac RehabilitationMarilou Sadsad VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabitationDocument4 pagesCardiac Rehabitationsundar_kumar0No ratings yet
- Preparation For Giving First AidDocument11 pagesPreparation For Giving First AidLarisa HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Fever: Supervision by DR - Nagwa Done by Enas NeyazDocument15 pagesRheumatic Fever: Supervision by DR - Nagwa Done by Enas NeyazEnas NeyazNo ratings yet
- Thermotherapy: by Ren Peterson, Laurel Petersen, Jason Neilsen, Angela PerkinsDocument104 pagesThermotherapy: by Ren Peterson, Laurel Petersen, Jason Neilsen, Angela PerkinsMaheswari DuraiNo ratings yet
- Physical Agents: Therapeutic ModalitiesDocument31 pagesPhysical Agents: Therapeutic Modalitiessinanhadeed100% (1)
- Comprehensive Cardiac Center OrganizationDocument45 pagesComprehensive Cardiac Center OrganizationRaigheil LayNo ratings yet
- Cardiac FailureDocument63 pagesCardiac FailureNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary SystemDocument75 pagesPulmonary Systemangeles_robert_71No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physical TherapyDocument204 pagesCardiovascular Physical Therapydivyam2008No ratings yet
- Cardiac Rehab: ND RD TH NDDocument3 pagesCardiac Rehab: ND RD TH NDDoodsDiagoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument37 pagesCardiac RehabilitationNafees AsgharNo ratings yet
- Burn RehabilitationDocument14 pagesBurn Rehabilitationoo2eeNo ratings yet
- MyocarditisDocument52 pagesMyocarditis7337man100% (1)
- Dr. Vinod K. Ravaliya, MPT Cardiothoracic Physiotherapy Shree Krishna Hospital KMPIP, KaramsadDocument54 pagesDr. Vinod K. Ravaliya, MPT Cardiothoracic Physiotherapy Shree Krishna Hospital KMPIP, KaramsadEvangelin Melvin100% (1)
- Mechanisms of Cardiac Pain PDFDocument27 pagesMechanisms of Cardiac Pain PDFLa Torre LeoNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation in Rheumatology12 Angli2Document37 pagesRehabilitation in Rheumatology12 Angli2sdsdsdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 50 Cardiopulmonary RehabilitationDocument22 pagesChapter 50 Cardiopulmonary RehabilitationShanin SalapuddinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument25 pagesMechanical VentilationmochkurniawanNo ratings yet
- The History of COPDDocument12 pagesThe History of COPDcarloscano1994No ratings yet
- RehabilitationDocument10 pagesRehabilitationasuratosNo ratings yet
- 7-3-9 - Chest PhysiotherapyDocument10 pages7-3-9 - Chest PhysiotherapyPrabu G SatiyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument5 pagesCardiac RehabilitationGian Carlo Poggi EscobarNo ratings yet
- Assigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationDocument15 pagesAssigmnt. On Cardiac RehabilitationSachin Singh100% (1)
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument114 pagesCardiac RehabilitationAfiqul RashyedNo ratings yet
- 26-Study Electrotherapy Modalities Vs Exercise Therapy PerkthDocument5 pages26-Study Electrotherapy Modalities Vs Exercise Therapy PerkthnakroNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PainDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic PainsukunathNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument1 pageBurnsHuzzain PangcogaNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument4 pagesBurnsMartin KoaNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument93 pagesBURNSRobin Mathew0% (1)
- Arianne Bernardo BSN-3B1: Erythema Pain Epidermis Sunburns Blistering Nerve DermisDocument5 pagesArianne Bernardo BSN-3B1: Erythema Pain Epidermis Sunburns Blistering Nerve DermisArianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Classification: by DegreeDocument10 pagesClassification: by DegreeSonny Dizon PareñasNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument12 pagesIntegumentary SystemJeffrey KauvaNo ratings yet
- Burn Injury. Frostbite. Elrctrotrauma: Department of General SurgeryDocument135 pagesBurn Injury. Frostbite. Elrctrotrauma: Department of General SurgeryIbrahim AlmahmoudNo ratings yet
- Burns and ShockDocument13 pagesBurns and Shockjames garciaNo ratings yet
- PhysiotherapyinburnsDocument93 pagesPhysiotherapyinburnsFinal internalNo ratings yet
- By: Aileen C. Contreras-Limjoco M.DDocument48 pagesBy: Aileen C. Contreras-Limjoco M.Dclara jocomilNo ratings yet
- Burns Etiology & ClassificationDocument31 pagesBurns Etiology & Classificationahmedzakaria0No ratings yet
- BurnDocument4 pagesBurngreshel254981No ratings yet
- bURNS NCLEXDocument10 pagesbURNS NCLEXpapa.pradoNo ratings yet
- Arsuri Burns ENGDocument82 pagesArsuri Burns ENGRomanescu RalucaNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument16 pagesBurnsSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument31 pagesBurnsLouis Carlos RoderosNo ratings yet
- Notes About BurnsDocument11 pagesNotes About BurnsMichelle Ann GacudNo ratings yet
- Burn Nursing CareDocument132 pagesBurn Nursing CareIntan Lestari RadiusNo ratings yet
- Review and Comprehension P. 108 (Madayag, Rachel Eve G)Document2 pagesReview and Comprehension P. 108 (Madayag, Rachel Eve G)Rachel MadayagNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument19 pagesSkinMHKNo ratings yet
- Define BurnsDocument2 pagesDefine BurnsJohn Paolo OrioNo ratings yet
- Burns (Deep Partial Thickness) : Characteristics of Burns of Different DepthsDocument8 pagesBurns (Deep Partial Thickness) : Characteristics of Burns of Different DepthsHencynt SoriaNo ratings yet
- Burns (Including Sunburn)Document7 pagesBurns (Including Sunburn)MattMorelloNo ratings yet
- BurnsDocument1 pageBurnsHanif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Medical Classification of BurnsDocument1 pageMedical Classification of Burnsscartoneros_1No ratings yet
- Neurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? AnswerDocument9 pagesNeurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? Answerdrng48No ratings yet
- MCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural MechanismsDocument3 pagesMCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural Mechanismsdrng48No ratings yet
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National PhyDocument1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phydrng48No ratings yet
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3Document1 pagePages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3drng480% (1)
- توزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيDocument3 pagesتوزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيdrng48No ratings yet
- Stomacolostomy 161108133919Document3 pagesStomacolostomy 161108133919drng48100% (1)
- Cerebral Palsy MCQDocument2 pagesCerebral Palsy MCQdrng4882% (11)
- Assessment of Development and GrowthDocument21 pagesAssessment of Development and Growthdrng48No ratings yet
- Infections: (2013 - 2017)Document1 pageInfections: (2013 - 2017)drng48No ratings yet
- Shenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXDocument281 pagesShenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXJeronim H'gharNo ratings yet
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 pagesMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (9)
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 pagesPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Table: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest PainDocument2 pagesTable: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest Paindrng48No ratings yet
- Contraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania HospitalDocument20 pagesContraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospitaldrng48No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal Paindrng48100% (1)
- Epidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1Document3 pagesEpidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1drng48No ratings yet
- 31 Da 7 CBB 2 eDocument2 pages31 Da 7 CBB 2 edrng48No ratings yet
- WC500022748 2 PDFDocument0 pagesWC500022748 2 PDFMostofa RubalNo ratings yet
- Binaural Frequency List GuideDocument30 pagesBinaural Frequency List GuideChristopher Parker100% (7)
- Beast Huge: For Those Who Want To Gain Muscle MassDocument6 pagesBeast Huge: For Those Who Want To Gain Muscle Massdevitulasi100% (1)
- BSC2011 Study Guide DouglasDocument7 pagesBSC2011 Study Guide DouglasPetey 书维 ChangNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.5 HomeostasisDocument11 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.5 Homeostasisjohn nigussieNo ratings yet
- Pink Salt BenifitsDocument12 pagesPink Salt BenifitsakhtarNo ratings yet
- Roth Williams 2010Document84 pagesRoth Williams 2010GisselaMaldonado100% (1)
- Muscular System NotesDocument40 pagesMuscular System NotesWindhy Dzakiyyah Aurora100% (1)
- Handout Orthopedic Nursing Assisstive DevicesDocument14 pagesHandout Orthopedic Nursing Assisstive DevicesPaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (2)
- 10 Current Research Articles Related To Our SystemDocument11 pages10 Current Research Articles Related To Our Systemhomework solutionNo ratings yet
- A Resounding TinkleDocument73 pagesA Resounding TinkleSula Douglas FolkesNo ratings yet
- Yoga AssignmentDocument9 pagesYoga AssignmentSharunieRavikumar77% (13)
- Cardiology Case 1Document2 pagesCardiology Case 1vil62650% (2)
- Introduction To The Body As A WholeDocument29 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Wholekhizer hayatNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus IIDocument20 pagesDiabetes Mellitus IIMa R Dy100% (1)
- Cont. Diagnostic Test 2 (61-150)Document13 pagesCont. Diagnostic Test 2 (61-150)Sheila Tolentino-BelanioNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionDocument11 pagesNCM 116 - Nursing Care of Patients With Neurologic DysfunctionRigel Kent C. TobiasNo ratings yet
- (Equine Veterinary Journal 2010-Jan 05 Vol. 37 Iss. 2) W. W. MUIR - Pain Therapy in Horses (2010) (10.2746 - 0425164054223831) - Libgen - LiDocument3 pages(Equine Veterinary Journal 2010-Jan 05 Vol. 37 Iss. 2) W. W. MUIR - Pain Therapy in Horses (2010) (10.2746 - 0425164054223831) - Libgen - LiAcupuntura de EquinosNo ratings yet
- Bio ACE Form 4Document3 pagesBio ACE Form 4Myramel KlarisNo ratings yet
- Lab On Transpiration BioDocument8 pagesLab On Transpiration BioNigg100% (1)
- Psychology StudiesDocument9 pagesPsychology StudiesaaravNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesPathophysiologypaul andrew laranjo asuncionNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination in Forensic OdontologyDocument3 pagesSex Determination in Forensic OdontologyAtika RahmasariNo ratings yet
- Resusitasi Pada AnakDocument43 pagesResusitasi Pada AnakSondang Herikson PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol SynthesisDocument19 pagesCholesterol Synthesisbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Identify The 6 Classes ofDocument21 pagesLearning Objectives Identify The 6 Classes ofhahmed78No ratings yet
- Identification of Invertebrate Taxonomic CharacterDocument6 pagesIdentification of Invertebrate Taxonomic CharacterDaisy KavinskyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fluid Therapy On The Basis ofDocument29 pagesPrinciples of Fluid Therapy On The Basis ofhendrytzNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Head, Hand, Face ExamDocument29 pagesCH 11 Head, Hand, Face ExamDyan Karla Cosare - BacayanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Blood VesselsDocument12 pagesCardiovascular Blood VesselswatuwaitingforNo ratings yet