Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fibroid Tumor: Something That Every Women Should Know About
Uploaded by
Tarushi ChoudharyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fibroid Tumor: Something That Every Women Should Know About
Uploaded by
Tarushi ChoudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
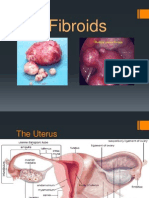
Fibroid Tumor: Something that every women should know about.
Generally know as Uterine fibroids, myomas or fibromyomas, fibroid tumors are non-cancerous tumors formed by the muscle layers of the uterus. Growth of smooth muscles and fibrous tissues forms Uterine Fibroma. Women between the age of 30 to 50 are most likely to develop fibroids. Tumor may start to form in women when they are in their 20s but symptoms can only be seen in late 30s or 40s. Fibroids increases in size during the pregnancy period since the level of estrogens rises. Generally after the menopause the growth of tumor decreases due to the fall in the level of estrogens. Categorised into 4 types: Intramural- Most common type of fibroids located in the wall of the uterus. Subserosal fibroids-Found on the wall of the uterus. They can become large since they develop into pedunculated fibroids or stalks. Submucosal fibroids- Found in the muscle beneath the lining of uterus wall. Cervical fibroids-Found on the neck of the cervix. Bleeding, backache, frequent urination, pain during sex and longer menstrual cycles, this all are small symptoms or indication of formation of tumor. Fibroids can be diagnosed by pelvic exam or ultrasound. Other techniques such as CT (computer tomography) or MR (Magnetic Resonance) also helps, and they are painless methods to diagnose. Sometimes Diagnostic Hysteroscopy can be used to know the presence of Submucosal Fibroids. This can be painful and can cause discomfort and hence it can be performed with local anesthesia. A new minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of fibroid tumors is Fibroid embolization or Uterine artery embolization, which is performed by a trained physician and interventional radiologist. Patient feels sedated and drowsy and no pain. Even though fibroid tumors are generally non-cancerous, in some extreme cases they can lead to a type of cancer called Leiomyosarcoma, which occurs in one of every 1000 women.
You might also like
- RDA 2020 - Short ReportDocument10 pagesRDA 2020 - Short ReportRuchira Ghosh100% (2)
- Uterine MyomaDocument15 pagesUterine Myomaanon_302623176100% (1)
- Understanding Uterine FibroidsDocument52 pagesUnderstanding Uterine FibroidsDoctor JitNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma Treatment with HomeopathyDocument14 pagesFibroadenoma Treatment with HomeopathypawajeeNo ratings yet
- Benign and malignant ovarian tumors: a comprehensive overviewDocument67 pagesBenign and malignant ovarian tumors: a comprehensive overviewZEMENAY TRUNEHNo ratings yet
- Boron - Growing Evidence For Human Health BenefitsDocument12 pagesBoron - Growing Evidence For Human Health BenefitsFrançois-Xavier SarfatiNo ratings yet
- Types, locations, symptoms and treatment of uterine fibroidsDocument4 pagesTypes, locations, symptoms and treatment of uterine fibroidsRomeo ReyesNo ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Uterine FibroidsDocument2 pagesUterine FibroidsKarlo BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Medical AstrologyDocument777 pagesMedical AstrologyRao Lakkoju100% (3)
- Fibroadenoma and HomoeopathyDocument5 pagesFibroadenoma and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- Top Medical Topics for NLE ExamDocument9 pagesTop Medical Topics for NLE ExamWilmaBongotanPadawilNo ratings yet
- Fibroids Miracle Cure: The Ultimate Fibroids Diet To Heal NaturallyFrom EverandFibroids Miracle Cure: The Ultimate Fibroids Diet To Heal NaturallyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Complex Ovary Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandComplex Ovary Cyst, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fibroid UterusDocument12 pagesFibroid Uterusvincentsharon100% (3)
- Uterine Fibroid SeminarDocument11 pagesUterine Fibroid Seminarvarshasharma05100% (2)
- Inspection Total Cholesterol Levels KB Injection Users for 3 Months in Ngumpul Village, JombangDocument57 pagesInspection Total Cholesterol Levels KB Injection Users for 3 Months in Ngumpul Village, JombangJuniver RiryNo ratings yet
- Fibroids PowerpointDocument27 pagesFibroids Powerpointteritohaha100% (3)
- Questionário Ii - Fundamentos Etimológicos Do InglêsDocument4 pagesQuestionário Ii - Fundamentos Etimológicos Do InglêsDébora Bandeira David100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Uterine MYOMADocument5 pagesUterine MYOMARoss Manalang100% (2)
- Uterine FibroidsDocument25 pagesUterine FibroidsMarie Eulie PatinoNo ratings yet
- Uterine TumorsDocument11 pagesUterine TumorsMuhammad Bilal DosaniNo ratings yet
- Fibroids by EasterDocument7 pagesFibroids by EasterIGA ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Myoma Treatment Options MR Guided Focused Ultrasound (Mrgfus)Document3 pagesMyoma Treatment Options MR Guided Focused Ultrasound (Mrgfus)Marvi Hollanda SalandananNo ratings yet
- Fibroid Uterine Article ScribdDocument2 pagesFibroid Uterine Article Scribdivarnor1570No ratings yet
- Myoma Uteri: Pregnancy PubertyDocument9 pagesMyoma Uteri: Pregnancy PubertyJaja RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4Lennie LennieNo ratings yet
- Fi Bro AdenomaDocument11 pagesFi Bro AdenomaRain RoneNo ratings yet
- Signs & Symptoms: NeoplasmDocument2 pagesSigns & Symptoms: NeoplasmKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Definition of Myoma:: Uterine Fibroid Treatments MR Guided Focused UltrasoundDocument1 pageDefinition of Myoma:: Uterine Fibroid Treatments MR Guided Focused UltrasoundQueenie BryantNo ratings yet
- Myoma: Three Types of TreatmentsDocument3 pagesMyoma: Three Types of TreatmentsjessamariesabioNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma and HomoeopathyDocument5 pagesFibroadenoma and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNo ratings yet
- Description of MyomaDocument1 pageDescription of MyomaLovelyn DatuNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumors of Female Genital OrgansDocument37 pagesBenign Tumors of Female Genital Organssimi yNo ratings yet
- Bab IiDocument11 pagesBab IiArika AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma of BreastDocument3 pagesFibroadenoma of BreastmuflikhasofianaNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumors of BreastDocument16 pagesBenign Tumors of BreastChanDa DasNo ratings yet
- Case Study of a-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesCase Study of a-WPS Officearmiigabby48No ratings yet
- Myoma Case StudyDocument2 pagesMyoma Case StudyKristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Is Leiomyoma of The UterusDocument16 pagesWhat Is Leiomyoma of The Uterusjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- What Is Breast Cancer?Document122 pagesWhat Is Breast Cancer?Rizki SariWahyuniNo ratings yet
- What Is Breast Cancer?Document122 pagesWhat Is Breast Cancer?deasyNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma What Is Fibroadenoma?Document4 pagesFibroadenoma What Is Fibroadenoma?Farah AmeliaNo ratings yet
- 2 Ovarian Cyst UG4-Dr AllanDocument13 pages2 Ovarian Cyst UG4-Dr AllanAza BabanNo ratings yet
- Myoma: Causes of Uterine Fibroid or MyomaDocument15 pagesMyoma: Causes of Uterine Fibroid or MyomaHannah Katrina Almoro AlmedaNo ratings yet
- Uf Patient GuideDocument12 pagesUf Patient Guideadza30No ratings yet
- Fibroids 102307Document44 pagesFibroids 102307bazuu mbwegzeNo ratings yet
- Myoma Uteri/Fibroids/ Leiomyomata: Symptoms of Uterine Myoma May IncludeDocument3 pagesMyoma Uteri/Fibroids/ Leiomyomata: Symptoms of Uterine Myoma May IncludeDiane MargretNo ratings yet
- BREAST DISORDERS.PPT.Document34 pagesBREAST DISORDERS.PPT.Muskan TiwariNo ratings yet
- Also Called Uterine Leiomyoma, Myoma, Myomata Uteri, FibromyomaDocument25 pagesAlso Called Uterine Leiomyoma, Myoma, Myomata Uteri, Fibromyomashygirl72No ratings yet
- Tumor PamphletDocument3 pagesTumor PamphletRodel Aguila SañoNo ratings yet
- What are uterine fibroids? Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatmentDocument4 pagesWhat are uterine fibroids? Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatmentmkarjunNo ratings yet
- Fibroids: DR F HoveDocument18 pagesFibroids: DR F HoveKelvin MaikanaNo ratings yet
- MSN Ii An-Uterine FibroidDocument33 pagesMSN Ii An-Uterine FibroidSifanaNo ratings yet
- Fibriod: Women Barrier To Pregnancy Brief Discription of Fibriod and How It DevelopsDocument10 pagesFibriod: Women Barrier To Pregnancy Brief Discription of Fibriod and How It DevelopsRahil ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids PDFDocument3 pagesUterine Fibroids PDFmervat_aastNo ratings yet
- Myoma EndometrialDocument26 pagesMyoma EndometrialYulia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 11 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocument61 pages11 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDevy Eryn TobingNo ratings yet
- Myoma Overview, Bibliography and ObjectivesDocument5 pagesMyoma Overview, Bibliography and ObjectivesicesexyNo ratings yet
- Fi Bro AdenomaDocument2 pagesFi Bro AdenomafebrianaayupNo ratings yet
- Uterine Fibroids: Noncancerous Growths in the UterusDocument3 pagesUterine Fibroids: Noncancerous Growths in the UterusNeha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Gynecology of Uterine FibroidsDocument33 pagesGynecology of Uterine FibroidsD.A.B.MNo ratings yet
- Clinical anatomy of the uterusDocument12 pagesClinical anatomy of the uterusAsha dsouzaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Medical TerminologyDocument26 pagesPresentation Medical TerminologySunaina BhartiNo ratings yet
- Uterine MyomaDocument24 pagesUterine MyomabemnetNo ratings yet
- FibromaDocument2 pagesFibromaDevita Indyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Adolescent ParentingDocument29 pagesAdolescent ParentingTarushi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Career in Financial PlanningDocument29 pagesCareer in Financial PlanningTarushi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- How To Teach or Learn Anything 8 Different Ways Multiple IntellienceDocument7 pagesHow To Teach or Learn Anything 8 Different Ways Multiple IntellienceTarushi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Traning Material On Implementation of Accounting StandardsDocument308 pagesTraning Material On Implementation of Accounting StandardsAnupam GoyalNo ratings yet
- Dutasteride 0.5mg (Avodart)Document14 pagesDutasteride 0.5mg (Avodart)ddandan_2No ratings yet
- Euglycemic Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument6 pagesEuglycemic Diabetic KetoacidosisMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Mellitus New OnsetMOHANNADNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucDocument11 pagesNeonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucAnaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nalin, AIMSS, New DelhiDocument12 pagesDr. Nalin, AIMSS, New DelhiSyed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Pi e LDH 21 Ifcc 3Document2 pagesPi e LDH 21 Ifcc 3Osama Ben DawNo ratings yet
- Opt' Eijnde 2001Document6 pagesOpt' Eijnde 2001Prefeitura de FloresNo ratings yet
- Judul Kti D3 Kep Ta 2122-3Document6 pagesJudul Kti D3 Kep Ta 2122-3A channelNo ratings yet
- Grave's DiseaseDocument1 pageGrave's DiseaseCJMALNo ratings yet
- Bleeding and ThrombosisDocument27 pagesBleeding and Thrombosisswathi bsNo ratings yet
- Buku Biopsi InterpretationDocument552 pagesBuku Biopsi InterpretationelisasitohangNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument16 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapydamion clarkeNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis QuestionDocument6 pagesHomeostasis Questionmarwani mat nasirNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1001 Reviewand Viva Voce Qand ADocument13 pagesBiochemistry 1001 Reviewand Viva Voce Qand AKhadija BukhadNo ratings yet
- ABG made simple: A 4-step approachDocument19 pagesABG made simple: A 4-step approachBimantoko Hadi Sriyono100% (1)
- Potassium Homeostasis & DisordersDocument20 pagesPotassium Homeostasis & DisordersHassan SalamehNo ratings yet
- Endophrin - Google SearchDocument1 pageEndophrin - Google SearchNurindah AyuNo ratings yet
- CLASS - 10th Chapter - 7 (Control and Coordination) : A Synapse or Neuromuscular JunctionDocument10 pagesCLASS - 10th Chapter - 7 (Control and Coordination) : A Synapse or Neuromuscular JunctionAnupama BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds of Red Seaweed A MiniReviewDocument10 pagesNutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds of Red Seaweed A MiniReview180221 Huỳnh Thanh NguyênNo ratings yet
- Bolinao, Pangasinan: Luna National High SchoolDocument6 pagesBolinao, Pangasinan: Luna National High SchoolMayda RiveraNo ratings yet
- 21 - Thyroid Function TestsDocument2 pages21 - Thyroid Function Testshamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Science DLL Q2W1Document5 pagesScience DLL Q2W1ANGELBERT PEDNGANo ratings yet