Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DBMS Keys With Example
Uploaded by
kritzzy1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DBMS Keys With Example
Uploaded by
kritzzy1Copyright:
Available Formats
Super Keys : Super key stands for superset of a key.
A Super Key is a set of one or more attributes that are taken collectively and can identify all other attributes uniquely.
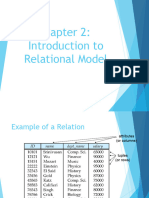
Candidate Keys Candidate Keys are super keys for which no proper subset is a super key. In other words candidate keys are minimal super keys. Primary Key: It is a candidate key that is chosen by the database designer to identify entities with in an entity set. Primary key is the minimal super keys. In the ER diagram primary key is represented by underlining the primary key attribute. Ideally a primary key is composed of only a single attribute. But it is possible to have a primary key composed of more than one attribute. Composite Key Composite key consists of more than one attributes. Example: Consider a Relation or Table R1. Let A,B,C,D,E are the attributes of this relation. R(A,B,C,D,E) ABCDE This means the attribute 'A' uniquely determines the other attributes B,C,D,E. BCADE This means the attributes 'BC' jointly determines all the other attributes A,D,E in the relation. Primary Key :A Candidate Keys :A, BC Super Keys : A,BC,ABC,AD ABC,AD are not Candidate Keys since both are not minimal super keys.
You might also like
- Relational ModelDocument30 pagesRelational Modelcrybert zinyamaNo ratings yet
- Relational ModelDocument16 pagesRelational ModelTech force hindiNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit2Document23 pagesDBMS Unit2pranay dodiyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Keys in DBMSDocument2 pagesTypes of Keys in DBMSVirat Kumar Jain50% (2)
- Fundamentals of Database Systems: Prepared By: Ms. Roda Flor Andrea B. TeodocioDocument30 pagesFundamentals of Database Systems: Prepared By: Ms. Roda Flor Andrea B. TeodocioDrei GuetaNo ratings yet
- Game Ing Cafe ReportDocument4 pagesGame Ing Cafe ReportPothina KarthikNo ratings yet
- Database and ER modeling conceptsDocument2 pagesDatabase and ER modeling conceptsAadhar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Key Terms Chap 02Document4 pagesKey Terms Chap 02rm_khanNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Schema and KeysDocument20 pagesRelational Database Schema and Keyswaleed amjadNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Relational Data Model Ict200Document56 pagesTopic 3 Relational Data Model Ict200Hafizuddin RosliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Converting ERD To Relational ModelDocument16 pagesChapter 6 Converting ERD To Relational ModelLeong Chee HaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Relational Model and Relational Algebra (T2: Page 196-232)Document37 pagesChapter 3: Relational Model and Relational Algebra (T2: Page 196-232)Bahlol JabarkhailNo ratings yet
- Database Analysis-Unit-1I Mapping ConstraintsDocument28 pagesDatabase Analysis-Unit-1I Mapping Constraintszaibakhan8No ratings yet
- Part2 - Ch5 - Relational Database Design by ER and ERR To Relational MappingDocument20 pagesPart2 - Ch5 - Relational Database Design by ER and ERR To Relational MappingLayan AlajoNo ratings yet
- RDBMS (Relational Database Management Systems) Part 1Document11 pagesRDBMS (Relational Database Management Systems) Part 1Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Relational Data ModelDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Relational Data ModelHildana TamratNo ratings yet
- Chp2 DatabaseDocument8 pagesChp2 DatabaseNway Nway Wint AungNo ratings yet
- CH 4-1 Relational Datamodel&constraintsDocument31 pagesCH 4-1 Relational Datamodel&constraintsAnshuman021No ratings yet
- CH_3 Fundamentals of a Database System (1)Document15 pagesCH_3 Fundamentals of a Database System (1)abrehamcs65No ratings yet
- Lect 2 Relational ModelDocument46 pagesLect 2 Relational ModelShreya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Dropping Constraints:: Alter Table Employees Drop Constraint Employees - PKDocument15 pagesDropping Constraints:: Alter Table Employees Drop Constraint Employees - PKBala KumarNo ratings yet
- CHP 3Document5 pagesCHP 3rumioceanNo ratings yet
- Relational and ER ModelsDocument6 pagesRelational and ER Modelsminiature testNo ratings yet
- What Are Entity Relationship DiagramsDocument10 pagesWhat Are Entity Relationship DiagramsELIENo ratings yet
- Data Models: How To Structure DataDocument22 pagesData Models: How To Structure DataDayton Good Kush AllenNo ratings yet
- DBMS QuestionsDocument9 pagesDBMS QuestionsKasyap NaniNo ratings yet
- MS SQLDocument95 pagesMS SQLsakunthalapcsNo ratings yet
- Presentation Errelational Model 1450265989 18156Document37 pagesPresentation Errelational Model 1450265989 18156Ramajayam GNo ratings yet
- DBMS Keys: Candidate, Super, Primary, Foreign Key Types With ExampleDocument7 pagesDBMS Keys: Candidate, Super, Primary, Foreign Key Types With ExampleMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Relational Model Concepts & TablesDocument29 pagesRelational Model Concepts & TablesSweety AvalaNo ratings yet
- Relational Database ModelsDocument5 pagesRelational Database Modelsdextermartins608No ratings yet
- Seession 4Document4 pagesSeession 4AhnNo ratings yet
- Dbms 2Document54 pagesDbms 2Pooja Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- HE170786 - Nguyen Quy DuongDocument5 pagesHE170786 - Nguyen Quy DuongNguyen Quy Duong (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- Unit-III NotesDocument33 pagesUnit-III NotesathirayanpericseNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document26 pagesWeek 5ابتهاج عبدالسلامNo ratings yet
- Database Keys: Super KeyDocument2 pagesDatabase Keys: Super KeyGoutham YeluriNo ratings yet
- Relational ModelDocument9 pagesRelational ModelrituNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Hw5 PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info Hw5 PRJamal Al-jaziNo ratings yet
- HW5Document7 pagesHW5Rahul Patil100% (1)
- DBMS Keys: (I) Super KeyDocument5 pagesDBMS Keys: (I) Super KeybivafelikeNo ratings yet
- DBMS CHAPTER4 KEY CONCEPTSDocument33 pagesDBMS CHAPTER4 KEY CONCEPTSSachin KondawarNo ratings yet
- Integrity Key: Means Rules Set On Database Tables. There Are 3 Types of Integrity in DatabaseDocument5 pagesIntegrity Key: Means Rules Set On Database Tables. There Are 3 Types of Integrity in Databaseaniqa_bhutto8767No ratings yet
- Er ModelDocument68 pagesEr ModelKeshav Sehgal100% (1)
- Database Fundamentals Chapter 3: The Relational Data ModelDocument51 pagesDatabase Fundamentals Chapter 3: The Relational Data ModelYohannes DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week2Document27 pagesLecture Week2A DanNo ratings yet
- Keys in Data Base Management SystemDocument14 pagesKeys in Data Base Management SystemRaghav KhemkaNo ratings yet
- 5 KeysDocument32 pages5 KeysEshaNo ratings yet
- Xii Cs Unit III Database MGMT 2020 21Document36 pagesXii Cs Unit III Database MGMT 2020 21SamhithNo ratings yet
- Relational Data Model and ConstraintsDocument30 pagesRelational Data Model and ConstraintsMohammad DiabNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship (ER) ModelingDocument64 pagesEntity Relationship (ER) Modelingnaqibullah2022faryabNo ratings yet
- 03 DB Modeling Using ERDDocument44 pages03 DB Modeling Using ERDSyeda Areeba RashidNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Database TermsDocument7 pagesDefinitions of Database TermsJoshuaNo ratings yet
- MC0067 - Database Management System (DBMS and Oracle 9i) 1Document7 pagesMC0067 - Database Management System (DBMS and Oracle 9i) 1Srini K DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Database Management - Session 5Document39 pagesDatabase Management - Session 5Jinen MirjeNo ratings yet
- CH#4 - UpdateDocument38 pagesCH#4 - Updatelusan.alahmadiNo ratings yet
- Relational Database FeaturesDocument8 pagesRelational Database FeaturesBonzowoNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Design by ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingDocument39 pagesRelational Database Design by ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingAhmad Shdifat100% (2)
- CH 02 Relational Model & Relational AlgebraDocument23 pagesCH 02 Relational Model & Relational AlgebraShubham waghuleNo ratings yet
- FDP - 93 BrochureDocument5 pagesFDP - 93 Brochurekritzzy1No ratings yet
- A Must For LR Information Systems Research - INFORMS PDFDocument2 pagesA Must For LR Information Systems Research - INFORMS PDFkritzzy1No ratings yet
- SM Unit 4Document1 pageSM Unit 4kritzzy1No ratings yet
- Sharing Is GoodDocument1 pageSharing Is Goodkritzzy1No ratings yet
- Case Study - How Horlicks Has Avoided Getting DatedDocument4 pagesCase Study - How Horlicks Has Avoided Getting Datedkritzzy1No ratings yet
- Celebrity endorsement strategy of Turkish AirlinesDocument8 pagesCelebrity endorsement strategy of Turkish Airlineskritzzy1No ratings yet
- Principles AND Practices of ManagementDocument36 pagesPrinciples AND Practices of ManagementRodgers OkutoiNo ratings yet
- Johari Window1Document8 pagesJohari Window1kritzzy1No ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting: Made By:Dharmesh Nagdev. Class:Vi-C ROLLNO:11Document11 pagesRain Water Harvesting: Made By:Dharmesh Nagdev. Class:Vi-C ROLLNO:11kritzzy1No ratings yet
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataFrom EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLFrom EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IBM DB2 Administration Guide: Installation, Upgrade and Configuration of IBM DB2 on RHEL 8, Windows 10 and IBM Cloud (English Edition)From EverandIBM DB2 Administration Guide: Installation, Upgrade and Configuration of IBM DB2 on RHEL 8, Windows 10 and IBM Cloud (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Agile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceFrom EverandAgile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceNo ratings yet
- Mastering Amazon Relational Database Service for MySQL: Building and configuring MySQL instances (English Edition)From EverandMastering Amazon Relational Database Service for MySQL: Building and configuring MySQL instances (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveFrom EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Big Data and Analytics: The key concepts and practical applications of big data analytics (English Edition)From EverandBig Data and Analytics: The key concepts and practical applications of big data analytics (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics: Disruptive Technologies for Changing the GameFrom EverandBig Data Analytics: Disruptive Technologies for Changing the GameRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- COBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2From EverandCOBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- R: Recipes for Analysis, Visualization and Machine LearningFrom EverandR: Recipes for Analysis, Visualization and Machine LearningNo ratings yet