Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics Practice Soln
Uploaded by
Naury N OliveiraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics Practice Soln
Uploaded by
Naury N OliveiraCopyright:
Available Formats
1. (a)Given the following standard enthalpies of combustion (298K, 1 atmos.): C(s) -393 kJ mol-1; H2(g) -285.
6 kJ mol-1; C2H6(g) -1560 kJ mol-1 (note: the first two enthalpies correspond to the enthalpy of formation of carbon dioxide and water respectively) Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of ethane, C2H6(g) Solution: We will use the enthalpy of combustion of ethane to find its enthalpy of formation: 7 2 6 + 2 2 2 + 3 2 2
The enthalpy of combustion is then given by,
We note that (2 ) = 0 according to the definition of standard enthalpy. Therefore, unknown (2 6 ) can be solved for (2 6 ) = 2 (2 ) + 3 (2 )
= 2 (2 ) + 3 (2 ) (2 6 )
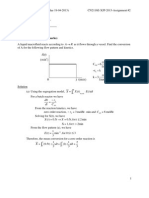
(2 6 ) = 2(393) + 3(285) (1560) = 81 / (b) Given the following bond enthalpies (bond energies) in kJ mol-1; C-H 412; C-C 347; O-H 464; O=O 498; C=O 805 (for CO2); C-O 358 calculate the enthalpy of combustion of ethane. You will not get -1560 kJ mol-1. The bond enthalpy method is much less accurate than tabulated enthalpies of formation. Solution: Construct a reaction scheme that shows the individual bonds
H H C H
H C H H + 3 1/2 O O 2 O C O + 3 H O H
Count the bonds broken :
6 C-H bonds + 1 C-C 3.5 O=O double bonds = 6(412)+347+3.5(498) = 4562 kJ/mol Count the bonds formed : 4 C=O + 6 O-H = 4(804) + 6(464) = -6004 kJ/mol The total is 4562 6004 kJ/mol = -1442 kJ/mol
2. Given the following standard enthalpies of combustion (298K, 1 atmos.): C(s) -393 kJ mol-1; H2(g) -285.6 kJ mol-1; C8H18(l) -5512 kJ mol-1; Calculate the enthalpy of formation of octane, C8H18(l) Solution: Use Hess law. The enthalpy of formation of octane can be written as 8 () + 9 2 () 8 18 () (8 18 )
The enthalpies of combustion are 8 18 () +
(8 18 ) = 8 (393) + 9(285.6) (5512) = 202.4 / 3. Given the following standard enthalpies of combustion (298K, 1 atmos.): C(s) -393 kJ mol-1; H2(g) -285.6 kJ mol-1; and the enthalpy of formation of cyclohexane, C6H12(l) -156 kJ mol-1; Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of cyclohexane, C6H12(l) Solution: Use Hess law. The enthalpy of combustion of cyclohexane can be written as 6 12 () + 15 2 () 6 2 () + 6 2 () (6 12 )
(8 18 ) = 8 (2 ) + 9 (2 ) (8 18 )
1 2 () + 2 () 2 () 2
() + 2 () 2 ()
25 () 8 2 () + 9 2 () (8 18 ) 2 2 (2 ) (2 )
To obtain this we use the known enthalpies of formation 6 () + 6 2 () 6 12 () 1 2 () + 2 () 2 () 2 () + 2 () 2 () (6 12 )
(2 )
(6 12 ) = 6(393) + 6(285.6) (156) = 3915.6 / 4. (a) Given the following standard enthalpies of combustion (298K, 1 atmos.): C(s) -393 kJ mol-1; H2(g) -285.6 kJ mol-1; and the enthalpy of formation of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(l) -487 kJ mol-1 Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(l)
(6 12 ) = 6 (2 ) + 6 (2 ) (6 12 )
(2 )
Solution: Use Hess law. The enthalpy of combustion of ethanoic acid (acetic acid) can be written as 3 () + 2 2 () 2 2 () + 2 2 () (3 ) 2 () + 2 2 () + 2 () 3 () 1 2 () + 2 () 2 () 2 () + 2 () 2 () (3 )
To obtain this we use the known enthalpies of formation
(2 ) = 393
(6 12 ) = 2 (2 ) + 2 (2 ) (3 )
(2 ) = 286
(3 ) = 2(393) + 2(286) (487) = 871 / 5. Given the following standard Enthalpies of Formation (298K, 1 atmos.): NH3(g) -46.2 kJ mol-1; HCl(g) -92.3 kJ mol-1; NH4Cl(s) -315.0 kJ mol-1; Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g) Solution: = (3 ) + () (4 )
= (46.2) + (92.3) (315) = +218.5 /
You might also like
- CHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-AnsDocument2 pagesCHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-Ansnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- STA 247 - Answers For Practice Problem Set #1Document5 pagesSTA 247 - Answers For Practice Problem Set #1aakasNo ratings yet
- 303 - 11 Final Exam KEY-1 PDFDocument22 pages303 - 11 Final Exam KEY-1 PDFaegaisNo ratings yet
- Raman Spectroscopy of Carbon TetrachlorideDocument8 pagesRaman Spectroscopy of Carbon TetrachlorideNikoNo ratings yet
- AIEEE - 2011 Paper With Solutions For Physics, Chemistry and MathsDocument16 pagesAIEEE - 2011 Paper With Solutions For Physics, Chemistry and Mathsstudysteps.inNo ratings yet
- 06 Petrucci10e CSMDocument54 pages06 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- RMN ProblemsDocument7 pagesRMN ProblemsAnonymous llSDP0tNo ratings yet
- Enu Tour1 TaskDocument9 pagesEnu Tour1 TaskĐinh Đại VũNo ratings yet
- Identification of An Unknown Amino AcidDocument7 pagesIdentification of An Unknown Amino AcidVanandiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - IsE FluorinityDocument5 pagesLab Report - IsE FluorinityJohn LamNo ratings yet
- HW1 Solns KineticsDocument10 pagesHW1 Solns Kineticsapb91781No ratings yet
- Final Exam 2012Document12 pagesFinal Exam 2012Mat MorashNo ratings yet
- Eat of Solution Data For Aqueous SolutionsDocument2 pagesEat of Solution Data For Aqueous SolutionsJúlio Gabriel Queiroz dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Experiment 14 - Post Lab PDFDocument2 pagesExperiment 14 - Post Lab PDFDoyeon KimNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment 2 - 2Document9 pagesHome Assignment 2 - 2Naurizbay SultanovNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium Properties of The Ternary Mixture Dibutylether + Toluene + Heptane at 313.15 KDocument5 pagesPhase Equilibrium Properties of The Ternary Mixture Dibutylether + Toluene + Heptane at 313.15 Kmurdanetap957No ratings yet
- BT HPTDocument31 pagesBT HPTLinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal TermokimiaDocument2 pagesLatihan Soal TermokimianindyadityaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumCarbuncle JonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document38 pagesChapter 13Lucy BrownNo ratings yet
- 7-Ode Ivp1Document12 pages7-Ode Ivp1rahulNo ratings yet
- Determination of o of Chromium Using Tanabe-Sugano DiagramDocument2 pagesDetermination of o of Chromium Using Tanabe-Sugano DiagramDozdiNo ratings yet
- 05-Rx Enthalpies Ws KeyDocument2 pages05-Rx Enthalpies Ws KeyMel LeeNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Final ReviewerDocument7 pagesOrg Chem Final ReviewerblessaNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Reactor KineticsDocument2 pagesSolutions For Reactor Kineticszy_yfNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 AeroelasticidadDocument12 pagesTaller 2 AeroelasticidadPablo Cesar Ruiz GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 28 Petrucci10e CSMDocument35 pages28 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocument43 pages07 Petrucci10e CSMPhương Ngân HồNo ratings yet
- Tutorial + Solutions 27 August 2010Document2 pagesTutorial + Solutions 27 August 2010Jailene Gómez CollazoNo ratings yet
- Kinetics 1Document3 pagesKinetics 1JuarezNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Curcumin From TurmericDocument2 pagesIsolation of Curcumin From TurmericyadranNo ratings yet
- Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram: dP dT TΔVDocument8 pagesBinary Solid-Liquid Phase Diagram: dP dT TΔVKevin CruzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 With AnswersDocument1 pageProblem Set 1 With AnswersMelvin CastrosantoNo ratings yet
- PCHEMDocument11 pagesPCHEMMika PelagioNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Chemical Equilibrium: BG BGJudith Del Valle MorejonNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Isobutyl AcetateDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Isobutyl AcetateRandy DavenportNo ratings yet
- Exercises SynthesisDocument7 pagesExercises SynthesisharulyNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Equilibrium ConstantsDocument96 pages7.2 Equilibrium ConstantsScotrraaj Gopal0% (1)
- Enthalpy StoichiometryDocument1 pageEnthalpy StoichiometrykjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Set6ans 10Document4 pagesSet6ans 10Natália FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Aquino Lab04Document18 pagesAquino Lab04Ai RahNo ratings yet
- 25 Petrucci10e CSMDocument25 pages25 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Achem PDFDocument12 pagesTutorial 4 Achem PDFyassinroslanNo ratings yet
- Нome Assignment 4Document3 pagesНome Assignment 4Abdu M. HabsyiNo ratings yet
- Problems SetDocument10 pagesProblems SetSajith KurianNo ratings yet
- NMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionDocument8 pagesNMR Kinetics: Study of A Reversible Hydrolysis ReactionOldbooklover100% (2)
- Post-Laboratory Assignment. PROP 344Document3 pagesPost-Laboratory Assignment. PROP 344bencleese100% (3)
- Peter Atkins Julio de Paula Ron Friedman Physical Chemistry Quanta (0664-0714)Document51 pagesPeter Atkins Julio de Paula Ron Friedman Physical Chemistry Quanta (0664-0714)Administracion OTIC IVICNo ratings yet
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocument43 pages07 Petrucci10e CSMAlex100% (3)
- Percent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingDocument11 pagesPercent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingdhavaleshNo ratings yet
- Adama Science and Technology University School of Applied Natural Science Department of Applied MathematicsDocument9 pagesAdama Science and Technology University School of Applied Natural Science Department of Applied MathematicsALEMAYEHUNo ratings yet
- Eisermann Et Al - 1980Document15 pagesEisermann Et Al - 1980Felipe0% (1)
- 2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (L) F 2 (L) - 1 (S) 2 (G) 2 (G) F 2 (G) - 1Document27 pages2 (G) 2 (G) 2 (L) F 2 (L) - 1 (S) 2 (G) 2 (G) F 2 (G) - 1SMJK KatholikNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Exercise 2 - Bond Dissocation EnthalpiesDocument2 pages2.1 Exercise 2 - Bond Dissocation EnthalpiesHamzaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument20 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionsanushka shagunNo ratings yet
- SQA-Hess's Law QuestionsDocument4 pagesSQA-Hess's Law QuestionsWidya GrantinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Review SolutionDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Review SolutionSFDLSFHIOANo ratings yet
- Quiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Chemical ThermodynamicsOliric FabiolasNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHess's Law WorksheetsaadixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- Name: Maturan, Renz Myko B. Date: November 28, 2022 Subject & Section: EE 330 AC/DC Machineries - CDocument7 pagesName: Maturan, Renz Myko B. Date: November 28, 2022 Subject & Section: EE 330 AC/DC Machineries - CRenz MykoNo ratings yet
- MK3000L BrochureDocument2 pagesMK3000L BrochureXuân QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Op Starchem 611Document1 pageOp Starchem 611Sinead1990No ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization: Intel 80386 ProcessorDocument15 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization: Intel 80386 ProcessorAtishay GoyalNo ratings yet
- Project of Telephone DirectoryDocument15 pagesProject of Telephone DirectoryShree CyberiaNo ratings yet
- Tapiwa Steve Mandaa - 165070 - Assignsubmission - File - Innovation Management Paper DraftDocument7 pagesTapiwa Steve Mandaa - 165070 - Assignsubmission - File - Innovation Management Paper DraftTapiwaNo ratings yet
- Rwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputyDocument1 pageRwanda National Examinations Council Organisational Chart DeputymugobokaNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document10 pagesHW 3Hande ÖzerNo ratings yet
- Iso 3675 en PDFDocument6 pagesIso 3675 en PDFGery Arturo Perez AltamarNo ratings yet
- Suzanne Cardenas Uesj Thesis 2020Document92 pagesSuzanne Cardenas Uesj Thesis 2020api-262960549No ratings yet
- Y-Axis Free Guide On IELTSDocument12 pagesY-Axis Free Guide On IELTSSheikismail PatelNo ratings yet
- Glazing Risk AssessmentDocument6 pagesGlazing Risk AssessmentKaren OlivierNo ratings yet
- The Journal of The Acoustical Society of AmericaDocument12 pagesThe Journal of The Acoustical Society of Americadr01dNo ratings yet
- HOSTILE - Colony Module Schematics (Updated)Document18 pagesHOSTILE - Colony Module Schematics (Updated)Oleksandr TrifanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics DPPDocument10 pagesElectrostatics DPPhimesh2006hNo ratings yet
- Lambda Calculus CLCDocument38 pagesLambda Calculus CLCDan Mark Pidor BagsicanNo ratings yet
- BE Physics-Solution PDFDocument235 pagesBE Physics-Solution PDFRajeev PaudelNo ratings yet
- Courses Offered in Spring 2015Document3 pagesCourses Offered in Spring 2015Mohammed Afzal AsifNo ratings yet
- Fractions Math 6 DLP 1Document13 pagesFractions Math 6 DLP 1Dess DotimasNo ratings yet
- Middle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Document56 pagesMiddle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Mohamed987No ratings yet
- ECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibDocument19 pagesECE - 1551 Digital Logic Lecture 15: Combinational Circuits: Assistant Prof. Fareena SaqibAll aboutNo ratings yet
- IASDocument3 pagesIASankit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Language and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersDocument1,184 pagesLanguage and The Pursuit of Hap - Chalmers BrothersGeorge Adrian Oprea100% (2)
- RBI Assistant Prelims 14 Feb 2020 Memory Based Paper (English)Document27 pagesRBI Assistant Prelims 14 Feb 2020 Memory Based Paper (English)AbhiNo ratings yet
- Borland C++Document3 pagesBorland C++Sanjay SethNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of Depressurization Rate During Blowdown Based On Lumped Model AnalysisDocument11 pagesNumerical Study of Depressurization Rate During Blowdown Based On Lumped Model AnalysisamitNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Document3 pagesPhysics Notes AJk 9th Class Chap6Khizer Tariq QureshiNo ratings yet
- Lyra Kate Mae P. Salvador BSA-1 MANSCI-446 Course Final RequirementDocument5 pagesLyra Kate Mae P. Salvador BSA-1 MANSCI-446 Course Final RequirementLyra Kate Mae SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Components of Emotional IntelligenceDocument5 pagesComponents of Emotional IntelligenceSteven AdongoNo ratings yet
- Ramana Cell: +91 7780263601 ABAP Consultant Email Id: Professional SummaryDocument4 pagesRamana Cell: +91 7780263601 ABAP Consultant Email Id: Professional SummaryraamanNo ratings yet