Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Highlights of The 2010 American Heart Association
Uploaded by
Anthony Salazar RodríguezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Highlights of The 2010 American Heart Association
Uploaded by
Anthony Salazar RodríguezCopyright:
Available Formats
Highlights of the 2010 American Heart Association
Guidelines for CPR & ECC
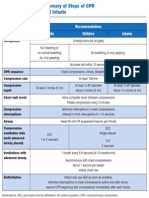
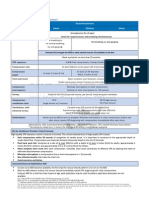
Summary of Key BLS Components for Adults, Children, and Infants* Recommendations Component Adults Children
Unresponsive (for all ages) Recognition No breathing or no normal breathing (ie, only gasping) No breathing or only gasping
Infants
No pulse palpated within 10 seconds for all ages (HCP only) CPR sequence Compression rate Compression depth At least 2 inches (5 cm) C-A-B At least 100/min At least AP diameter About 2 inches (5 cm) Allow complete recoil between compressions HCPs rotate compressors every 2 minutes Minimize interruptions in chest compressions Attempt to limit interrruptions to <10 seconds Head tiltchin lift (HCP suspected trauma: jaw thrust) 30:2 Single rescuer 15:2 2 HCP rescuers Compressions only 1 breath every 6-8 seconds (8-10 breaths/min) Ventilations with advanced airway (HCP) Asynchronous with chest compressions About 1 second per breath Visible chest rise Attach and use AED as soon as available. Minimize interruptions in chest compressions before and after shock; resume CPR beginning with compressions immediately after each shock. At least AP diameter About 1 inches (4 cm)
Chest wall recoil
Compression interruptions Airway Compression-to-ventilation ratio (until advanced airway placed) Ventilations: when rescuer untrained or trained and not proficient
30:2 1 or 2 rescuers
Defibrillation
Abbreviations: AED, automated external defibrillator; AP, anterior-posterior; CPR, cardiopulmonary resuscitation; HCP, healthcare provider. *Excluding the newly born, in whom the etiology of an arrest is nearly always asphyxial.
Reprinted from Highlights of the 2010 AHA Guidelines for CPR & ECC; http://static.heart.org/eccguidelines/guidelines-highlights.html; copyright 2010.
www.heart.org/cpr
2010 American Heart Association DS4309 11/10
You might also like
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandPediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Bls HandoutDocument1 pageBls HandoutjeffNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Healthcare Provider Summary of Steps of CPR For Adults, Children, and InfantsDocument1 pageAppendix: Healthcare Provider Summary of Steps of CPR For Adults, Children, and InfantsfjnNo ratings yet
- BLS SummaryDocument2 pagesBLS Summaryreyes markNo ratings yet
- Pengantar SL CPRDocument19 pagesPengantar SL CPRHana SinurayaNo ratings yet
- BLS AlgorithmDocument9 pagesBLS AlgorithmDr VJ GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Abdul QodirDocument39 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Abdul QodirDessy Christiani Part IINo ratings yet
- 2021.06.26 L6. Resuscitation Management in Operating Theatre - Ms. Carmen LUIDocument71 pages2021.06.26 L6. Resuscitation Management in Operating Theatre - Ms. Carmen LUIElaine LeeNo ratings yet
- AHA CPR Guidelines-AdultDocument7 pagesAHA CPR Guidelines-Adultr_ayuNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Provider CAB of CPR Helpful HintsDocument2 pagesHealthcare Provider CAB of CPR Helpful HintsDarrell BrightNo ratings yet
- BLS 2010 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesBLS 2010 GuidelinesArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association: ACLS 2010Document9 pagesAmerican Heart Association: ACLS 2010I Gede AdityaNo ratings yet
- AclsDocument44 pagesAclsArchana GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Provider Summary of Steps of CPR For Adults, Children and InfantsDocument2 pagesHealthcare Provider Summary of Steps of CPR For Adults, Children and InfantsMARK LENAND ESPIRITUNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Yohanes Rudijanto, DR., SpanDocument63 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Yohanes Rudijanto, DR., SpanPadrepio R RahadiNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument31 pagesCPRMilda InayahNo ratings yet
- ALS Adult and ChildDocument1 pageALS Adult and ChildPiet Pogen PoelNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocument50 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightNo ratings yet
- BLS Guidelines 2015Document9 pagesBLS Guidelines 2015Avicenna Zahara BungaNo ratings yet
- BLS Aha - 2010 Refresher Course For Junior Clerks 2015Document28 pagesBLS Aha - 2010 Refresher Course For Junior Clerks 2015Kalpana ShahNo ratings yet
- BLS With MCQDocument37 pagesBLS With MCQKIMS quality100% (1)
- American Heart Association: Precourse Review MaterialsDocument10 pagesAmerican Heart Association: Precourse Review MaterialsmedmnhmNo ratings yet
- ACLS PresentationDocument79 pagesACLS PresentationHumaira YasserNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support: Dr. Aatir Fayyaz Nishtar Medical University MultanDocument42 pagesBasic Life Support: Dr. Aatir Fayyaz Nishtar Medical University MultanShahzeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Ompressions: Irway: Reathing:: Center For Professional Practice of Nursing CPR Guidelines For Health-Care ProvidersDocument11 pagesOmpressions: Irway: Reathing:: Center For Professional Practice of Nursing CPR Guidelines For Health-Care Providersmonir61No ratings yet
- CPR LectureDocument9 pagesCPR LecturejacnpoyNo ratings yet
- AlsalgoDocument1 pageAlsalgoIsuru RupasinghaNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument3 pagesBasic Life Supportjc_sibal13No ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation For AdultsDocument26 pagesCardio Pulmonary Resuscitation For AdultsShiv ShahNo ratings yet
- BLS Study Guide 2010Document2 pagesBLS Study Guide 2010sofiaserrano9218No ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation 2010: Djayanti SariDocument26 pagesCardio Pulmonary Resuscitation 2010: Djayanti SariAlessandro AlfieriNo ratings yet
- BLS, ACLS DR Dagmawi FebrauruyDocument33 pagesBLS, ACLS DR Dagmawi FebrauruyTemesgen GeletaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary R Ry Resuscitation 2010Document26 pagesCardio Pulmonary R Ry Resuscitation 2010Fatahillah NazarNo ratings yet
- 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines For Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular CareDocument28 pages2010 American Heart Association Guidelines For Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular CareRay SadisNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonar Y ResuscitationDocument34 pagesCardiopulmonar Y ResuscitationRatuSitiKhadijahSarahNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Unresponsive?Document1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support: Unresponsive?gio477No ratings yet
- Adult Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)Document1 pageAdult Advanced Life Support: Resuscitation Council (UK)gio477No ratings yet
- CPR PFTDocument19 pagesCPR PFTmusiyamahNo ratings yet
- CPR LectureDocument10 pagesCPR LecturejacnpoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support: Based On Guidelines byDocument28 pagesBasic Life Support: Based On Guidelines byshrithyNo ratings yet
- Materi Dan Checklist BLSDocument9 pagesMateri Dan Checklist BLSZo RoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support (Adult Basic Life Support) : RS Santa Maria Pekanbaru 2015Document38 pagesBasic Life Support (Adult Basic Life Support) : RS Santa Maria Pekanbaru 2015christin nataliaNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Document18 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Savita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- BLS (Basic Life Support)Document10 pagesBLS (Basic Life Support)harpreetNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument27 pagesBasic Life SupportPisay Shehannah Grail Medina100% (1)
- Perkembanga CPR: Support Ini Terdiri Dari Beberapa Elemen: Penyelamatan Pernapasan (Juga Dikenal DenganDocument4 pagesPerkembanga CPR: Support Ini Terdiri Dari Beberapa Elemen: Penyelamatan Pernapasan (Juga Dikenal DenganElisabeth Martha SihombingNo ratings yet
- BLS (Bantuan Hidup Dasar)Document42 pagesBLS (Bantuan Hidup Dasar)Sam YahyaNo ratings yet
- Masuri Prim AjutorDocument143 pagesMasuri Prim AjutorHojbota Otilia Constantina100% (1)
- American Hearts Association (Aha) / European Resuscitation Council (Erc)Document15 pagesAmerican Hearts Association (Aha) / European Resuscitation Council (Erc)Elsa AlamandaNo ratings yet
- American Hearts Association (Aha) / European Resuscitation Council (Erc)Document15 pagesAmerican Hearts Association (Aha) / European Resuscitation Council (Erc)safiraNo ratings yet
- BHD PediatriDocument84 pagesBHD PediatriDian Pratiwi BurnamaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Resusitasi Jantung Paru: BY: Ns. Anita Dwi Ariyani, S.Kep,.M.KepDocument31 pagesKonsep Resusitasi Jantung Paru: BY: Ns. Anita Dwi Ariyani, S.Kep,.M.KepFa An RaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Basic Life SupportDocument30 pagesPediatric Basic Life Supportkariuki90406978No ratings yet
- Table of Comparison On Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For Adul1Document1 pageTable of Comparison On Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation For Adul1Luigi GeduqueNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation 2015Document31 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation 2015Clarissa Maya TjahjosarwonoNo ratings yet
- Updates American Heart Association Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation GuidelineDocument32 pagesUpdates American Heart Association Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation GuidelineramzishindiNo ratings yet
- A (ACLS) - 2015: Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument52 pagesA (ACLS) - 2015: Dvanced Cardiac Life SupportNajmussaqibNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Cardiac ArrestDocument19 pagesIntraoperative Cardiac ArrestMark Andrew CruzNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Provider Basic Life Support CPR Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandHealthcare Provider Basic Life Support CPR Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Hematuria:: Sunil Agrawal 1 Year MD Pediatrics, IOMDocument42 pagesApproach To A Child With Hematuria:: Sunil Agrawal 1 Year MD Pediatrics, IOMAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Hematuria:: Sunil Agrawal 1 Year MD Pediatrics, IOMDocument42 pagesApproach To A Child With Hematuria:: Sunil Agrawal 1 Year MD Pediatrics, IOMAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Antidesmoglein 3Document5 pagesAntidesmoglein 3Anthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- adasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdDocument38 pagesadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdadasdasdAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Factors That Predict Poor Clinical Course Among Patients Hospitalized With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument6 pagesFactors That Predict Poor Clinical Course Among Patients Hospitalized With Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa1312173 AppendixDocument14 pagesNejmoa1312173 AppendixAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Pelvic DiseaseDocument17 pagesInflammatory Pelvic DiseaseAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Kalyanakrishnan Ramakrishnan, MD, Frcse, and Robert C. Salinas, MDDocument8 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: Kalyanakrishnan Ramakrishnan, MD, Frcse, and Robert C. Salinas, MDMonika WerdiningsihNo ratings yet
- Summit 2 WB Unit 5Document12 pagesSummit 2 WB Unit 5Anthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Crit Drugs TinyDocument1 pageCrit Drugs TinyAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Scalable NetworkingDocument79 pagesScalable NetworkingAnthony Salazar RodríguezNo ratings yet