100% found this document useful (9 votes)
10K views49 pagesUnderstanding Competency Models
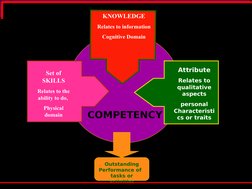
A competency model is a list of the knowledge, skills, behaviors, and attributes required for outstanding performance in a specific role. It is developed by analyzing the behaviors of top performers in that role. Competency models help organizations align HR systems like recruitment, performance management, training, development, and compensation to strategic goals. They also provide clear performance standards and development areas for employees. Developing a competency model involves gathering data on key jobs, identifying competencies exhibited by top performers, defining behaviors for each competency, and validating the final model.
Uploaded by
kamdicaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (9 votes)
10K views49 pagesUnderstanding Competency Models
A competency model is a list of the knowledge, skills, behaviors, and attributes required for outstanding performance in a specific role. It is developed by analyzing the behaviors of top performers in that role. Competency models help organizations align HR systems like recruitment, performance management, training, development, and compensation to strategic goals. They also provide clear performance standards and development areas for employees. Developing a competency model involves gathering data on key jobs, identifying competencies exhibited by top performers, defining behaviors for each competency, and validating the final model.
Uploaded by
kamdicaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction: Introduction to the presentation on competency approach and the resource site.
- Understanding Competency: Defines the concept of competency in the context of human resources and its importance.
- Competency Inputs: Describes competencies as clusters of knowledge, skills, and attitudes affecting performance.
- Behavioral Indicators of Competency: Outlines behaviors that indicate competencies in a workplace setting.
- Example of a Competency: Provides a specific example of a competency, focusing on analytical thinking.
- Competency Model: Explains the framework of a competency model and its components.
- HR Systems Alignment: Discusses the integration of competencies within HR systems for aligning strategies.
- Competency-Based Applications: Explores various applications of competency-based approaches in recruitment, appraisal, training, and development.
- Methodology in Competency Modeling: Presents methodologies for competency model building, including steps and data collection methods.
- Competency Mapping Process: Discusses the process of designing a competency mapping questionnaire and its factors.
- Final Thoughts: Summarizes the processes of data collection, drafting, and finalizing competencies.