Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cuprate Addition
Uploaded by
Shyam BhaktaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cuprate Addition
Uploaded by
Shyam BhaktaCopyright:
Available Formats
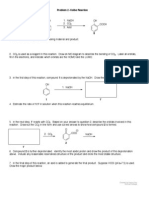
Problem 5- Dialkylcuprate Additions Cu Li O
1. 2. H2O
1. How many conjugated p-orbitals are there in the starting material? How many in the product?
2. Indicate the bond dipoles present in the lithium-copper reagent used in this reaction. Cu Li 3. This reagent acts as a nucleophile in this reaction. Draw the products of the reaction shown below. Hint: The lithium breaks its ionic interaction with copper and forms a new ionic interaction.
O Li Cu Intermediate 4. The water is used as an acid to give the nal product. Use curved arrows to propose a mechanism for product formation from the intermediate you drew above.
Intermediate 5. Construct six Newman projects to show the relative energy levels of the product as the bond shown in bold is rotated in 60 degree increments. Plot the energies on a graph.
Relative Energy
Degrees of Rotation
Created by Hanna Key Grinnell College
6. Suppose this cuprate-lithium reagent is used in this reaction instead. Draw the product of the reaction.
6. Suppose this cuprate-lithium reagent is used in this reaction instead. Draw the product of the reaction.
1. 2. H2O
Cu Li
7. Construct six Newman projects to show the relative energy levels of the product as the same bond as in the previous product is rotated in 60 degree increments.
8. Onto the axes below, copy your plot from the original product. Then, plot the relative energies of the six conformations of the new product. In each case, decide whether the original or new product would be more highly strained.
Relative Energy
Degrees of Rotation 9. For the following possible products of this reaction type, determine the longest carbon chain and provide a name for the circled branched substituent.
O O O
You might also like
- Metal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreFrom EverandMetal Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and MoreArmin de MeijereNo ratings yet
- Mcmurry Oc8e Ev Ch09Document17 pagesMcmurry Oc8e Ev Ch09MúslimÄhIslamNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis - 2: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Organic SynthesisFrom EverandOrganic Synthesis - 2: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Organic SynthesisS. SarelNo ratings yet
- WK 2-1 Energy Diagram and Arrow Pushing Mechanism Jan 16Document40 pagesWK 2-1 Energy Diagram and Arrow Pushing Mechanism Jan 16cerelia.dkuNo ratings yet
- Research Statement 05Document4 pagesResearch Statement 05ram6025No ratings yet
- Post Lecture Activity 2 - Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesPost Lecture Activity 2 - Acids and BasesSophia Aliyah Miel MacabeoNo ratings yet
- CHP 6 Class Review ChemDocument15 pagesCHP 6 Class Review ChemNatalie RussellNo ratings yet
- Exp-3 Schiff Base - Metal ComplexDocument5 pagesExp-3 Schiff Base - Metal ComplexRahulSureshNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Equilibrium and ConcentrationDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Equilibrium and ConcentrationEmma AssaadNo ratings yet
- 07 - Ws 3 With SmoresDocument9 pages07 - Ws 3 With Smorestracie_schroederNo ratings yet
- Ch08 LeeDocument39 pagesCh08 LeeOrnella Arnia FlorensiaNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Assessment Period 1 WWW-EBI 1Document6 pagesYear 12 Assessment Period 1 WWW-EBI 13t4e5yuezryhNo ratings yet
- Limiting ReagentDocument6 pagesLimiting ReagentdsaafaNo ratings yet
- Wphs Chemistry Unit 5 Packet Stoichiometry: Bergmann-SamsDocument56 pagesWphs Chemistry Unit 5 Packet Stoichiometry: Bergmann-SamsShin SasakiNo ratings yet
- FCJJ-16 Stoichiometry CH StudentDocument5 pagesFCJJ-16 Stoichiometry CH StudentHermes Polanco J.No ratings yet
- Public Exam Question Bank for ChemistryDocument7 pagesPublic Exam Question Bank for ChemistrybiopharmacyNo ratings yet
- KWINORGCHEM-PROBLEM SET 1 - THERMODYNAMICS AND ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument1 pageKWINORGCHEM-PROBLEM SET 1 - THERMODYNAMICS AND ELECTROCHEMISTRYmaeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sure Shot QuestionsDocument57 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sure Shot Questionsconnectrishabh666No ratings yet
- 6.07 Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument5 pages6.07 Balancing Chemical Equationsitz123.johnNo ratings yet
- Retrosynthetic Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesRetrosynthetic Analysis PDFNoleNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Dated 10 September 2018 Instructions: Write Your Answers in This Bundle Itself. You Can Use Extra Sheets For Rough Work ButDocument11 pagesQuiz 1 Dated 10 September 2018 Instructions: Write Your Answers in This Bundle Itself. You Can Use Extra Sheets For Rough Work ButSGuruVikneshNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?Document49 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Physical Change and A Chemical Reaction?nkznghidsnidvNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Haloalkanes PDFDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Haloalkanes PDFPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell EfficiencyDocument13 pagesFuel Cell EfficiencySashideran ThilagesuaryNo ratings yet
- Braxton Limiting Reactant LabDocument6 pagesBraxton Limiting Reactant Labapi-292541816No ratings yet
- Chemistry Capsule 30Document32 pagesChemistry Capsule 30Rohith SNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Reaction Yields: Limiting ReactantDocument8 pages4.4 Reaction Yields: Limiting ReactantJohn Lloyd LangcoNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Optimization of an Existing Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation ReactorDocument5 pagesSimulation and Optimization of an Existing Ethylbenzene Dehydrogenation ReactorÉrico CavalcantiNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Plustwo Most Important 137 Questions Answers 2023Document18 pagesHsslive Plustwo Most Important 137 Questions Answers 2023Janet RoyNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent C 11-3-14Document8 pagesLimiting Reagent C 11-3-14Filarius Peter UsopNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Capsule 30.DocxDocument31 pagesChemistry Capsule 30.Docxcarsk403No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9JajejijojuNo ratings yet
- Multiple Reactions in Series and ParallelDocument22 pagesMultiple Reactions in Series and ParallelMonil KoradiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations Made EasyDocument6 pagesChemical Equations Made EasydongwonNo ratings yet
- Diels Alder LabDocument8 pagesDiels Alder Labfatevilcow0% (1)
- CHAPTER 7 - HaloalkanesDocument42 pagesCHAPTER 7 - HaloalkanesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Principles (65 Items)Document3 pagesPhysical and Chemical Principles (65 Items)Daphne Lianne DegayNo ratings yet
- SCH 4U Energy Test: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument9 pagesSCH 4U Energy Test: Identify The Letter of The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionalexandra SmithNo ratings yet
- Additions Practice 2021Document5 pagesAdditions Practice 2021Hannah LiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (65 itemsDocument3 pagesPHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (65 itemszaiNo ratings yet
- Isaac Heredia - 4.3 - Molecular - Models - For - Potato - Photosynthesis - WorksheetDocument2 pagesIsaac Heredia - 4.3 - Molecular - Models - For - Potato - Photosynthesis - WorksheetIsaac HerediaNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document42 pagesCH 07Samantha Louise MondonedoNo ratings yet
- ACJC H2 Prelim Paper 3 Question PaperDocument13 pagesACJC H2 Prelim Paper 3 Question PaperMelisa YeapNo ratings yet
- 2022 Ke Kelekema Elimination Round Questions 1 PDFDocument5 pages2022 Ke Kelekema Elimination Round Questions 1 PDFXave BajetNo ratings yet
- G10 Manual (Phy Che)Document15 pagesG10 Manual (Phy Che)nadheeranewNo ratings yet
- Battery Storage for Grid-Scale EnergyDocument3 pagesBattery Storage for Grid-Scale EnergySarbajitMannaNo ratings yet
- IBO Worksheet ChemistryDocument26 pagesIBO Worksheet ChemistryAarav PatelNo ratings yet
- A Method of Atomic Transformation, I: Peter GrandicsDocument6 pagesA Method of Atomic Transformation, I: Peter GrandicsTony GaryNo ratings yet
- Checkup On Chapter 9: Questions Revision ChecklistDocument2 pagesCheckup On Chapter 9: Questions Revision ChecklistShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Chemistry IAL EdexcelDocument7 pagesDefinitions - Chemistry IAL EdexcelPanagiotis ScordisNo ratings yet
- Fu Catalyst 2Document9 pagesFu Catalyst 2Rahn NaNo ratings yet
- Hybridization 1Document37 pagesHybridization 1Anzari MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Reactions Alkenes & AlkynesDocument62 pagesReactions Alkenes & AlkynesDeniseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases: Short Answer Exhibit 2-1Document7 pagesChapter 2-Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases: Short Answer Exhibit 2-1CarmenPalaciosNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1St Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmisstepmonocarp1b69100% (7)
- Alkyl Halides PDFDocument66 pagesAlkyl Halides PDFAhmed Sideeg83% (6)
- + Highly Active Ni-Wa1203 Catalyst For Upgrading Unconventional FeedstocksDocument4 pages+ Highly Active Ni-Wa1203 Catalyst For Upgrading Unconventional FeedstocksElkin Andrés Gómez MejíaNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter Chemical Equilibrium Short QuestionsDocument6 pages8 Chapter Chemical Equilibrium Short QuestionsUmair MirNo ratings yet
- Operation A Tube Wall Methanation Reactor: Literature CitedDocument7 pagesOperation A Tube Wall Methanation Reactor: Literature CitedChemsys SunnyNo ratings yet
- Homework 16-1 Modern ChemistryDocument8 pagesHomework 16-1 Modern Chemistryg3hqgges100% (2)
- Organic Compound Separation Using Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocument8 pagesOrganic Compound Separation Using Liquid-Liquid ExtractionShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Universalism and Animal CultureDocument27 pagesUniversalism and Animal CultureShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Separation of Organic Compounds Using Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocument5 pagesSeparation of Organic Compounds Using Liquid-Liquid ExtractionShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- ChemE 140 Design Project 1Document5 pagesChemE 140 Design Project 1Shyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- RICHARD DAWKINS - Religion of ScienceDocument23 pagesRICHARD DAWKINS - Religion of Scienceanon-991322100% (11)
- A Scientist's ViewDocument1 pageA Scientist's ViewShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- ChemE 140 Design Project 2Document4 pagesChemE 140 Design Project 2Shyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Flash ChromatographyDocument3 pagesFlash ChromatographyHanyu ZhangNo ratings yet
- Proto-Indo-European Etymological DictionaryDocument283 pagesProto-Indo-European Etymological DictionarywoodwyseNo ratings yet
- Don't Turn Your Back On Science - An Open LetterDocument15 pagesDon't Turn Your Back On Science - An Open LetterShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Acidic PropertiesDocument1 pageAmino Acid Acidic PropertiesShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 4 KeyDocument3 pagesNMR Worksheet 4 KeyShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Tips For StereochemistryDocument1 pageTips For StereochemistryShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- A Scientist's ViewDocument1 pageA Scientist's ViewShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- All Our YesterdaysDocument4 pagesAll Our YesterdaysShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Review Reactivity of Functional Groups and ReagentsDocument1 pageReview Reactivity of Functional Groups and ReagentsShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Control: Reaction ADocument2 pagesThermodynamic and Kinetic Control: Reaction AShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 4 CorrectionsDocument1 pageNMR Worksheet 4 CorrectionsShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 1 CorrectionsDocument1 pageNMR Worksheet 1 CorrectionsShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 1 KeyDocument2 pagesNMR Worksheet 1 KeyShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet Analysis and PredictionsDocument14 pagesNMR Worksheet Analysis and PredictionsShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 2Document5 pagesNMR Worksheet 2Shyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 2 KeyDocument4 pagesNMR Worksheet 2 KeyShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Properties & Reactions of AlkenesDocument2 pagesProperties & Reactions of AlkenesShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- NMR Worksheet 1Document2 pagesNMR Worksheet 1Shyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Grignard Reaction Formal Report InstructionsDocument2 pagesGrignard Reaction Formal Report InstructionsShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Edman Degradation IIDocument1 pageEdman Degradation IIShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Common Arrow Pushing MistakesDocument1 pageCommon Arrow Pushing MistakesShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2-Kolbe Reaction: Created by Hanna Key Grinnell CollegeDocument1 pageProblem 2-Kolbe Reaction: Created by Hanna Key Grinnell CollegeShyam BhaktaNo ratings yet