Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metal Forming Processes-Mmft
Metal Forming Processes-Mmft
Uploaded by
Onkar KakadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metal Forming Processes-Mmft
Metal Forming Processes-Mmft
Uploaded by
Onkar KakadCopyright:
Available Formats
Metal Forming Processes
Metal Forming Processes
Dr.
Dr.
Pulak
Pulak
M.
M.
Pandey
Pandey
http://
http://
paniit.iitd.ac.in/~pmpandey
paniit.iitd.ac.in/~pmpandey
Introduction
Introduction
Practically all metals, which are not used in cast form are
Practically all metals, which are not used in cast form are
reduced to some standard shapes for subsequent processing.
reduced to some standard shapes for subsequent processing.
Manufacturing companies producing metals supply metals
Manufacturing companies producing metals supply metals
in form of ingots which are obtained by casting liquid metal
in form of ingots which are obtained by casting liquid metal
into a square cross section.
into a square cross section.
Slab (500 Slab (500- -1800 mm wide and 50 1800 mm wide and 50- -300 mm thick) 300 mm thick)
Billets (40 to 150 sq mm) Billets (40 to 150 sq mm)
Blooms (150 to 400 sq mm) Blooms (150 to 400 sq mm)
Sometimes continuous casting methods are also used to cast
Sometimes continuous casting methods are also used to cast
the liquid metal into slabs, billets or blooms.
the liquid metal into slabs, billets or blooms.
These shapes are further processed through hot rolling,
These shapes are further processed through hot rolling,
forging or extrusion, to produce materials in standard form
forging or extrusion, to produce materials in standard form
such as plates, sheets, rods, tubes and structural sections.
such as plates, sheets, rods, tubes and structural sections.
Sequence of operations for obtaining
Sequence of operations for obtaining
different shapes
different shapes
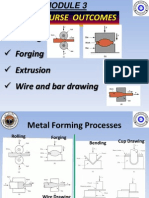
Primary Metal Forming Processes
Primary Metal Forming Processes
Rolling
Rolling
Forging
Forging
Extrusion
Extrusion
Tube and wire drawing
Tube and wire drawing
and Deep drawing
and Deep drawing
Although Punching and Blanking operations are
Although Punching and Blanking operations are
not metal forming processes however these will be
not metal forming processes however these will be
covered due to similarity with deep drawing
covered due to similarity with deep drawing
process.
process.
Rolling
Rolling
Change in grains structure in rolling
Change in grains structure in rolling
Salient points about rolling
Salient points about rolling
Rolling is the most extensively used metal forming
Rolling is the most extensively used metal forming
process and its share is roughly 90%
process and its share is roughly 90%
The material to be rolled is drawn by means of friction
The material to be rolled is drawn by means of friction
into the two revolving roll gap
into the two revolving roll gap
The compressive forces applied by the rolls reduce the
The compressive forces applied by the rolls reduce the
thickness of the material or changes its cross sectional
thickness of the material or changes its cross sectional
area
area
The geometry of the product depend on the contour of
The geometry of the product depend on the contour of
the roll gap
the roll gap
Roll materials are cast iron, cast steel and forged steel
Roll materials are cast iron, cast steel and forged steel
because of high strength and wear resistance
because of high strength and wear resistance
requirements
requirements
Hot rolls are generally rough so that they can bite the
Hot rolls are generally rough so that they can bite the
work, and cold rolls are ground and polished for good
work, and cold rolls are ground and polished for good
finish
finish
In rolling the crystals get elongated in the rolling direction.
In rolling the crystals get elongated in the rolling direction.
In cold
In cold
rolling crystal more or less retain the elongated shape but in h
rolling crystal more or less retain the elongated shape but in h
ot
ot
rolling they start reforming after coming out from the deformati
rolling they start reforming after coming out from the deformati
on
on
zone
zone
The peripheral velocity of rolls at entry exceeds that of the
The peripheral velocity of rolls at entry exceeds that of the
strip, which is dragged in if the interface friction is high
strip, which is dragged in if the interface friction is high
enough.
enough.
In the deformation zone the thickness of the strip gets reduced
In the deformation zone the thickness of the strip gets reduced
and it elongates. This increases the linear speed of the at the
and it elongates. This increases the linear speed of the at the
exit.
exit.
Thus there exist a neutral point where roll speed and strip
Thus there exist a neutral point where roll speed and strip
speeds are equal. At this point the direction of the friction
speeds are equal. At this point the direction of the friction
reverses.
reverses.
When the angle of contact
When the angle of contact
exceeds the friction angle
exceeds the friction angle
the
the
rolls cannot draw fresh strip
rolls cannot draw fresh strip
Roll torque, power etc. increase with increase in roll work
Roll torque, power etc. increase with increase in roll work
contact length or roll radius
contact length or roll radius
Pressure during rolling
Pressure during rolling
Typical pressure variation along
the contact length in flat rolling.
The peak pressure is located at
the neutral point. The area
beneath the curve, represents
roll force.
Friction in rolling: It depends on lubrication,
work material and also on the temperature. In
cold rolling the value of coefficient of friction
is around 0.1 and in warm working it is
around 0.2. In hot rolling it is around 0.4. In
hot rolling sticking friction condition is also
seen and then friction coefficient is observed
up to 0.7. In sticking the hot wok surface
adheres to roll and thus the central part of the
strip undergoes with a severe deformation.
Roll passes to get a 12 mm rod
Roll passes to get a 12 mm rod
from 100 x 100 mm billet
from 100 x 100 mm billet
Roll
Roll
configurations
configurations
in rolling mills
in rolling mills
Two
Two
-
-
high and three
high and three
-
-
high mills are generally
high mills are generally
used for initial and intermediate passes during
used for initial and intermediate passes during
hot rolling, while four
hot rolling, while four
-
-
high and cluster mills
high and cluster mills
are used for final passes.
are used for final passes.
Last two arrangements are preferred for cold
Last two arrangements are preferred for cold
rolling because roll in these configurations are
rolling because roll in these configurations are
supported by back
supported by back
-
-
up rolls which minimize
up rolls which minimize
the deflections and produce better tolerances.
the deflections and produce better tolerances.
Various Roll Configurations (a) Two Various Roll Configurations (a) Two- -high (b) Three high (b) Three- -high high
(c) Four (c) Four- -high (d) Cluster mill (e) Tandem mill high (d) Cluster mill (e) Tandem mill
back
Other deformation processes related to rolling
Other deformation processes related to rolling
Forging
Forging
Forging is perhaps oldest metal working process and was
Forging is perhaps oldest metal working process and was
known even during prehistoric days when metallic tools
known even during prehistoric days when metallic tools
were made by heating and hammering.
were made by heating and hammering.
Forging is basically involves plastic deformation of
Forging is basically involves plastic deformation of
material between two dies to achieve desired
material between two dies to achieve desired
configuration. Depending upon complexity of the part
configuration. Depending upon complexity of the part
forging is carried out as
forging is carried out as
open die forging and closed die
open die forging and closed die
forging.
forging.
In open die forging, the metal is compressed by repeated
In open die forging, the metal is compressed by repeated
blows by a mechanical hammer and shape is manipulated
blows by a mechanical hammer and shape is manipulated
manually.
manually.
In closed die forging, the desired configuration is
In closed die forging, the desired configuration is
obtained by squeezing the
obtained by squeezing the
workpiece
workpiece
between two shaped
between two shaped
and closed dies.
and closed dies.
On squeezing the die cavity gets completely filled and
On squeezing the die cavity gets completely filled and
excess material comes out around the periphery of the
excess material comes out around the periphery of the
die as
die as
flash
flash
which is later trimmed.
which is later trimmed.
Press forging and drop forging are two popular
Press forging and drop forging are two popular
methods in closed die forging.
methods in closed die forging.
In press forging the metal is squeezed slowly by a
In press forging the metal is squeezed slowly by a
hydraulic or mechanical press and component is
hydraulic or mechanical press and component is
produced in a single closing of die, hence the
produced in a single closing of die, hence the
dimensional accuracy is much better than drop
dimensional accuracy is much better than drop
forging.
forging.
Both open and closed die forging processes are carried
Both open and closed die forging processes are carried
out in hot as well as in cold state.
out in hot as well as in cold state.
In forging
In forging
favorable grain orientation
favorable grain orientation
of metal is
of metal is
obtained
obtained
Open and closed die forging
Open and closed die forging
back
Grain orientation in forging
Grain orientation in forging
Forging Machining
back
Barreling in
Barreling in
forging
forging
Flash less forging or
Flash less forging or
precision forging
precision forging
Self reading in forging
Self reading in forging
Fullering
Fullering
Edging
Edging
Cogging
Cogging
Upsetting
Upsetting
Heading
Heading
Swaging
Swaging
Radial forging etc.
Radial forging etc.
Go through any book on
Manufacturing processes
by Kalpakjian, Groover
or Degarmo
Extrusion
Extrusion
It is a relatively new process and its commercial
It is a relatively new process and its commercial
exploitation started early in the nineteenth century with the
exploitation started early in the nineteenth century with the
extrusion of lead pipes. Extrusion of steels became
extrusion of lead pipes. Extrusion of steels became
possible only after 1930 when extrusion chambers could
possible only after 1930 when extrusion chambers could
be designed to withstand high temperature and pressure.
be designed to withstand high temperature and pressure.
In extrusion, the material is compressed in a chamber and
In extrusion, the material is compressed in a chamber and
the deformed material is forced to flow through the die.
the deformed material is forced to flow through the die.
The die opening corresponds to the cross section of the
The die opening corresponds to the cross section of the
required product.
required product.
It is basically a hot working process, however, for softer
It is basically a hot working process, however, for softer
materials cold extrusion is also performed.
materials cold extrusion is also performed.
Direct and Indirect Extrusion
Direct and Indirect Extrusion
In direct extrusion metal flows in the In direct extrusion metal flows in the
same direction as that of the ram. same direction as that of the ram.
Because of the relative motion between Because of the relative motion between
the heated billet and the chamber walls, the heated billet and the chamber walls,
friction is severe and is reduced by using friction is severe and is reduced by using
molten glass as a lubricant in case of molten glass as a lubricant in case of
steels at higher temperatures. At lower steels at higher temperatures. At lower
temperatures, oils with graphite powder temperatures, oils with graphite powder
is used for lubrication. is used for lubrication.
In indirect extrusion process metal In indirect extrusion process metal
flows in the opposite direction of the flows in the opposite direction of the
ram. It is more efficient since it reduces ram. It is more efficient since it reduces
friction losses considerably. The process, friction losses considerably. The process,
however, is not used extensively because however, is not used extensively because
it restricts the length of the extruded it restricts the length of the extruded
component. component.
Impact Extrusion
Impact Extrusion
It is similar to indirect It is similar to indirect
extrusion. Here the punch extrusion. Here the punch
descends rapidly on to the descends rapidly on to the
blank which gets indirectly blank which gets indirectly
extruded on to the punch and extruded on to the punch and
to give a tubular section. The to give a tubular section. The
length of the tube formed is length of the tube formed is
controlled by the amount of controlled by the amount of
metal in the slug or by the metal in the slug or by the
blank thickness. Collapsible blank thickness. Collapsible
tubes for pastes are extruded tubes for pastes are extruded
by this method. by this method.
Hydrostatic Extrusion
Hydrostatic Extrusion
In this process the In this process the
friction between friction between
container wall and billet container wall and billet
is eliminated, however, is eliminated, however,
this process has got this process has got
limited applications in limited applications in
industry due to industry due to
specialized equipment & specialized equipment &
tooling and low tooling and low
production rate due to production rate due to
high set up time. high set up time.
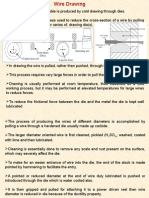
Drawing
Drawing
Large quantities of wires, rods, Large quantities of wires, rods,
tubes and other sections are tubes and other sections are
produced by drawing process produced by drawing process
which is basically a cold which is basically a cold
working process. In this working process. In this
process the material is pulled process the material is pulled
through a die in order to through a die in order to
reduce it to the desired shape reduce it to the desired shape
and size. and size.
In a typical wire drawing In a typical wire drawing
operation, once end of the wire operation, once end of the wire
is reduced and passed through is reduced and passed through
the opening of the die, gripped the opening of the die, gripped
and pulled to reduce its and pulled to reduce its
diameter. diameter.
By successive drawing operation through dies of
By successive drawing operation through dies of
reducing diameter the wire can be reduced to a very
reducing diameter the wire can be reduced to a very
small diameter.
small diameter.
Annealing before each drawing operation permits
Annealing before each drawing operation permits
large area reduction.
large area reduction.
Tungsten Carbide dies are used to for drawing hard
Tungsten Carbide dies are used to for drawing hard
wires, and diamond dies is the choice for fine wires.
wires, and diamond dies is the choice for fine wires.
Tube drawing
Tube drawing
Tube drawing is also similar to wire drawing, except that a mand Tube drawing is also similar to wire drawing, except that a mandrel rel
of appropriate diameter is required to form the internal hole. of appropriate diameter is required to form the internal hole.
Here two arrangements are shown in figure (a) with a floating pl Here two arrangements are shown in figure (a) with a floating plug ug
and (b) with a moving mandrel and (b) with a moving mandrel
The process reduces the diameter and thickness of the tube. The process reduces the diameter and thickness of the tube.
Deep Drawing
Deep Drawing
This operation is
This operation is
extensively used to for
extensively used to for
making cylindrical
making cylindrical
shaped parts such as cups,
shaped parts such as cups,
shells, etc from sheet
shells, etc from sheet
metal.
metal.
As the blank is drawn into
As the blank is drawn into
the die cavity
the die cavity
compressive stress
compressive stress
is set
is set
up around the flange and
up around the flange and
it tends to
it tends to
wrinkle or
wrinkle or
buckle
buckle
the flange.
the flange.
Deformation of
Deformation of
workpiece
workpiece
during punch travel
during punch travel
Back
Defects in drawing
Defects in drawing
(a)Wrinkling in the flange or (b) in the wall (c) tearing, (a)Wrinkling in the flange or (b) in the wall (c) tearing,
(d) (d) earing earing, (e) surface scratches , (e) surface scratches
The effect of wrinkling and buckling can be seen from The effect of wrinkling and buckling can be seen from
the way a trapezoid on the outer surface of the blank is the way a trapezoid on the outer surface of the blank is
stretched in one direction and compressed in another stretched in one direction and compressed in another
direction to become a rectangle on the cup drawn. direction to become a rectangle on the cup drawn.
Wrinkling and buckling is avoided by applying a
Wrinkling and buckling is avoided by applying a
blank holder force through a blank holder.
blank holder force through a blank holder.
Blank holder force increases friction and hence the
Blank holder force increases friction and hence the
required punch load. Therefore, blank holder force
required punch load. Therefore, blank holder force
should be just enough to prevent wrinkling of the
should be just enough to prevent wrinkling of the
flange.
flange.
The edges of the punch and die are rounded for the
The edges of the punch and die are rounded for the
easy and smooth flow of metal.
easy and smooth flow of metal.
Sufficient clearance is also provided so that sheet
Sufficient clearance is also provided so that sheet
metal could be easily accommodated. In sufficient
metal could be easily accommodated. In sufficient
or large clearance may result into shearing and
or large clearance may result into shearing and
tearing of sheet.
tearing of sheet.
A drawn cup can be redrawn into a smaller cup
A drawn cup can be redrawn into a smaller cup
but it must be annealed to prevent failure.
but it must be annealed to prevent failure.
Punching and Blanking
Punching and Blanking
Punching and blanking Punching and blanking
operations are not metal operations are not metal
forming operations but are forming operations but are
discussed together with metal discussed together with metal
forming because of their forming because of their
similarity with deep drawing similarity with deep drawing
operation. operation.
Objective of punching and Objective of punching and
blanking is to remove blanking is to remove
material from the sheet metal material from the sheet metal
by causing rupture, the punch by causing rupture, the punch
and die corners are not and die corners are not
provided with the any radius. provided with the any radius.
Tool steel is the most Tool steel is the most
common material for tool and common material for tool and
die. Carbides are also used die. Carbides are also used
when high production is when high production is
needed. needed.
Comparison of metal forming processes
Comparison of metal forming processes
Self reading for your interest
Self reading for your interest
Defects in metal forming processes
Defects in metal forming processes
and their remedies. (use
and their remedies. (use
Kalpakjian
Kalpakjian
s
s
book)
book)
Defects in Rolling
Defects in Rolling
Defects in forging
Defects in forging
Defects in extrusion
Defects in extrusion
Surface cracking Surface cracking
piping piping
Internal cracking Internal cracking
You might also like
- Eyelet DrawingDocument49 pagesEyelet DrawingPra Vee33% (3)
- Soft Vs Hard ToolingDocument17 pagesSoft Vs Hard ToolingSurya Raghavendar100% (1)
- Progressive Die Design PDFDocument1 pageProgressive Die Design PDFSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Pattern AllowancesDocument19 pagesPattern Allowancesimamuddeen100% (3)
- Mechanical Working of MetalsDocument76 pagesMechanical Working of MetalsPradip GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tool DesignDocument48 pagesTool DesignPAVIN ENGGNo ratings yet
- Injection MouldingDocument12 pagesInjection MouldingBalasubramaniam MuruganNo ratings yet
- Forging Design ConsiderationsDocument81 pagesForging Design ConsiderationssuneethaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument26 pagesSheet Metal Workingvelavansu0% (1)
- Introduction To Flip ChipDocument58 pagesIntroduction To Flip ChipLakshman Yandapalli100% (1)
- My ForgingDocument20 pagesMy ForgingRam Janm SinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report HydroformingDocument11 pagesSeminar Report HydroformingAnuj Mandloi100% (2)
- ForgingDocument37 pagesForgingchris mushunjeNo ratings yet
- G2 DiscBrakeDocument33 pagesG2 DiscBrakesiddout2006No ratings yet
- ForgingDocument19 pagesForgingSarthakNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformation Processes in Metal Forming: Part 1-RollingDocument53 pagesBulk Deformation Processes in Metal Forming: Part 1-RollingFirdaus Muhamad RifqiNo ratings yet
- Broach and Form ToolDocument20 pagesBroach and Form Toolsonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Metal FormingDocument49 pagesMetal FormingtejasNo ratings yet
- Tool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghDocument15 pagesTool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Chemical - Mechanical PolishingDocument7 pagesChemical - Mechanical PolishingMorcos Nashaat Daneil100% (1)
- Extrusión-Rolling and Forming ProcessDocument50 pagesExtrusión-Rolling and Forming Processquiron2010No ratings yet
- Rolling Lab PresentationDocument35 pagesRolling Lab PresentationNareshNo ratings yet
- Study of Wear Characteristics of Hardfaced Layers Made by E430 and E410 Electrodes Using SMAW ProcessDocument8 pagesStudy of Wear Characteristics of Hardfaced Layers Made by E430 and E410 Electrodes Using SMAW ProcessIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Deep Drawing Literature ReviewDocument37 pagesDeep Drawing Literature ReviewS T100% (3)
- Metal FormingDocument40 pagesMetal Formingsreeeram100% (1)
- Extrusion and DrawingDocument19 pagesExtrusion and DrawingBatuhan YildizNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping Full Seminar Report 989Document17 pagesRapid Prototyping Full Seminar Report 989Girish JawalageriNo ratings yet
- TB Grinding EnglishDocument20 pagesTB Grinding EnglishVk PrabakranNo ratings yet
- EIN 3390 Chap 17 Sheet-Forming Processes Part 1 Spring 2012Document50 pagesEIN 3390 Chap 17 Sheet-Forming Processes Part 1 Spring 2012sudharsans88No ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping and Surface Modification TechniquesDocument46 pagesRapid Prototyping and Surface Modification TechniquesmanuNo ratings yet
- Compound Die Design: A Case Study: Sneha S. Pawar, R. S. DaluDocument4 pagesCompound Die Design: A Case Study: Sneha S. Pawar, R. S. DaluchupchapNo ratings yet
- Dies and Its TypesDocument2 pagesDies and Its TypesRajat AhujaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Theory All Inc Casting PDFDocument65 pages2013 Theory All Inc Casting PDFaamir_00No ratings yet
- Casting TheoryDocument22 pagesCasting TheoryJairam Atluri100% (1)
- Study of Forging Process Equipemnts-Practical-3Document12 pagesStudy of Forging Process Equipemnts-Practical-3prashantNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prototyping (RP) : Cad/Cam/CaeDocument45 pagesRapid Prototyping (RP) : Cad/Cam/CaePrashant AmbadekarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic FormingDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic FormingHimanshu Gupta50% (4)
- Casting: Shival Dubey Assistant Professor Mechanical EngineeringDocument31 pagesCasting: Shival Dubey Assistant Professor Mechanical EngineeringChirag TaterNo ratings yet
- Design of Components With Casting ConsiderationsDocument49 pagesDesign of Components With Casting ConsiderationsOrville SutariNo ratings yet
- Title: Objective: Electrode Discharge Machine Wirecut (EDM Wirecut)Document23 pagesTitle: Objective: Electrode Discharge Machine Wirecut (EDM Wirecut)Nur Shaheera Zainurin33% (3)
- Cold and Hot ForgingDocument6 pagesCold and Hot ForgingAnonymous vvO0nZWflrNo ratings yet
- Welding Processes and TechniqueDocument49 pagesWelding Processes and TechniqueRanendraNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations With Powder MetallurgyDocument15 pagesDesign Considerations With Powder MetallurgyTagaytayan MaritesNo ratings yet
- TALAT Lecture 3704: Deep DrawingDocument15 pagesTALAT Lecture 3704: Deep DrawingCORE MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Chips TypeDocument4 pagesChips TypeWajahat RasoolNo ratings yet
- Plastic Metal Forming of Metals and PowdersDocument20 pagesPlastic Metal Forming of Metals and Powdersيوسف عادل حسانينNo ratings yet
- Advanced Metal Cutting Technology (MAT-514 A) Patr 1Document25 pagesAdvanced Metal Cutting Technology (MAT-514 A) Patr 1Bizuayehu Tadesse100% (1)
- Processes Used To Form Metallic MaterialsDocument23 pagesProcesses Used To Form Metallic MaterialsHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Drilling Reaming & TappingDocument17 pagesDrilling Reaming & TappingLeo HsiehNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slide Metrology and Inspection - PPT PDFDocument30 pagesLecture Slide Metrology and Inspection - PPT PDFEdo EdgarNo ratings yet
- Milling and Turning OperationsDocument17 pagesMilling and Turning OperationsMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Presses & Press Work 2Document27 pagesPresses & Press Work 2Sahil ShethNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 (Metal Forming Processes)Document37 pagesLecture 05 (Metal Forming Processes)Mubashar ZahidNo ratings yet
- Cold FormingDocument7 pagesCold FormingglaxionNo ratings yet
- Rolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Document27 pagesRolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Kazal ArefinNo ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalDocument19 pagesWire Drawing Shearing Processes FinalJairam AtluriNo ratings yet
- MT 2nd AssignmentDocument72 pagesMT 2nd AssignmentDixitNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformatin Processes and EquipmentDocument46 pagesBulk Deformatin Processes and EquipmentarhlboyNo ratings yet
- Extrusion FundamentalsDocument5 pagesExtrusion FundamentalsJoNo ratings yet