Professional Documents
Culture Documents
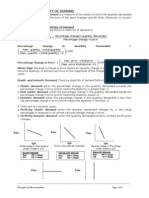
Elasticity of Demand
Uploaded by
Nheha Pallath0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views35 pagesElasticity of Demand
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElasticity of Demand
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views35 pagesElasticity of Demand
Uploaded by
Nheha PallathElasticity of Demand
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
LAW OF DEMAND
Law of Demand states that if price of a commodity
increases quantity demanded will falls and if the price
of a commodity decreases quantity demanded will
increase.
Law of demand indicates only direction of change in
quantity demanded in response to change in price but
Elasticity of Demand states how much and as to what
extent the quantity demanded will change in response
to change in price.
ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
Elasticity of Demand is defined as percentage change in
quantity demanded divided by percentage change in price.
Marshall
Three types of Elasticity of Demand
1. Income Elasticity of demand
2. Cross Elasticity of demand
3. Price Elasticity of demand
Price elasticity of demand
Price Elasticity of Demand measures the responsiveness
of quantity demanded of a good due to change in its
price
Percentage change in quantity demanded
Ed =___________________________________
Percentage change in price
Degrees of ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
1. Perfectly Elastic -: It is a situation where the slightest
rise in price cause the quantity demanded of a
commodity to fall to zero.
Perfectly elastic
demand curve
Perfectly Elastic Demand Curve
0
Quantity
2. Perfectly inelastic -: It is a situation where there is
no change in quantity demanded when price changes.
Perfectly inelastic
demand curve
0
Quantity
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Curve
Unitary elastic demand -: It is a situation where
percentage change in price is same as change in
quantity demanded.
Elasticity
Price
Quantity Demanded (000s)
D
If the firm decides to
decrease price to (say) 3,
the degree of price
elasticity of the demand
curve would determine the
extent of the increase in
demand and the change
therefore in total revenue. 5
100
3
140
Total Revenue
Greater than unitary elastic demand -: It is a situation
where percentage change in quantity demanded is
greater than percentage change in price.
Elasticity
Price ()
Quantity Demanded
D
10
5
20
Producer decides to reduce price to increase sales
7
% in Price = - 30%
% in Demand = + 300%
Ped = - 10 (Elastic)
Total Revenue rises
Less than unitary elastic demand -: It is a situation
where percentage change in quantity demanded is less
than price.
Price ()
Quantity Demanded
10
D
5
5
6
% Price = -50%
% Quantity Demanded = +20%
Ped = -0.4 (Inelastic)
Total Revenue would fall
Producer decides to lower price to attract sales
Not a good move!
Elasticity Along a Demand Curve
P
r
i
c
e
$10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Quantity
Elasticity declines along
demand curve as we move
toward the quantity axis
E
d
= 1
E
d
= 0
E
d
< 1
E
d
> 1
E
d
=
DETERMINANTS OF ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
1. Availability of substitutes
2. Proportion of income spent
3. Different uses of commodities
4. Habits of consumer
5. Nature of commodities
6. Postponement of use
7. Joint demand
IMPORTANCE OF PRICE ELASTICITY OF
DEMAND
1. To a monopolist
2. To the finance minister
3. Useful in international trade
4. useful in factor pricing
5. Explanation of paradox of poverty of farmers
Measurement of Elasticity of
Demand
There are five methods of measuring price elasticity of
demand
1.Total Expenditure Method
2. Proportionate Method
3. Point Elasticity method
4. Arc Elasticity Method
5. Revenue Method
Total Expenditure Method
In order to measure the
elasticity of demand it is
essential to know how much
and in what direction total
expenditure has incurred
Elasticity
of
demand
Price Total
Expenditure
Greater
than
Unity
Rise
Fall
Down
Up
Unity Rise
Fall
Unchanged
Unchanged
Less than
Unity
Rise
Fall
Up
Down
Proportionate Method
As per this method Elasticity of Demand is equal to
Proportionate change in demand for good-X
Ed = (-) _____________________________________
Proportionate change in price of good-X
Change in quantity demanded
___-------------------------------_
Initial demand
Ed =(-)__--------------------------------------------------
change in price
--------------------________________
Initial Price
Point Method
Elasticity of demand computed on a single point on a
demand curve for an infinitely small changes in price
is called point elasticity of demand.
Two types of demand curve
1. Linear demand curve : This is a straight line demand
curve.
Lower Segment
Eod =------------------------
Upper Segment
Non linear demand curve : In this case the demand
curve is non-linear , a tangent is drawn so as to touch a
point on the demand curve .
lower segment
Eod =------------------------------------
Upper segment
Arc Elasticity
The formula of proportionate method to measure the
elasticity of demand at a given point on the demand
curve is relevant if there is infinitely small changes in
demand and price , but if the changes are considerable
then this formula will be of little use.
Arc Elasticity
D
P
Q
What is the price elasticity of
demand between A and B?
$20
10
$26
14
Midpoint
B
A
E
D
=
%Q
%P
Q2Q1
(Q2+Q1)
P2P1
(P2+P1)
=
C
12
$23
=
1014
(10+14)
2620
(26+20)
-.33
.26
=
1.27
=
7-26
Revenue method
Total revenue : sale proceeds that a firm obtains by
selling its products is called its total revenue.
Average Revenue : when this total revenue is divided by
number of units sold we get the average revenue per
unit.
Marginal Revenue : Addition made to the total revenue
by selling one more unit of the commodity is called
marginal revenue.
A
E=-------------
A-M
Elasticity
Income Elasticity of Demand:
The responsiveness of demand to changes in incomes
Normal Good demand rises as income rises and vice
versa
Inferior Good demand falls as income rises and vice
versa
Elasticity
Income Elasticity of Demand:
A positive sign denotes a normal good
A negative sign denotes an inferior good
Elasticity
If demand is price
elastic:
Increasing price would
reduce TR (% Qd > %
P)
Reducing price would
increase TR
(% Qd > % P)
If demand is price
inelastic:
Increasing price would
increase TR
(% Qd < % P)
Reducing price would
reduce TR (% Qd < %
P)
Elasticity
Cross Elasticity:
The responsiveness of demand of one good to
changes in the price of a related good either a
substitute or a complement
Xed =
% Qd of good t _________________
% Price of good y
Elasticity
Goods which are complements:
Cross Elasticity will have negative sign (inverse
relationship between the two)
Goods which are substitutes:
Cross Elasticity will have a positive sign (positive
relationship between the two)
Elasticity
Price Elasticity of Supply:
The responsiveness of supply to changes in price
If Peos is inelastic - it will be difficult for suppliers
to react swiftly to changes in price
If Peos is elastic supply can react quickly to
changes in price
Pes =
% Quantity Supplied
____________________
% Price
Determinants of Elasticity
Time period the longer the time under consideration the
more elastic a good is likely to be
Number and closeness of substitutes the greater the
number of substitutes the more elastic
The proportion of income taken up by the product
the smaller the proportion the more inelastic
Luxury or Necessity - for example, addictive drugs
Importance of Elasticity
Relationship between changes in price and total
revenue
Importance in determining what goods to tax (tax
revenue)
Importance in analysing time lags in production
Influences the behaviour of a firm
Effect of employment
International Trade
Paradoxes of poverty
Price discrimination
You might also like
- Elasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDDocument24 pagesElasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDVikas RockNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument24 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityparthabhiNo ratings yet
- ME 2021 Session 5 6 - Supply Demand Analysis II IIIDocument55 pagesME 2021 Session 5 6 - Supply Demand Analysis II IIIDevyani GroverNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument47 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityFaizan QudsiNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument47 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityFaizan QudsiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument38 pagesElasticity of DemandimadNo ratings yet
- The Elasticity of DemandDocument53 pagesThe Elasticity of DemandShekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply and ElasticityDocument39 pagesDemand, Supply and ElasticityRia Gupta100% (1)
- Elasticity & Forecasting IimmDocument58 pagesElasticity & Forecasting IimmPriyanka_Bagdi_1938No ratings yet
- Concept of Elasticty and Its Application (+ Handwritten Notes Too)Document41 pagesConcept of Elasticty and Its Application (+ Handwritten Notes Too)Aishwarya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument8 pagesElasticity of Demandgyanendra_paudelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (II) - ElasticityDocument44 pagesChapter 2 (II) - ElasticityWeining OoiNo ratings yet
- 04 Elasticity of DemandDocument17 pages04 Elasticity of DemandrahulbawaNo ratings yet
- DIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandDocument5 pagesDIHE - Notes.elasticiy of DemandjavedhanifNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyMochimNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument25 pagesElasticity of DemandYane TimaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Its ApplicationsDocument44 pagesElasticity and Its ApplicationsFahadNo ratings yet
- Elasticity OkDocument26 pagesElasticity OkAmri Satria NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 4 Demand AnalysisDocument30 pages4 Demand Analysisমোহাম্মাদ রাশেদুর রহমান রাশেদNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument9 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyAlex HongoNo ratings yet
- Me 4pptDocument55 pagesMe 4pptarchana_anuragiNo ratings yet
- Slide LSE 2 EkonomiDocument24 pagesSlide LSE 2 EkonomiLuna LedezmaNo ratings yet
- Slide LSE 2 EkonomiDocument24 pagesSlide LSE 2 EkonomiPriti DollyNo ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument5 pagesELASTICITYRaymark Raymundo MejiaNo ratings yet
- Man EcoDocument18 pagesMan EcoRicha mae JumadiaoNo ratings yet
- CH 4 ElasticityDocument31 pagesCH 4 Elasticityshaheduzaman ShahedNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument42 pagesElasticity of Demandchetankhanna42No ratings yet
- Demand and Supply ElasticityDocument19 pagesDemand and Supply ElasticityNikita RathiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply Lecture NotesNastya CurcubetNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand-1Document15 pagesElasticity of Demand-1sunny mantriNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand Together: - Three Steps To Analyzing Changes in EquilibriumDocument10 pagesSupply and Demand Together: - Three Steps To Analyzing Changes in Equilibriumlinh leNo ratings yet
- Economics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategyDocument20 pagesEconomics: Chapter 2 .Managerial Economics & Business StrategySwathy SidharthanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument62 pagesElasticity of DemandVikku AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Elasticity of Demand & Supply: Mba/Pgdm (2009-2011) New Delhi Institute of ManagementDocument32 pagesProject Report ON Elasticity of Demand & Supply: Mba/Pgdm (2009-2011) New Delhi Institute of ManagementNitin Rana71% (7)
- Managerial Economics CompleteDocument18 pagesManagerial Economics CompleteAmlan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesElasticity of Demand and Supply: ObjectivesJoanne FerrerNo ratings yet
- M2 ElasticityDocument28 pagesM2 ElasticityYASHAS MOHAN 2150240No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument59 pagesElasticity of Demand: Price, Income and Cross Elasticitynithinsp92No ratings yet
- Module 2 BasicDocument9 pagesModule 2 BasicJessica BallesterNo ratings yet
- Elasticity 1Document13 pagesElasticity 1nervasmith21No ratings yet
- ECO 101 Principles of Microeconomics: Lecturer: Dr. Joshua SebuDocument47 pagesECO 101 Principles of Microeconomics: Lecturer: Dr. Joshua SebuYimer FentawNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument61 pagesLecture 2 Elasticity of Demand and SupplyJoanne FerrerNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandManoj KNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument29 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyEmily Canlas DalmacioNo ratings yet
- Ch03 - Demand and Supply - Part 2Document35 pagesCh03 - Demand and Supply - Part 2Robert AxelssonNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesCh. 4 Elasticity: Price Elasticity of DemandVarun SanjayNo ratings yet
- ECO101 Lec 8Document17 pagesECO101 Lec 8Mostafa haqueNo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document19 pagesChap 3Annie DuolingoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsDocument15 pagesModule 1 - Topics in Demand and Supply Analysis - HandoutsAyman Al HakimNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument69 pagesElasticityAmit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Price, Income and Cross ElasticityDocument20 pagesPrice, Income and Cross ElasticityEshaan ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument16 pagesElasticity of DemandHumayun95% (20)
- Chap 2 Elasticity and Its Application Part 3Document48 pagesChap 2 Elasticity and Its Application Part 3The TwitterNo ratings yet
- NMIMS Global Access School For Continuing Education (NGA-SCE) Course: Business EconomicsDocument6 pagesNMIMS Global Access School For Continuing Education (NGA-SCE) Course: Business EconomicstanmayNo ratings yet
- Assignment ECON 260Document13 pagesAssignment ECON 260Mohammed AwadNo ratings yet
- Econ 24 CH1 To CH3Document18 pagesEcon 24 CH1 To CH3Muyano, Mira Joy M.No ratings yet
- CH. 3 Applications of Supply and DemandDocument26 pagesCH. 3 Applications of Supply and Demandsamah.fathi3No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Keat Et Al: Managerial Economics, Prof A.K. WaithimaDocument24 pagesChapter 4: Keat Et Al: Managerial Economics, Prof A.K. WaithimaIvy Bucks WanjikuNo ratings yet
- Course: Business EconomicsDocument4 pagesCourse: Business Economicsjitendra.jgec8525No ratings yet
- Extended AbstractDocument10 pagesExtended AbstractSarang GohNo ratings yet
- Q1 Reconciliation by SKUsDocument38 pagesQ1 Reconciliation by SKUsErineNo ratings yet
- AKPAKPANDocument7 pagesAKPAKPANErwin SugiartoeNo ratings yet
- Steering Gear PrincipalDocument21 pagesSteering Gear PrincipaljanuarNo ratings yet
- CDCP - 02.28.11 - Titration Excel PracticeDocument2 pagesCDCP - 02.28.11 - Titration Excel PracticeSeleneblueNo ratings yet
- Ag 180ao MMM 000Document294 pagesAg 180ao MMM 000sergey62No ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 3 Module 1Document32 pagesScience 6 Quarter 3 Module 1Mitzi Faye Cabbab100% (2)
- Lesson 10Document9 pagesLesson 10Siakap PutihNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Systems. Vol. I. Electric NetworksDocument843 pagesElectric Power Systems. Vol. I. Electric Networksluciantoma75% (4)
- Model 5Document4 pagesModel 5m hNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Database: Quick Installation Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) For Linux x86Document26 pagesOracle® Database: Quick Installation Guide 11g Release 2 (11.2) For Linux x86kchukkapalliNo ratings yet
- PHUL Sheet TemplateDocument3 pagesPHUL Sheet TemplatetiandalfaNo ratings yet
- Speed PDFDocument1 pageSpeed PDFhendrik koesumaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics Test Examples (NY)Document15 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics Test Examples (NY)yyanan1118No ratings yet
- Math 115 Uiuc Written Homework 6 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMath 115 Uiuc Written Homework 6 Solutionsafmspqvdy100% (1)
- Marantz SR-7001 Service ManualDocument206 pagesMarantz SR-7001 Service ManualLucianoNo ratings yet
- Ebook How To Design and Evaluate Research in Education 11Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook How To Design and Evaluate Research in Education 11Th Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFwayne.edwardson742100% (25)
- Sap Faq FF ModuleDocument11 pagesSap Faq FF ModuleSharandeepNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Plant Growth Factors and Latest Trend in Crop ScienceDocument26 pagesModule 4: Plant Growth Factors and Latest Trend in Crop ScienceNorhanah Dionisio BarubaNo ratings yet
- SPC1 Single Phase Power Controller PDFDocument6 pagesSPC1 Single Phase Power Controller PDFMin ZayarNo ratings yet
- Prime NumbersDocument2 pagesPrime NumbersDarkas2100% (1)
- Double InterlockDocument11 pagesDouble Interlocklazhar75No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - ElectrostaticsMary Kate BacongaNo ratings yet
- Projection of Planes: Problem 1Document2 pagesProjection of Planes: Problem 1Ravi ParkheNo ratings yet
- Shivani Mehan - ResumeDocument1 pageShivani Mehan - ResumeShivani MehanNo ratings yet
- CompletionDocument128 pagesCompletionMelgie Mae Matulin DikitananNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetDocument6 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetAli ALEBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- 2nd Exp. Electronic Spectra - Cu in ComplexesDocument5 pages2nd Exp. Electronic Spectra - Cu in ComplexeskofinyameNo ratings yet
- GS Quantify IITMDocument27 pagesGS Quantify IITMRishabh Kumar100% (1)
- Spatial vs. Frequency DomainDocument6 pagesSpatial vs. Frequency DomainakhorshidinetNo ratings yet