Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reference Model
Uploaded by
Harsha NaiduOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reference Model
Uploaded by
Harsha NaiduCopyright:
Available Formats
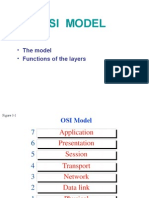
OSI Reference Model
1. Physical Layer
Transmit raw bits over a communication channel.
Make sure
when one side sends 1 bit, the other side should also
receive 1 bit. But not 0
Questions here are:
1. How many volts should be used to represent 1 and
How many volts should be used to represent 0.
2. How many nanoseconds a bit lasts.
3. Weather transmission proceeds in both directions.
4. How the initial connection is established and
How it is torn down when both sides are finished.
5. How many pins the network connector has and
2. Data link layer
The Data-Link layer is the protocol layer in a program that
handles the moving of data in and out across a physical link
in a network.
The Data-Link layer contains two sublayers that are
described in the IEEE-802 LAN standards:
1. Media Access Control (MAC)
2. Logical Link Control (LLC)
The Data-Link layer ensures that
1. an initial connection has been set up,
2. divides output data into data frames and
3. If the data frame is received the receiver will send
back the acknowledgement frame.
3. Network Layer
The Data-Link layer is the protocol layer in a program that
handles the moving of data in and out across a physical link
in a network.
The Data-Link layer contains two sublayers that are
described in the IEEE-802 LAN standards:
1. Media Access Control (MAC)
2. Logical Link Control (LLC)
The Data-Link layer ensures that
1. an initial connection has been set up,
2. divides output data into data frames and
3. If the data frame is received the receiver will send
back the acknowledgement frame.
You might also like
- Advance Computer Networks: Spring 2020-21 Lect. #01Document8 pagesAdvance Computer Networks: Spring 2020-21 Lect. #01Ishwar MhtNo ratings yet
- 7 Layers of OSI ModelDocument21 pages7 Layers of OSI ModelCatherine LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- University Institute of Engineering Department of Computer Science & EngineeringDocument33 pagesUniversity Institute of Engineering Department of Computer Science & EngineeringRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 - The OSI Model Net ProtclsDocument121 pages2 - The OSI Model Net ProtclsAhmad FakhrullahNo ratings yet
- BIT 03204 L4 Data Communication Media Access ControlDocument64 pagesBIT 03204 L4 Data Communication Media Access ControlsimonnjauNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Introduction: Mr. Upendra Verma Asst. Prof., MPSTME Shirpur Campus, SVKM'S NMIMS Shirpur CampusDocument19 pagesUnit-I: Introduction: Mr. Upendra Verma Asst. Prof., MPSTME Shirpur Campus, SVKM'S NMIMS Shirpur CampusManish choudharyNo ratings yet
- Che 3Document33 pagesChe 3pukaleatharvaNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument63 pagesOSI ModeluselessNo ratings yet
- DCN - 3 - Introduction To Data Link LayerDocument97 pagesDCN - 3 - Introduction To Data Link LayerShiza SahooNo ratings yet
- 4.osi LayersDocument48 pages4.osi LayersSami AhmedNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworksDocument68 pagesData Communication & NetworksSajid MumtazNo ratings yet
- CN UNIT-3 MaterialDocument28 pagesCN UNIT-3 MaterialAparna GattimiNo ratings yet
- OSI Model - pdf3Document13 pagesOSI Model - pdf3itachigood980No ratings yet
- Computer Network Architecture Module 1Document11 pagesComputer Network Architecture Module 1Victor SarmacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Control System 2MARKSDocument36 pagesControl System 2MARKSSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document19 pagesModule 6Ryan AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument96 pagesChapter IVhariye2225No ratings yet
- CN Module 2Document98 pagesCN Module 2OmNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitecturesDocument64 pagesNetwork Architecturesdeepank singhNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument5 pagesOSI ModelJana RthanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Network ModelsDocument9 pagesFundamental Network ModelsSailas Khulumani TshabanguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 6Document58 pagesChapter 2 6Rana GaballahNo ratings yet
- Defining Networks With The OSI ModelDocument39 pagesDefining Networks With The OSI ModelmashoodNo ratings yet
- ch5 OsiDocument52 pagesch5 OsiBalaji GaikwadNo ratings yet
- W 2 SKR 3200Document47 pagesW 2 SKR 3200Laili JamlusNo ratings yet
- CN U5 Datalink LayerDocument29 pagesCN U5 Datalink LayerAravind SNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledHimanshu RaiNo ratings yet
- Layered ArchitectureDocument54 pagesLayered ArchitectureFrancis PulaiziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Layered ModelsDocument53 pagesChapter 3 - Layered ModelsDanny KirooNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Networks LAN DesignDocument94 pagesData Communication Networks LAN DesignMichelle NasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: InternetworkingDocument26 pagesChapter 1: InternetworkingPeter CiankNo ratings yet
- CN Unit IiDocument55 pagesCN Unit Iidhosheka123No ratings yet
- 5 DataLink LayerDocument7 pages5 DataLink Layera NaniNo ratings yet
- Slide-5 Data Link LayerDocument10 pagesSlide-5 Data Link LayerRobbie SolimanNo ratings yet
- Network and System UNIT 2 NotesDocument24 pagesNetwork and System UNIT 2 Notespinkyjaiswal7890No ratings yet
- Osi ModelDocument51 pagesOsi Modelapi-3703205No ratings yet
- Computer Networks-Module1Document34 pagesComputer Networks-Module1Sreedevi YashpalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document73 pagesUnit 1Francis Densil RajNo ratings yet
- CIT 118 Lecture 2 (A) Protocols and ArchitectureDocument6 pagesCIT 118 Lecture 2 (A) Protocols and ArchitectureJames GitongaNo ratings yet
- What Is The OSI ModelDocument17 pagesWhat Is The OSI ModelBilisumaNo ratings yet
- Presentation TruyenThongDuLieu Group3-1Document30 pagesPresentation TruyenThongDuLieu Group3-1Thiện Nguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Layered ModelsDocument52 pagesChapter 3 - Layered Modelsomika494100% (1)
- Osi Data Link Layer: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 7 Sandra Coleman, CCNA, CCAIDocument23 pagesOsi Data Link Layer: Network Fundamentals - Chapter 7 Sandra Coleman, CCNA, CCAIAna Marie SuganobNo ratings yet
- L3 OSI LayersDocument19 pagesL3 OSI LayersAnurag RanaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 NP MNDocument31 pagesUnit-1 NP MNCSE - Roshan PradhanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 OSI ModelDocument6 pages3.1 OSI ModelSuyasha JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CNDDocument74 pagesUnit 1 CNDSAURAV JAGTAPNo ratings yet
- UCCN1004 - Lect8 - Intro To Layered Model and ProtocolsDocument31 pagesUCCN1004 - Lect8 - Intro To Layered Model and ProtocolsVickRam RaViNo ratings yet
- Network Model ArchitectureDocument27 pagesNetwork Model ArchitectureS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Principle of Layering Concept: by Ms - Sarika ChoudahriDocument58 pagesUnit 2 Principle of Layering Concept: by Ms - Sarika Choudahrimanasi kumbharNo ratings yet
- Osi ModelsDocument12 pagesOsi ModelsAkpevwe IsireNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - UNIT IIDocument54 pagesComputer Networks - UNIT IIjanilajaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document19 pagesChapter 13zakiya hassanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 and 2Document185 pagesUnit 1 and 2Vaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-7@networking ModelsDocument94 pagesChapter 4-7@networking ModelsSilabat AshagrieNo ratings yet
- 5Document40 pages5ty juNo ratings yet
- CP1402 Week 2 I OSI and Troubleshooting STUDENTDocument27 pagesCP1402 Week 2 I OSI and Troubleshooting STUDENTasdasdNo ratings yet
- III B.Tech CSSE Ist SEMESTER SyllabusDocument11 pagesIII B.Tech CSSE Ist SEMESTER SyllabusHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- CD Lab ManualDocument30 pagesCD Lab ManualTejasvi QueenyNo ratings yet
- MATRIX ConverterDocument15 pagesMATRIX ConverteranuragrathoreNo ratings yet
- HT AccessDocument1 pageHT AccessHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Combinational MultiplierDocument5 pagesCombinational Multipliersouvik1112No ratings yet
- Seed Block Algorithm: A Remote Smart Data Back-Up Technique For Cloud ComputingDocument1 pageSeed Block Algorithm: A Remote Smart Data Back-Up Technique For Cloud ComputingHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Term Paper GuidelineDocument2 pagesTerm Paper GuidelineHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Components of EnvironmentDocument5 pages1.1 Components of EnvironmentRathnavel Ponnuswami86% (36)
- Surface ChemistryDocument23 pagesSurface ChemistryHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- CP LabproramsDocument46 pagesCP LabproramsDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- CPP ProgramsDocument34 pagesCPP ProgramsGAN SA KINo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document27 pagesUnit 7Harsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) TcsDocument22 pages(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) TcsAsim SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Connoisseur, Mother Teresa Essays in EnglishDocument20 pagesConnoisseur, Mother Teresa Essays in EnglishHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Computer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorDocument25 pagesComputer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document11 pagesUnit 8Harsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- C Data Types:: Primary Data Types Derived Data Types User-Defined Data TypesDocument9 pagesC Data Types:: Primary Data Types Derived Data Types User-Defined Data TypesHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Modularizing and Reusing of Code Through FunctionsDocument9 pagesModularizing and Reusing of Code Through FunctionsHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- ProfileDocument1 pageProfileHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Typedef - To Define New Datatype BitfiedsDocument17 pagesTypedef - To Define New Datatype BitfiedsHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document17 pagesUnit 6Harsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document16 pagesUnit 3Harsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- Computer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorDocument25 pagesComputer - Hardware: Arithmetic and Logic Unit Micro ProcessorHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet
- C QuestionsDocument3 pagesC QuestionsHarsha NaiduNo ratings yet