Professional Documents
Culture Documents
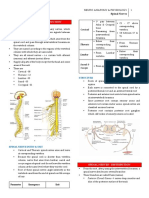
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Renata V C0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Uploaded by
Renata V CCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
C.N.
TYPE CRANIAL EXIT
POINT
NUCLEUS
NAME
NUCLEUS
LOCATION
PERIPHERAL INNERVATION FUNCTION SIGN OF DAMAGE
I
Olfactory
SENSORY Cribiform plate Anterior Olfactory Olfactory Tract Mucosa of nasal cavity Smell Anosmia or dysosmia (fracture of
cribiform plate)
II
Optic
SENSORY
Optic foramen
Lateral Geniculate
Thalamus
Retina of the eye
Vision
Anopsia: visual field deficits
Loss of light reflex w/ III
Only CN affected by MS
III
Oculomotor
MOTOR
Superior
Orbital Fissure
Oculomotor
Upper Midbrain
Levator palpebrae superioris Raises eyelid Ptosis
Extraocular muscles
Superior Rectus m: SR
Medial Rectus m: MR
Inferior Rectus m: IR
Iinferior Oblique m: IO
Eye movement
MR: adduction (most
important muscle)
Diplopia
Loss of parallel gaze
External strabismus (loss of adduction)
Edinger Westphal
(Preganglionic PS)
Upper Midbrain Sphincter Pupillae Pupil constriction Midriasis
Cilliary muscle Lens accomodation Cyclopegia , loss of near response
IV
Trochlear
MOTOR
Superior
Orbital Fissure
Trochlear
Dorsal to cerebellar
peduncle, ventral to
cerebral aqueduct
Arise from the DORSAL
part , CROSS, and go
below inferior colliculus
to the ventral part.
Lower Midbrain
Superior Oblique m: SO
Downward gaze & abducts
eye
Weakness looking down (reading)
Diplopia
Intortion Tilts head AWAY from lesion
V
Trigeminal
V1: Ophtalmic
V2: Maxillary
V3: Mandibular
Corticobulbar
innervation
MIXED
(actually,
the only
one
mixed is
V3, the
rest are
sensory
only!)
V1: Superior
Orbital Fissure
Mesencephalic
Above entry point of V
Propioceptive imput
Monosynaptic reflex
Jaw jerk reflex
Motor
Point of entry of V
Medial to main sensory
nucleus
Supply muscles of
MASTICATION
Main Sensory (or
Chief or Principal)
Point of entry of V
Lateral to motor nucleus
TACTILE AFFERENTS =>
synapse 2 neuron =>
croos midline => VPM
thalamus =>
somotosensory cortex
Spinal tract & nuclei
Caudal continuation of
main sensory nucleus
Elongate nuclei
Position analogous to
dorsal horns of SC
(meaning: posteriorly
PAIN & T afferents =>
descend in spinal tract
=> reach nucleus =>
croos midline => VPM
thalamus =>
somotosensory cortex
Midbrain
Middle Pons
Middle Pons
Lower Pons to
Spinal cord
(C2)
V1:
Skin of forehead
Scalp
Cornea
V1:
General sensation (touch, pain &
T)
V1:
Loss of general sensation
Loss of blink reflex w/ VII
V2: Foramen
Rotundum
V2:
Palate
Nasal cavity
Maxillary face & teeth
V2:
General sensation
V2:
Loss of general sensation
Trigeminal Neuralgia
V3: Foramen
ovale
V3: Sensory
Anterior 2/3 of tongue
Mandibular face & teeth
V3:
General sensation
V3:
Loss of general sensation
Trigeminal Neuralgia
V3 : Motor
Muscles of mastication:
o Temporalis
o Masseter
o Medial pterygoid
o Lateral pterygoid
Anterior belly of digastric
Mylohyoid
Tensor tympani
Tensor palati
V3:
Mastication
V3:
Weakness in chewing
Jaw deviation TOWARDS weak side
Remember!!!
Complete V lesion (at entry or exit point of V) in ROSTRAL PONS, results in COMPLETE ANESTHESIA OF IPSILATERAL FACE & JAW
WEAKNESS (bc the Motor & Main Nuclei are fucked up)
Lesion in LATERAL LOWER PONS or LATERAL MEDULLA, results in COMPLETE ANESTHESIA and LOSS OF T SENSATION OF
IPSILTAREAL FACE ONLY, muscle function & tactile sensation would be intact. (bc spinal nuclei it the only one fucked up)
VI
Abducens
MOTOR
Superior
Orbital Fissure
Abducens
Found near the midline,
in the floor of the 4
th
v.
VI fibers encircled by VII
fibers (genu)
Pons
Lateral Rectus
Abduction
Diplopia
Internal Strabismus: medial eye
deviation
Loss of parellal gaze
Pseudoptosis
VII
Facial
Corticobulbar
innervations
(partially bilateral)
Bilateral upper face
innervation
Contralateral lower
face innervatoin
MIXED
Entry: Internal
Acoustic
meatus
Exit:
stylomastoid
foramen
Motor
Ventrolateral to VI
nuclei
Anterior Genu of Facial
Nerve: Fibers curve
around the posterior
side of VI nuclei, then
pass ventrolaterally
Solitary
Respond to visceral
sensation (taste,
respiratory, GI)
Superior Salivatory
Pons
Facial expression muscles
Posterior belly of digastric
Stylohyoid
Stapedius ---------------------->
Facial expression
Controls amplitude of sound
Corner mouth drops, cant close eye,
cant wrinkle forehead, no blink reflex
Hyperacusis
Submandibular & sublingual g. Salivation (preganglionic PS)
Skin behind ear Pain behind ear
Anterior 2/3 tongue palate Taste Ageusia (loss of taste), disgeusia
Lacrimal gland Tears (preganglionic PS) Dry, red eye. Loss of lacrimation, complete
VII lesion
Right Corticobulbar fibers ( UMN Lesion) Left lower face weakness= mouth droops (pt CAN blink, wrinkle
forehead, bc pt still have the left corticobulbar fibers innervating the upper face)
Left LMN lesion(VII) Complete left face weakness = Bell Palsy
VIII
Vestibulocochlear
SENSORY
Internal
Acoustic
Meatus
Vestibular
Posterior surface of
Pons
Cochlear
Dorsal & Ventral
Pons
Medulla
Ponto-
medullary
junction
Inner ear laberynth structures
Semicircular canal
Cochlear apparatus
Hearing
Balance
Angular acceleration (head
turning)
Linear acceleration (gravity)
Sensorineural hearing loss
Profound & unilateral lesion is in
cochlear nuclei or cochlear part of VIII
Slight bilateral hearing loss & decrease
ability to localize sound lesion above
superior olivary nucleus
Loss of balance
Nystagmus
IX
Glossopharyngeal
MIXED
Jugular
Foramen
Ambiguus
LMN muscles
Behind inferior ollive
Solitary
Same as X
Inferior Salivatory
Medulla
Stylopharyngeus Elevation of pharynx
Loss of Gag reflex with X
Oropharynx Sensation
Carotid sinus/body Chemoreceptor
Parotid gland Salivation
Posterior 1/3 tongue Taste
X
Vagus
Corticobulbar
innervation
MIXED
Jugular
Foramen
Ambiguus
LMN skeletal
muscles
Behind inferior ollive
Dorsal Motor Vagal
Major
Parasympathetic
nuclei preganglionic
fibers to thorax and GI
(foregut & midgut)
Lateral to XII nucleus,
in the floor of 4
th
v.
Solitary
Respond to visceral
sensation (taste,
respiratory, GI)
Imput of carotid sinus
and body
Medulla
Muscles of palate and
pharynx; except tensor palate
(V) and stylopharyngeous (IX)
Swallowing
Dysphagia
Palate droop (ipsilateral paralysis of
soft palate Uvula pointing AWAY
from lesion
Nasal regurgitation
Larynx muscles
(recurrent laryngeal)
Fonation
Nasal speech
Hoarseness
Fixed vocal cord
Larynx and Laryngopharynx
Sensory Loss of gag reflex w/ IX
Loss of cough reflex
Delayed gastric emptying
GI tract & GI smooth muscle &
glands (foregut & midgut)
Sensory
PS
Delayed gastric emptying
Carotid sinus/body
Chemoreceptor
XI
Accesory
Corticobulbar inn.
MOTOR
Jugular
Foramen
Spinal Accesory
Cervical spinal
cord
Sternocleidomastoid Head rotation to opposite side Weakness turning chin to opposite side
Trapezius Elevates and rotates scapula Shoulder droop
Remember: Intramedullary lesions DONT affect this CN!!!
XII
Hypoglossal
Corticobulbar inn.
MOTOR
Hypoglossal
canal
Hypoglossal
Medulla
Styloglossus
Hypoglossus
Genioglossus
Intrinsic tongue muscles
(except palatoglossus by X)
Tongue movement
Tongue pointing TOWARDS affected side
on protrusion
You might also like
- ENT by Rajiv Dhawan 2023Document165 pagesENT by Rajiv Dhawan 2023CastleKG100% (1)
- HEMATOLOGJIA (ARBEN IVANAJ) (Cut) PDFDocument354 pagesHEMATOLOGJIA (ARBEN IVANAJ) (Cut) PDFEnea HysaNo ratings yet
- Leo's Anatomy Notes-Leotrim AliuDocument606 pagesLeo's Anatomy Notes-Leotrim AliuLeotrim Aliu86% (7)
- STEPHEN SCHEIDT-Basic Electrocardiography-CIBA (1993)Document51 pagesSTEPHEN SCHEIDT-Basic Electrocardiography-CIBA (1993)Marsiano Qendro100% (3)
- Tema e Diplomes Kanceri GastrikDocument35 pagesTema e Diplomes Kanceri GastrikDorisa BahjaNo ratings yet
- Systemi Respirator 14-21 RSDocument44 pagesSystemi Respirator 14-21 RSRejhan SadikuNo ratings yet
- Receta Mjekesore - UnlockedDocument63 pagesReceta Mjekesore - UnlockedKoli Kolargoli100% (3)
- Anatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and NeckDocument21 pagesAnatomy Tables-Muscles of The Head and NeckTracie YW100% (1)
- B16M01L07 - Cranial Nerves ExaminationDocument13 pagesB16M01L07 - Cranial Nerves ExaminationDonnaBells Hermo LabaniegoNo ratings yet
- Neck Axilla BackDocument24 pagesNeck Axilla BackmoregutsNo ratings yet
- DR NajeebDocument3 pagesDR NajeebByeongsu Park100% (1)
- Part Ii Medulla SpinalisDocument46 pagesPart Ii Medulla SpinalisSuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Teza PsikiatrieDocument12 pagesTeza PsikiatrieMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves ListDocument4 pagesCranial Nerves Listashdmb217No ratings yet
- Lista e Librave MjekesoreDocument4 pagesLista e Librave MjekesoreEmily OwenNo ratings yet
- Psikiatri 51Document51 pagesPsikiatri 51Marsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Anatomski Atlas PDFDocument68 pagesAnatomski Atlas PDFIVANANo ratings yet
- Anatomia - Prof. Ibrahim Behluli PDFDocument222 pagesAnatomia - Prof. Ibrahim Behluli PDFRinor Mujaj100% (10)
- Lipidet BiokimiDocument118 pagesLipidet BiokimiEmir Cerkezi100% (1)
- Most CommonDocument24 pagesMost CommonTarek TarekNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves DiagramDocument15 pagesCranial Nerves DiagramSpellkingNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro NeckDocument12 pagesGRDA Intro NeckKingNo ratings yet
- ENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADDocument22 pagesENT Deferential Diagnosis MEDADReham AshourNo ratings yet
- The Topography of Upper LimbDocument5 pagesThe Topography of Upper LimbLorena DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves and BranchesDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves and Branchesballer0417No ratings yet
- 9 ENT ImagesDocument45 pages9 ENT ImagesMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Benign Diseases of Vulva and VaginaDocument6 pagesBenign Diseases of Vulva and VaginaTj Kevin P-DoctorNo ratings yet
- Tanveer Notes - CPSP Imortant PointsDocument103 pagesTanveer Notes - CPSP Imortant PointsAyisha NazNo ratings yet
- Antidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSDocument13 pagesAntidiabetic Drugs - AMBOSSOpio IsaacNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument25 pagesBonesJohnvee Magana100% (2)
- Genetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesDocument1 pageGenetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesJ KPNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument46 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsMini ManraiNo ratings yet
- Spinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Document5 pagesSpinal Nerves - Introduction: Neuro Anatomy & Physiology 1Dr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Concise of Equations PhysiologyDocument4 pagesConcise of Equations PhysiologyFer Pineda MinaNo ratings yet
- Kimi FarmaceutikeDocument64 pagesKimi FarmaceutikeHabib Berisha100% (1)
- ImpetigoDocument31 pagesImpetigoUmmu Insyirah100% (1)
- Step-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - SampleDocument8 pagesStep-Wise Approaches in Clinical Examination - Samplecsbully913No ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument11 pagesChemotherapyNedaAbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesDocument4 pages1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Nose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018Document63 pagesNose & Paranasal Sinuses 2018yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- SkizofreniaDocument1 pageSkizofreniaMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Ent 1.07 NoseDocument4 pagesShanz - Ent 1.07 NosePetrina XuNo ratings yet
- 07e - UMN & LMN Lesions - Ninja Nerd & DR NajeebDocument9 pages07e - UMN & LMN Lesions - Ninja Nerd & DR Najeebhiba jasimNo ratings yet
- 05 HypoxiaDocument75 pages05 HypoxiaShri PravallikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesAnatomy - Cranial NervesKaradex DexondNo ratings yet
- Pathology Checklist DR Preeti SharmaDocument5 pagesPathology Checklist DR Preeti SharmaAvi Khanna100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve Cheat SheetAli SyedNo ratings yet
- Nystagmus: Dr. Enny Lestari, M. Biomed, SP.SDocument39 pagesNystagmus: Dr. Enny Lestari, M. Biomed, SP.SPuji Yunisyah100% (1)
- BiopsyDocument19 pagesBiopsyQendrim BerishaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy ReviewDocument107 pagesNeuroanatomy ReviewAlan Magpantay100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument9 pagesCranial Nervesangrypandasaredangerous100% (4)
- Mnemonic SDocument8 pagesMnemonic Smueen hashmiNo ratings yet
- Adekunle Seminar in Cranial NervDocument34 pagesAdekunle Seminar in Cranial NervBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tulang Tengkorak Manusia: Pembimbing: Dr. Fadil, SP - BSDocument28 pagesAnatomi Tulang Tengkorak Manusia: Pembimbing: Dr. Fadil, SP - BSichacloudiacNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3572289752270573946Document92 pagesInbound 3572289752270573946Viola BlenteNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Limb NervesDocument6 pagesUpper and Lower Limb NervesTaimoor DogarNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System TractsDocument4 pagesCentral Nervous System TractsSpencer ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Airway Innervations To KnowDocument118 pagesAirway Innervations To KnowDIANANo ratings yet
- Upper-limb-1Document31 pagesUpper-limb-1AnuNo ratings yet
- PONSDocument40 pagesPONSveegeer100% (1)
- Nervus KranialisDocument28 pagesNervus Kranialisnovy rosalia chandraNo ratings yet
- Anterior Rami Spinal Nerves: 4 Bimonthly Oral Exam QUESTIONS and ANSWERS Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesAnterior Rami Spinal Nerves: 4 Bimonthly Oral Exam QUESTIONS and ANSWERS Nervous SystemRay PerezNo ratings yet
- Farmakologjia KlinikeDocument130 pagesFarmakologjia KlinikeMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Farmakologji KlinikeDocument17 pagesFarmakologji KlinikeMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Fletore e Shenimeve Te Ortopedise PDFDocument63 pagesFletore e Shenimeve Te Ortopedise PDFMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Teza Gastro 2Document64 pagesTeza Gastro 2Marsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Teza Gastro 1Document29 pagesTeza Gastro 1Marsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- FCPS Pretest Series Golden File 3Document224 pagesFCPS Pretest Series Golden File 3Marsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Fibrilacioni Atrial Trajtimi Dhe Diagnoza e TijDocument8 pagesFibrilacioni Atrial Trajtimi Dhe Diagnoza e TijMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Manual Nintendo 2dsDocument41 pagesManual Nintendo 2dsMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Farmakologji KlinikeDocument17 pagesFarmakologji KlinikeMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- SkizofreniaDocument1 pageSkizofreniaMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- BotulismDocument6 pagesBotulismMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- Koka Dhe QafaDocument57 pagesKoka Dhe QafaMarsiano Qendro100% (1)
- Hearing Conservation: Trina Redford, Industrial HygienistDocument34 pagesHearing Conservation: Trina Redford, Industrial HygienistNOrsaodah ZInNo ratings yet
- TuberkuloziDocument4 pagesTuberkuloziMarsiano QendroNo ratings yet
- AEA5000CE4Document6 pagesAEA5000CE4Marsiano QendroNo ratings yet