Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Feedforward
Uploaded by
a_m_shihaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Feedforward
Uploaded by
a_m_shihaCopyright:
Available Formats
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 1
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Feedforward Control
Feedforward Control
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 2
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Basis of Feedforward Control Basis of Feedforward Control
Basis of Feedforward Control
In some cases the major load
disturbance to a process may
be measured and utilized to
provide feedforward control.
The advantage feedforward
control is that corrective action
is taken for a change in a
disturbance input before it
affects the control parameter.
Feedforward control is used in
conjunction with feedback
control to provide multiple-
input single output (MISO)
control
+
Process
Feedback
Controller
Manipulated
Input
Disturbance
Input
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 3
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Feedforward Dynamic Compensation Feedforward Dynamic Compensation
Feedforward Dynamic Compensation
When the dynamic
response of the controlled
parameter to a change in
the disturbance input
differs significantly from
that for the manipulated
parameter, then dynamic
compensation should be
included in the feedforward
implementation.
It can be shown that a pure
deadtime and lead/lag unit
provide correct
compensation for first order
plus deadtime processes.
Measured
Disturbance
Controlled
Parameter
Information
needed to
Commissio
n
Feedforwar
d
L/L & DT
DeadTime
Lead/Lag
+
+
Dynamic
Compensation
Process
Feedback
Controller
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 4
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Feedforward Control in DeltaV Feedforward Control in DeltaV
Feedforward Control in DeltaV
Addition of
feedforward input and
scaling of feedforward
input by FFW_GAIN
is included as part of
the DeltaV PID.
DT and LL blocks are
used to implement the
lead-lag and deadtime
components of
dynamic
compensation
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 5
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Setup of Lead-Lag Block Setup of Lead
Setup of Lead
-
-
Lag Block
Lag Block
Set the
LEAD_TIME to
Tm
Set the
LAG_TIME to
Td.
The gain of the
L/L should be
set to :
- (Load Dist
Gain/Manip
Gain).
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 6
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Setup of Deadtime Block for Dynamic
Compensation
Setup of Deadtime Block for Dynamic
Setup of Deadtime Block for Dynamic
Compensation
Compensation
The
DEAD_TIME
parameter
should be set
to a value of
DT2 - DT1.
If DT1 is
greater than
DT2, then
compensation
for deadtime is
not required.
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 7
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Alternate Implementation - External
Feedforward Using Bias-Gain Block
Alternate Implementation
Alternate Implementation
-
-
External
External
Feedforward
Feedforward
Using Bias
Using Bias
-
-
Gain Block
Gain Block
The feedforward
input is added to the
PID output using the
Bias-Gain Block.
Advantage is that the
feedforward action
continues even if
PID is in Man mode
Feedback correction
is limited by the PID
output limits
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 8
Process Control
Feedforward Control
External Feedforward - Bias(Cont) External Feedforward
External Feedforward
-
-
Bias(Cont)
Bias(Cont)
Act on IR should be
selected to allow the
bias (SP) to be
initialized on
transition from IMAN
to CAS actual mode.
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 9
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Alternate Implementation - External
Feedforward - Ratio
Alternate Implementation
Alternate Implementation
-
-
External
External
Feedforward
Feedforward
-
-
Ratio
Ratio
Ratio block is
used to multiply
the PID output
with the
feedforward
input.
Feedforward
continued even
if PID is in Man
mode
Ratio correction
is limited by the
PID output
limits
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 10
Process Control
Feedforward Control
PID Feedforward Workshop PID Feedforward Workshop
PID Feedforward Workshop
TT
16
TC
16
50-200 DegF
TT
16A
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 11
Process Control
Feedforward Control
Feedforward Control Workshop
Feedforward Control Workshop
Step 1. Using the EXAMPLE_D_FF module, make a change in the process
disturbance value with the PID in automatic ( with Feedforward disabled).
What impact does the disturbance have on the process and the value of the
PID output value needed to maintain Setpoint?
Step 2. Change the mode of the PID to manual. Identify the process gain, lag and
deadtime for a step change in the PID output.
Step 3. With the PID in manual and the process at steady state, change the value of
the process disturbance by a step and identify the process gain, lag and
deadtime for a change in the disturbance input.
Step 4. Calculate the feedforward gain (See L/L setup for guidance) based on the
process responses. Enter this gain in the FF_GAIN parameter and enable
feedforward action through the FF_ENABLE parameter.
Step 5. Change the mode of the PID to AUTO and let the loop settle at a target SP
value. Make a change in the disturbance input and observe the controller
and process output. Did the feedforward action minimize the impact of the
disturbance?
2006 Fisher-Rosemount Systems, Inc.
Slide 7 - 12
Process Control
Feedforward Control
EXAMPLE_D_FF
EXAMPLE_D_FF
You might also like
- 9 OverrideControlDocument10 pages9 OverrideControlsamiran21No ratings yet
- Modbus Based DCS - Distributed Control SystemDocument70 pagesModbus Based DCS - Distributed Control Systemsujay pujari100% (1)
- MatrikonOPC Windows XPSP2 2003SP1 DCOM ConfigurationDocument26 pagesMatrikonOPC Windows XPSP2 2003SP1 DCOM ConfigurationmatteoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Alarm Management Software - TBDocument21 pagesConsolidated Alarm Management Software - TBbmw316No ratings yet
- Basic: Fieldmate R1.02 For The SalespersonDocument22 pagesBasic: Fieldmate R1.02 For The SalespersonNumanNo ratings yet
- OperTune QuickStart Guide OPR-R310.1-001Document1 pageOperTune QuickStart Guide OPR-R310.1-001Anonymous zLwP4FjLNo ratings yet
- Ehpm R2a 2012-08-24Document11 pagesEhpm R2a 2012-08-24Piush KumarNo ratings yet
- Fcs PerformanceDocument4 pagesFcs Performanceaden mngNo ratings yet
- Technical Product Guide For Tri GPDocument58 pagesTechnical Product Guide For Tri GPjuandals100% (1)
- Part#10 Tristation SOEDocument21 pagesPart#10 Tristation SOEsheikhusama91100% (1)
- New Centum VP Dcs With Network Io WhitepaperDocument4 pagesNew Centum VP Dcs With Network Io WhitepaperFarrukh MajeedNo ratings yet
- Dcs BtechDocument55 pagesDcs BtechGlan Devadhas100% (1)
- Manual and Feedback ControlDocument36 pagesManual and Feedback Controlesakkiraj1590No ratings yet
- Mulcom TokuchuDocument32 pagesMulcom TokuchuWalid AissaNo ratings yet
- F8628XDocument37 pagesF8628XscribdkhatnNo ratings yet
- Prosafe RSDocument3 pagesProsafe RSDavide ContiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 StudentsDocument59 pagesModule 1 StudentsMahesh M P NairNo ratings yet
- Experion Server Specifications and PDFDocument38 pagesExperion Server Specifications and PDFObinna Benedict ObiojiNo ratings yet
- Profibus Chapter 8Document20 pagesProfibus Chapter 8aromero888No ratings yet
- Flowchart Start: Device - I D Acquisiti On OK?Document22 pagesFlowchart Start: Device - I D Acquisiti On OK?cruzleenoNo ratings yet
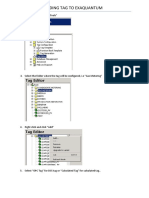
- Adding ExaQuantum TagDocument2 pagesAdding ExaQuantum TagHadi Kusuma RachmatNo ratings yet
- Process Control: An Introductory Guide To Control Concepts For Chemical Engineers (1 of 4)Document34 pagesProcess Control: An Introductory Guide To Control Concepts For Chemical Engineers (1 of 4)tonful143100% (1)
- 6.5.11 Modify Existing Point - Via Reconstitute MethodDocument2 pages6.5.11 Modify Existing Point - Via Reconstitute MethodFrediNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa Giza PDFDocument187 pagesYokogawa Giza PDFWalid AissaNo ratings yet
- 1 OMC2015 ISA YOKOGAWA Optimization Vs PerformanceDocument43 pages1 OMC2015 ISA YOKOGAWA Optimization Vs PerformanceWalid AissaNo ratings yet
- CS3000 R3 Engineering Course Day 1: Yokogawa Engineering Asia Singapore Training CentreDocument60 pagesCS3000 R3 Engineering Course Day 1: Yokogawa Engineering Asia Singapore Training CentreNuman100% (1)
- Yokogawa Terminal BoardsDocument4 pagesYokogawa Terminal BoardsMohammed Abd El RazekNo ratings yet
- VPEG Day3 R6.03Document44 pagesVPEG Day3 R6.03Bilal MubashirNo ratings yet
- World's First Truly Integrated Safety Controller: Safe, Reliable and Available Control Without CompromiseDocument6 pagesWorld's First Truly Integrated Safety Controller: Safe, Reliable and Available Control Without CompromiseDinesh JadavNo ratings yet
- Ongc Project ReportDocument29 pagesOngc Project ReportAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 12 - 04R201 - 1 - Configure Device Control ModuleDocument16 pages12 - 04R201 - 1 - Configure Device Control Modulemilaan favNo ratings yet
- Security&OpmarkDocument19 pagesSecurity&Opmarksina20795No ratings yet
- Centum VP His Builders Lesson 2: Objectives of This LessonDocument22 pagesCentum VP His Builders Lesson 2: Objectives of This LessonhalifNo ratings yet
- DCS Practical 4Document3 pagesDCS Practical 4Vj NadarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Division: FF/HART ConfigurationDocument34 pagesEngineering Division: FF/HART ConfigurationJorge Pérez FrisanchoNo ratings yet
- S56H1021Document50 pagesS56H1021saNo ratings yet
- Dcs Bu33g01a13 01e YokogawaDocument21 pagesDcs Bu33g01a13 01e Yokogawawira ekaNo ratings yet
- HI 800 439 E H41qH51q Maintenance Manual PDFDocument20 pagesHI 800 439 E H41qH51q Maintenance Manual PDFAli HadabeenNo ratings yet
- His ConfigurationDocument80 pagesHis ConfigurationIndraAtmajaNo ratings yet
- ELOP II-NT Resource TypeDocument243 pagesELOP II-NT Resource TypeAkoKhalediNo ratings yet
- 09 RS485 Communication Modbus RTU ALR121Document15 pages09 RS485 Communication Modbus RTU ALR121Fatholla SalehiNo ratings yet
- 04 ECG NormalDocument13 pages04 ECG NormalJevisco LauNo ratings yet
- CS3000 R3 Engineering Course Day 4: Yokogawa Engineering Asia Singapore Training CentreDocument50 pagesCS3000 R3 Engineering Course Day 4: Yokogawa Engineering Asia Singapore Training CentreNumanNo ratings yet
- Lesson02 Ident RSLogix SFTW SiemensDocument12 pagesLesson02 Ident RSLogix SFTW SiemensใบบอนสิชลNo ratings yet
- ELOP OverviewDocument8 pagesELOP Overviewsina20795No ratings yet
- CentumVP-Password ResetDocument2 pagesCentumVP-Password ResetDang Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Performance Tuning Fundementals Version 1Document49 pagesPerformance Tuning Fundementals Version 1j2pabloNo ratings yet
- Adcnas001 Users Dell HTML Training Document Uploads Docs PowerEdgeDocument116 pagesAdcnas001 Users Dell HTML Training Document Uploads Docs PowerEdgehulbertcNo ratings yet
- 02) CP Training-STARDOM-Overview of IEC - Programming - FuFb (With Hands-On)Document10 pages02) CP Training-STARDOM-Overview of IEC - Programming - FuFb (With Hands-On)Saad Bro100% (1)
- Im32q01e10 31eDocument86 pagesIm32q01e10 31eDo HungNo ratings yet
- CENTUM VP Documents - Yokogawa Electric CorporationDocument1 pageCENTUM VP Documents - Yokogawa Electric CorporationDhirender DagarNo ratings yet
- Centumvp1 PDFDocument86 pagesCentumvp1 PDFkishoreprithikaNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa Unified Gateway StationDocument6 pagesYokogawa Unified Gateway StationcarlitoxramosNo ratings yet
- S02B1021Document75 pagesS02B1021salaNo ratings yet
- 6 Man FeedbackControlDocument36 pages6 Man FeedbackControlNahid ReisiNo ratings yet
- 英文PID资料Document3 pages英文PID资料Richard LeeNo ratings yet
- RT522 92 - 96Document5 pagesRT522 92 - 96muhamad iqbalNo ratings yet
- Split Range Control and Valve Position ControlDocument36 pagesSplit Range Control and Valve Position ControlItss Mee HadiNo ratings yet
- AN190610-1 Rev B - P1-PIDDocument21 pagesAN190610-1 Rev B - P1-PIDHector Velez PizaNo ratings yet
- Handout - 1: Sub:Ipc Class:Be 5Document6 pagesHandout - 1: Sub:Ipc Class:Be 5Abhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solar Gas TurbineDocument4 pagesSolar Gas TurbineHamdi Makni100% (1)
- Cohen - Gas Turbine Theory PDFDocument42 pagesCohen - Gas Turbine Theory PDFHamdi MakniNo ratings yet
- Control Valve: Project: CPF Chergui and CercinaDocument1 pageControl Valve: Project: CPF Chergui and CercinaHamdi MakniNo ratings yet
- Ge Fanuc 90 70 PLC ManualDocument522 pagesGe Fanuc 90 70 PLC ManualHamdi MakniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Quarter 1 - Module 5: "Recognize Common Isotopes and Their Uses."Document13 pagesChemistry: Quarter 1 - Module 5: "Recognize Common Isotopes and Their Uses."Norman100% (2)
- Chrysler Customer Specifics For PPAP, AMEF 5th Edition August 2015Document8 pagesChrysler Customer Specifics For PPAP, AMEF 5th Edition August 2015Absalón Rocael Anzueto100% (1)
- Quality Control ProcedureDocument12 pagesQuality Control ProcedureZiya Ahmed100% (6)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/42Ashtav ArunNo ratings yet
- Credit Card NCC BANKDocument1 pageCredit Card NCC BANKKazi Foyez AhmedNo ratings yet
- RC3000Document2 pagesRC3000cipri_73No ratings yet
- 1 Haunted Perron ManorDocument185 pages1 Haunted Perron Manormiguel ghanemNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Man TemplateDocument1 pageInfrastructure Man Template1namillied08No ratings yet
- M012/M013 Service ManualDocument201 pagesM012/M013 Service ManualJean AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet CompressedDocument6 pagesData Sheet CompressedPrankitNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Prosthetic Marginal Fit and Implant SurvivalGustavo IsmaelNo ratings yet
- 70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedDocument46 pages70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedManish BansalNo ratings yet
- KPI Class KPI Name KPI Formula Unit: O - O ComparisionDocument3 pagesKPI Class KPI Name KPI Formula Unit: O - O ComparisionOptimizacion CCSNo ratings yet
- Legend of Legaia ArtsDocument5 pagesLegend of Legaia ArtsFlorian Marteein YambaliaNo ratings yet
- Politeness in Friends TV Series Does It Represent American Value?Document7 pagesPoliteness in Friends TV Series Does It Represent American Value?Dieu LinhNo ratings yet
- Cultural Anthropology: Appreciating Cultural Diversity by Conrad Kottak - 15e, TEST BANK 0078035007Document16 pagesCultural Anthropology: Appreciating Cultural Diversity by Conrad Kottak - 15e, TEST BANK 0078035007jksmtnNo ratings yet
- Titan T200 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesTitan T200 Spec SheetKim JunNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: Survey Camp Report 2015Document5 pagesAcknowledgement: Survey Camp Report 2015riyasNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument20 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchJewelrhey Radcliffe MiddletonNo ratings yet
- Rutgers University Intermediate Microeconomics Syllabus 2Document4 pagesRutgers University Intermediate Microeconomics Syllabus 2Sally MistyNo ratings yet
- ScorecardDocument15 pagesScorecardKarthik KadambiNo ratings yet
- 1 PTI Introduction1Document29 pages1 PTI Introduction1Creation YourNo ratings yet
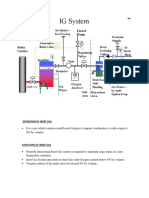
- IGS System-1Document11 pagesIGS System-1manojNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes RaDocument11 pagesLearning Outcomes Raapi-349210703No ratings yet
- Personal Nursing Leadership PaperDocument7 pagesPersonal Nursing Leadership Paperapi-625175559No ratings yet
- Interview Prep Packet!: Part 1: Talk The Talk!Document8 pagesInterview Prep Packet!: Part 1: Talk The Talk!koti3No ratings yet
- BRANIGAN - Eduard - A Point of View in The CinemaDocument6 pagesBRANIGAN - Eduard - A Point of View in The CinemaSonia RochaNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-608950669No ratings yet
- The Feminist Critique of Language ApproachDocument1 pageThe Feminist Critique of Language ApproachIstiaque Hossain LabeebNo ratings yet
- AEC 2018 Aluminum Extrusion ManualDocument191 pagesAEC 2018 Aluminum Extrusion ManualJuan Andrés Díaz RiveroNo ratings yet