Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toshiba IGBT BCE0010 - Catalog
Toshiba IGBT BCE0010 - Catalog
Uploaded by
Floricica Victor VasileOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Toshiba IGBT BCE0010 - Catalog
Toshiba IGBT BCE0010 - Catalog
Uploaded by
Floricica Victor VasileCopyright:
Available Formats
PRODUCT GUIDE
Discrete IGBTs
2009-3
http://www.semicon.toshiba.co.jp/eng
SEMI CONDUCTOR
SEMI CONDUCTOR SEMI CONDUCTOR
2
1
Features and Structure
C
o
lle
c
to
r
M
E
T
A
L
p
+
n
+
n
p+
n+
n
G
A
T
E
B
O
N
D
IN
G
P
A
D
G
A
T
E
M
E
T
A
L
P
O
L
Y
S
IL
IC
O
N
IN
S
U
L
A
T
O
R
p+
p+
p+
p+
p+
p
+
p
+
n
+
n
+
n
+
n
+
n
+
E
M
IT
T
E
R
M
E
T
A
L
p
+
p
+
p p p
n
+
Emitter
Gate
Collector
Electrode
n
+
n
+
n
+
n
Gate
Collector
Emitter
Collector
Emitter
Gate
Rn- (MOD)
Collector
Emitter
Gate
Rn- (MOD)
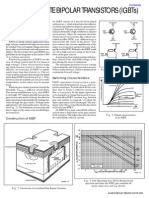
IGBT: Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
The Toshiba discrete IGBTs are available in high-voltage and high-current ratings. They are used in inverter and power
conversion circuits for such diverse applications as motor drivers, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, IH cookers,
plasma display panels (PDPs), strobe flashes and so on.
(1) IGBTs also featuring fast switching
(2) Low collector-emitter saturation voltage even in the large current area
(3) IGBTs featuring a built-in diode with optimal characteristics tailored to specific applications
(4) High input impedance allows voltage drives
(5) Available in a variety of packages
Features of the Toshiba Discrete IGBTs
The basic structure of the planar IGBT consists of four layers (pnpn), as shown in the following figure. Low
saturation voltage is achieved by using a pnp transistor to allow conductivity modulation during conduction. Unlike
MOSFETs, the IGBT does not have an integral reverse diode, since the collector contact is made on the p
+
layer.
Construction
IGBTs combine the MOSFET advantage of high input impedance with the bipolar transistor
advantage of high-voltage drive.
The conductivity modulation characteristics of a bipolar transistor make it ideal for load
control applications that require high breakdown voltage and high current.
Toshiba offers a family of fast switching IGBTs, which are low in carrier injection and
recombination in carrier.
Equivalent Circuit Planar Structure
3
2
IGBT Technical Overview
2006 2008 2010
(4) Soft switching (next gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
(1) High ruggedness (3rd gen): Low VCE(sat) and high ruggedness due to optimized carrier injection and thinner wafers
(2) Soft switching (5th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to trench gate structure
(3) High ruggedness (next gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
1200 V
(1) Soft switching (4th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to trench gate structure
(2) Soft switching (5th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to optimized carrier injection and trench gate structure
(3) Soft switching (6th gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
900 to
1500 V
(1) High ruggedness (3rd gen): Low VCE(sat) and high ruggedness due to optimized carrier injection and thinner wafers
(2) Fast switching (4th gen): High speedy tf due to optimized carrier injection
(3) Soft switching (4th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to trench gate structure
(4) High ruggedness (next gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
(5) Fast switching (next gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
(6) Soft switching (5th gen): Thinner wafers and finer process geometries
600 V
(1) Strobe flashes (5th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to trench gate structure
(2) Strobe flashes (6th gen): High current due to trench gate structure and optimized wafers
(3) Strobe flashes (7th gen): High current due to optimized wafers and finer process geometries
400 V
Year
(1) Plasma displays (4th gen): Low VCE(sat) due to trench gate structure and high IC due to life time control
(2) Plasma displays (4th gen): Improved transient performance due to Cu connector
(3) Plasma displays (next gen): Low turn-on loss due to thinner wafers and finer process geometries
300 to
400 V
0
2.8
2.6
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
High-speed: GT60M323
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
High-speed: GT50N322A(1000V)
Low-VCE(sat): GT60M303
GT60M324
Eoff(mJ) @VCC = 140 V, IC = 50 A, VGG = 20 V, RG = 10 , C = 0.33 F, L = 30 H
V
C
E
(
s
a
t
)
(
V
)
@
I
C
=
5
0
A
,
V
G
E
=
1
5
V
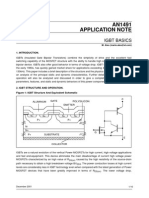
Prior to the development of IGBTs, power MOSFETs were used for power amplifier applications which require high input
impedance and fast switching. However, at high voltages, the on-state resistance rapidly increases as the breakdown voltage
increases. It is thus difficult to improve the conduction loss of power MOSFETs.
On the other hand, the IGBT structure consists of a PNP bipolar transistor and a collector contact made on the p
+
layer. The
IGBT has a low on-state voltage drop due to conductivity modulation.
The following figure shows the VCE(sat) curve of a soft-switching 900-V IGBT. Toshiba has offered IGBTs featuring fast switching by
using carrier lifetime control techniques. Now, Toshiba offers even faster IGBTs with optimized carrier injection into the collector Player.
In the future, Toshiba will launch IGBTs with varied characteristics optimized for high-current-conduction and high-frequency-
switching applications. The improvements in IGBTs will be spurred by optimized wafers, smaller pattern geometries and
improved carrier lifetime control techniques.
900-V IGBT for Soft-Switching
Discrete IGBT Development Trends
NEW
4
Version
Serial number
1: N-channel
2: P-channel
3: N-channel with built-in
freewheeling diode
Voltage rating (see Table 1.)
Collector current rating (DC)
Discrete IGBT
Letter Voltage (V) Letter Voltage (V) Voltage (V) Letter Example Table 1
C
D
E
F
G
H
150
200
250
300
400
500
J
K
L
M
N
P
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
Q
R
S
T
U
V
1200
1300
1400
1500
1600
1700
GT 60 M 3 03 A
TO-220FL
IGBT Current
Rating IC (A)
@Ta = 25C
DC Pulsed
TSSOP-8 TSON-8 SOP-8 TO-220NIS TO-220SIS
GT8G133
GT8G134
GT8G136
GT10G131
GT5G133
GT8G132
GF30F122
GF30F123
GT45F122
GT45F123
GT45F124
GT45F125
GT45F127
GT30G122
GT45G122
GT45G123
GT45G124
GT45G125
GT30G123
GT45G127
GT30J124
TO-220SM TO-220AB TO-3P(N) TO-3P(N)IS TO-3P(LH)
5
10
15
20
30
50
10
15
25
10
15
20
30
50
15
40
50
30
37
40
50
60
80
15
50
60
50
57
60
42
40
30
10
20
30
40
60
100
20
30
50
20
30
40
60
100
30
100
100
100
100
100
100
120
120
160
30
120
120
120
120
120
80
80
100
130
150
200
120
200
120
200
200
200
GT5J301
GT10J303
GT15J301
GT10J321
GT15J321
GT20J321
GT5J311
GT10J312
GT15J311
GT15J331
GT40G121
GT10J301
GT20J301
GT20J101
GT30J301
GT30J101
GT10Q301
GT10Q101
GT15Q301
GT15Q102
GT30J324
GT30J121
GT40J321
GT40J322
GT40J323
GT50J327
GT50J328
GT50J122
GT50M322
GT50N322A
GT50N324
GT40Q321
GT30J126
GT30J322
GT35J321
GT15M321
GT30J122
GT50J301
GT50J102
GT25Q301
GT25Q102
GT50J325
GT50J121
GT50G321
GT50J322
GT50J322H
GT60J321
GT60J323
GT60J323H
GT80J101B
GT60M303
GT60M323
GT60M324
GT60N322
GT60N321
GT40T302
General-purpose motors
General-purpose inverters
Hard switching
fc: up to 20 kHz
High ruggedness
Series
General-purpose inverters
Fast switching
Hard switching
fc: up to 50 kHz
FS series
General-purpose inverters
Low-VCE(sat) IGBT
Resonant switching
Soft switching
Soft-Switching
Series
Strobe flashes
Plasma display
panels
PFC
Applications and
Features
Breakdown
Voltage
VCES (V)
@Ta = 25C
600
1200
600
600
400
600
900
1000
1200
1500
600
400
300
400
430
600
: Under development
4
Part Numbering Scheme
3
Discrete IGBT Product List
5
80
60
40
20
0
0 4 8 12 16 20 24
Carrier Frequency, fC (kHz)
L
o
s
s
(
W
/
T
r
)
MOSFET
GT50J301
GT50J301:
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
MOSFET (500 V / 50 A):
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
GT50J301:
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
MOSFET (500 V / 50 A):
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
@VGE = 15 V
@ Ta = 125C
VCC = 300 V
VGE = + 15 V
di/dt 400 A/s
@fo = 50 Hz
Po = 7.5 kW
50
40
30
20
10
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Collector - Emitter Voltage, VCE (V)
C
o
l
l
e
c
t
o
r
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
,
I
C
(
A
)
GT50J301
MOSFET
VCE
Ic
t : 0.1s/div
V
C
E
:
1
0
0
V
/
d
i
v
I
C
:
1
0
A
/
d
i
vGT50J301
MOSFET
GT50J301
MOSFET
PL PL
Inverter
Rectifier
circuit
Input
Output
CB
Control
IC - VCE Temperature Characteristics Turn-On Waveform
Power Loss vs. Carrier Frequency Characteristics
Our 3rd generation low-loss and low-noise IGBTs are ideal for inverter applications to reduce switching loss and thus improve
energy efficiency. The following graphs compare the thermal and turn-on characteristics of our 3rd generation IGBTs and
500-V MOSFETs
Low saturation voltage with minimal temperature dependence
Simulation data for inverter applications
Fast reverse-recovery characteristics due to built-in
diode with optimal characteristics
For general-purpose inverters
The fast-switching (FS) series, a new addition to our third-generation IGBTs,
features high ruggedness which helps to improve the energy efficiency of electronic equipment.
General-Purpose
Inverters
Inverter Air
Conditioners
Inverter Washing
Machines
UPS
Discrete IGBT Trend
5-1
General-Purpose Inverter
6
5-1
General-Purpose Inverter
VGE
VCE
IC IC
VGE
VCE
IC
IC
GT20J321(4th generation, FS Series)
Ta = 25C
Ta = 125C
GT20J301(3rd generation)
(LOSS: 0.5 mJ/div)
(VCE: 50 V/div, IC: 5 A/div, VGE: 10 V/div, LOSS: 0.2 mJ/div, t: 0.2 s/div)
VGE
VCE
LOSS
IC IC
VGE
VCE
LOSS
IC IC
LOSS
LOSS
Eon = 0.6 mJ
Eoff = 0.47 mJ
Eon = 0.95 mJ
Eoff = 0.56 mJ
Eon = 1.1 mJ
Eoff = 1.0 mJ
Eon = 0.9 mJ
Eoff = 0.54 mJ
1.1 mJ
0.9 mJ
1.0 mJ
0.54 mJ
GT20J321
Fast-switching
4th generation
GT20J301
High ruggedness
3rd generation
GT20J321
Fast-switching
4th generation
GT20J301
High ruggedness
3rd generation
Typical Waveforms
Compared to the third-generation highly rugged series, the FS series is optimized for switching speed, reducing the total
switching loss (Eon + Eoff) by 30% (according to Toshibas comparative test).
Reduced switching loss of fast-switching IGBTs in comparison with high ruggedness IGBTs
Test condition: IC = 20 A, VGE = 15 V, RG = 33 , Ta = 125C, with inductive load, VCC = 300 V
Turn-On Loss
Fast-Switching (FS) Series
For general-purpose inverters
Turn-Off Loss
7
Single
Emitter
Built-in FRD
Gate
Collector
Gate
Collector
Emitter
*1 : Single
FRD: Fast Recovery Diode
*2 R : Resistive load
L : Inductive load
(FS: Fast Switching)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Package
VCE(sat) Typ. tf Typ.
Main
Applications
M
o
t
o
r
d
r
i
v
i
n
g
(
U
P
S
/
P
F
C
)
H
i
g
h
V
C
E
S
(
1
2
0
0
V
)
H
i
g
h
V
C
E
S
(
6
0
0
V
)
L
o
w
-
f
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
s
w
i
t
c
h
i
n
g
P
o
w
e
r
f
a
c
t
o
r
c
o
r
r
e
c
t
i
o
n
Features
Remarks
Part Number
Main
Applications
Features Part Number
Circuit
Configuration
(*1)
Load
(*2)
IC
DC
(A)
Pulsed
(A)
PC
Tc = 25C
(W) Type
VCES
(V)
@IC
(A)
@VGE
(V) (s) (V)
GT10J321
GT15J321
GT15J331
GT20J321
GT30J121
GT30J126
GT30J324
GT50J121
GT50J325
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
TO-220NIS
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-220NIS
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
10
15
15
20
30
30
30
50
50
20
30
30
40
60
60
60
100
100
29
30
70
45
170
90
170
240
240
2.0
1.9
1.75
2.0
2.0
1.95
2.0
2.0
2.0
10
15
15
20
30
30
30
50
50
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
0.05
0.03
0.10
0.04
0.05
0.05
0.05
0.05
0.05
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
Low VCE(sat)
Isolation Package
GT10Q101
GT10Q301
GT15Q102
GT15Q301
GT25Q102
GT25Q301
GT5J301
GT5J311
GT10J301
GT10J303
GT10J312
GT15J301
GT15J311
GT15J311
GT20J101
GT20J301
GT30J101
GT30J301
GT50J102
GT50J301
GT30J122
1200
1200
1200
1200
1200
1200
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
600
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-220NIS
TO-220FL
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)IS
10
10
15
15
25
25
5
5
10
10
10
15
15
15
20
20
30
30
50
50
30
20
20
30
30
50
50
10
10
20
20
20
30
30
30
40
40
60
60
100
100
100
140
140
170
170
200
200
28
45
90
30
60
35
70
70
130
130
155
155
200
200
75
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
2.1
10
10
15
15
25
25
5
5
10
10
10
15
15
15
20
20
30
30
50
50
50
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
0.16
0.16
0.16
0.16
0.16
0.16
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.15
0.25
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
R
SMD
SMD
SMD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Partial Switching
Converter
SMD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Built-in FRD
Package
VCE(sat) Typ. tf Typ.
I
n
v
e
r
t
e
r
p
o
w
e
r
s
u
p
p
l
i
e
s
(
U
P
S
/
P
F
C
/
m
o
t
o
r
)
F
a
s
t
s
w
i
t
c
h
i
n
g
Remarks
Circuit
Configuration
(*1)
Load
(*2)
IC
DC
(A)
Pulsed
(A)
PC
@VGE @IC
Tc = 25C
(W) Type
VCES
(V) (A) (V) (s) (V)
Circuit Configurations
For general-purpose inverters
Product List
600-V and 1200-V IGBTs (3rd Generation)
600-V Fast-Switching IGBTs (4th Generation)
8
5-2
Soft-Switching Applications
VCE
IC
VCE
IC
VCE
IC
VCE
IC
AC Input Voltage Circuit IGBT Rating
100 V to 120 V
200 V to 240 V
100 V to 240 V
VCES = 900 V to 1000 V
IC = 15 A to 60 A
VCES = 600 V
IC = 30 A to 80 A
VCES = 400 V
IC = 40 A to 50 A
VCES = 1200 V to 1500 V
IC = 40 A
Voltage Resonance Waveform
Current Resonance Waveform
Microwave Ovens IH Rice Cookers
IH Cookers MFPs
IH: Induction heating
MFP: Multifunction Printer
Static inverters in IH cooktops, IH rice cookers and microwave ovens utilize a
soft-switching technique which exhibits low switching loss. Toshiba offers IGBTs suitable
for soft-switching applications.
9
Gate
Collector
Emitter
Gate
Collector
Emitter
Built-in FRD Single
*1 : Single
FRD: Fast Recovery Diode
FWD: Free Wheeling Diode
*2 R : Resistive load
L : Inductive load
Product List
For soft switching
Circuit Configurations
GT40G121
GT50G321
GT30J322
GT35J321
GT40J321
GT40J322
GT40J323
GT50J322
GT50J322H
GT50J327
GT50J328
GT60J321
GT60J323
GT60J323H
GT15M321
GT50M322
GT60M303
GT60M323
GT60M324
GT50N321
GT50N322A
GT50N324
GT60N321
GT60N322
GT40Q321
GT40T302
400
600
900
1000
1200
1500
TO-220AB
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
40
50
30
37
40
40
40
50
50
50
50
60
60
60
15
50
60
60
60
50
50
50
60
57
40
40
80
100
60
100
100
100
80
100
100
100
120
120
120
120
30
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
120
80
80
100
130
75
75
110
110
120
130
130
140
140
200
170
170
55
156
170
200
150
156
156
150
170
200
170
200
1.8
1.8
2.1
1.9
2.1
2.0
2.0
2.1
2.2
1.9
2.0
1.55
1.9
2.1
1.8
2.1
2.1
2.3
1.65
2.5
2.2
1.9
2.3
2.4
2.8
3.7
40
50
50
50
40
40
40
50
50
50
50
60
60
60
15
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
40
60
40
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
15
0.30
0.30
0.25
0.19
0.15
0.24
0.06
0.25
0.16
0.19
0.10
0.30
0.16
0.12
0.20
0.25
0.25
0.09
0.11
0.25
0.10
0.12
0.25
0.11
0.41
0.23
R
Built-in FRD
Built-in FWD
Fast switching
5th generation
Fast switching
Fast switching
Fast switching
Fast switching
6th generation
6th generation
Fast switching
High VCES
Fast switching
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Package
VCE(sat) Typ. tf Typ.
Main
Applications
I
H
r
i
c
e
c
o
o
k
e
r
s
a
n
d
I
H
c
o
o
k
t
o
p
s
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
r
e
s
o
n
a
n
c
e
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
r
e
s
o
n
a
n
c
e
Features Remarks Part Number
Circuit
Configuration
(*1)
Load
(*2)
IC
DC
(A) (V)
Pulsed
(A)
PC
@VGE
(V)
@IC
(A)
TC = 25C
(W)
VCES
(s) (V)
AC 200 V
AC 200 V
AC 100 V
AC 100 V
IGBTs for Soft-Switching Applications
: Under development
10
5-3
Strobe Flash Applications
5-2
Soft-Switching Applications
Hard Switching Soft Switching
SOA Locus for Hard Switching SOA Locus for Soft Switching
Switching Characteristics
(Example)
SOA
IC
IC
IC
VCE
VCE
VCE
High-current,
high-voltage
locus
SOA
IC
VCE
High-current,
low-voltage and
low-current,
high-voltage locus
Thermal resistance limit area
S/B limit area
Current Resonance
(Example)
IC
VCE
Voltage Resonance
(Example)
Comparisons Between Hard and Soft Switching (diagrams shown only as a guide)
Strobe flash control is now prevalent in digital still cameras. Package sizes are getting smaller,
and logic levels are increasingly used to represent the gate drive voltage. Toshiba offers
compact IGBTs featuring low gate drive voltage.
As a voltage-controlled device, the IGBT requires only a few components for drive circuit.
IGBTs require fewer components for the strobe flash circuit (compared to SCRs).
Strobe flash IGBTs are capable of switching large currents.
Single-Lens Reflex Camera DSC, Compact Camera
11
5-3
Strobe Flash Applications
20 k
P-ch
N-ch
910
91
1.2 k
470
3.3-V
power supply
3 V
0
Trigger transformer
Xe lamp
Resistor
Main
Capacitor
Resonant capacitor
IGBT
GT8G134
*1: Board connection example
Collector
5,6,7,8
Gate
4
Emitter
1,2,3
Collector
5,6,7,8
Gate
4
3 1,2
Emitter Emitter for gate drive circuitry
All the emitter terminals should be connected together.
*2: Board connection example
GT8G132
GT8G133
GT10G131
2.3
2.9
2.3
1.1
1.1
1.9
SOP-8*
1
TSSOP-8*
1
SOP-8*
1
The IGBT can operate with a gate drive voltage of 2.5 V to 4.0 V. The common 3.3-V or 5-V internal power supply in a camera
can be used as a gate drive power supply to simplify the power supply circuitry. A zener diode is included between the gate
and emitter to provide ESD surge protection.
400 V / 150 A
400 V / 150 A
400 V / 200 A
VCES / IC Package
(V)
Part Number
PC (W)
@Ta = 25C
GT8G134 1.1 TSSOP-8*
2
Package
VCE(sat) (V)
VCE(sat) (V)
Part Number
PC (W)
@Ta = 25C
GT8G136 1.1 TSSOP-8*
2
Example of an IGBT Gate Drive Circuit (3.3-V Power Supply)
GT5G133
400 V / 150 A
VCES / IC
400 V / 150 A
400 V / 130 A
3.4
(V)
3.5
3.4 0.9
4.0 V / 150 A
4.0 V / 150 A
4.0 V / 200 A
VGE / IC
2.5 V / 150 A
VGE / IC
3 V / 150 A
2.5 V / 130 A TSON-8*
1
5th generation
5th generation
5th generation
Remarks
Remarks
6th generation
5th generation
7th generation
2.5-V to 4.0-V Gate Drive Series
3.3-V Power Supply
5-V Power Supply
For strobe flashes
Product List
: Under development
12
5-4
Plasma Display Panel Applications
PDP (Sustain circuit)
Sustain circuit Energy recovery circuit
Panel
Vsus
X drive circuit
Y drive circuit
X electrodes (X output)
Y electrodes (Y output)
C1
C2
Separation circuit
Example of a Plasma Display Panel Drive Circuit
Parallel MOSFETs have been used for the drive circuitry of plasma
display panels (PDPs). Recently, however, IGBTs are commonly used in
large current applications due to their superior current conduction
capability.
Plasma Displays
Product List
For plasma display panels
GT30F122
GT30F123
GT45F122
GT45F123
GT45F124
GT45F125
GT45F127
GT45F131
300 V / 120 A*
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
300 V / 200 A
25
25
25
26
29
29
26
160
*: @100 s
5th generation
6th generation
5th generation
5th generation
5th generation
5th generation
6th generation
5th generation
2.9 (@120 A)
2.1 (@120 A)
2.7 (@120 A)
2.4 (@120 A)
2.1 (@120 A)
1.45 (@120 A)
1.6 (@120 A)
2.1 (@120 A)
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SM
VCES / Icp @3 s Package Remarks VCE(sat) (V) Max Part Number
PC (W)
@Tc = 25C
300-V IGBTs
*: @100 s
5th generation
6th generation
5th generation
5th generation
5th generation
5th generation
6th generation
5th generation
GT30G122
GT30G123
GT45G122
GT45G123
GT45G124
GT45G125
GT45G127
GT45G131
400 V / 120 A*
430 V / 200 A
400 V / 200 A
400 V / 200 A
400 V / 200 A
400 V / 200 A
430 V / 200 A
400 V / 200 A
25
25
25
26
29
29
26
160
2.6 (@120 A)
2.2 (@120 A)
2.9 (@120 A)
2.6 (@120 A)
2.3 (@120 A)
1.6 (@120 A)
1.7 (@120 A)
2.3 (@120 A)
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SIS
TO-220SM
VCES / Icp @3 s Package Remarks VCE(sat) (V) Max Part Number
PC (W)
@Tc = 25C
400-V IGBTs
5th generation GT30J124 600 V / 200 A 26 2.4 (@120 A) TO-220SIS
VCES / Icp @3 s Package Remarks VCE(sat) (V) Max Part Number
PC (W)
@Ta = 25C
600-V IGBTs
13
6
Package Dimensions
SOP-8
TSON-8
TO-220NIS TO-220SIS
TSSOP-8
Unit: mm
1, 2, 3. Emitter
4. Gate
5, 6, 7, 8. Collector
1, 2, 3. Emitter
4. Gate
5, 6, 7, 8. Collector
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
1, 2, 3. Emitter
4. Gate
5, 6, 7, 8. Collector
10 0.3 2.7 0.2
0.69 0.15
2.54 2.54
3.2 0.2
1
5
0
.
3
0
.
6
4
0
.
1
5
2
.
6
0
.
1
4
.
5
0
.
2
1
3
0
.
5
2
.
8
m
a
x
3
.
0
3
.
9
1 2 3
1.14 0.15
0.25 M A
6
.
0
0
.
3
4
.
4
0
.
2
0.4 0.1
8 5
1 4
0.25 M
1.27
0
.
1
+
0
.
1
0
.
0
5
0
.
1
5
+
0
.
1
0
.
0
5
0.595 typ.
0.5 0.2
5.5 max
5.0 0.2
1
.
5
0
.
2
0.1
3.0 0.1
0
.
8
5
0
.
0
5
4
.
4
0
.
1
0.25 0.05
6
.
4
0
.
3
3.3 max
0
.
0
5
0
.
0
5
0
.
1
6
+
0
.
0
4
0
.
0
2
0.6 0.2
0.65
(0.525)
5 8
1 4
0.05
10 0.3 3.2 0.2 2.7 0.2
3
.
0
3
.
9
1
5
0
.
3
1
3
.
0
m
i
n
1.1
1.1
0.75 0.15
2.54 0.25 2.54 0.25
5
.
6
m
a
x
1 2 3
0
.
7
5
0
.
1
5
2
.
6
4
.
5
0
.
2
3
.
1
0
.
1
0.3 0.05
0
.
2
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
1
5
0
.
2
0.65 0.05
3
.
3
0
.
1
0
.
8
5
0
.
0
5
0
.
1
7
5
0
.
0
3
3.1 0.1
1 4
8 5
3.3 0.1
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
14
6
Package Dimensions
Unit: mm
10.3 max 1.32
1.3
1 2 3
0.76
3
.
0
2
.
5
m
a
x
1
2
.
6
m
i
n
1
5
.
7
m
a
x
6
.
7
m
a
x
3.6 0.2
2.54 0.25 2.54 0.25
0.5
2.6
4
.
7
m
a
x
2
.
0
3
.
3
m
a
x
2.0 0.3
1.0 0.25
+ 0.3
5.45 0.2 5.45 0.2
2
0
.
5
0
.
5
2
0
.
0
0
.
3
9
.
0
2
.
0
4
.
5
1
.
0
3.2 0.2 15.9 max
0
.
6
0
.
1
+
0
.
3
1
.
8
m
a
x
2
.
8
4
.
8
m
a
x
1 2 3
10.3 max
1
.
5
2.54
0.76
9
.
1
1
0
.
6
m
a
x
3
0
.
2
1.32
1 2 3
2
.
6
4
.
7
m
a
x
0
.
5
2.54
1
.
5
0.1
0
.
6
20.5 max 3.3 0.2
6
.
0
1
1
.
0
2
.
0
4
.
0
2
6
.
0
0
.
5
2
.
5
0
2.5
3.0
1.0 0.25
+ 0.3
5.45 0.15 5.45 0.15
0
.
6
0
.
1
0
+
0
.
2
5
1 2 3
2
.
8
5
.
2
m
a
x
2
0
.
0
0
.
6
1
.
5
1.5
2
.
0
1
.
5
5.45 0.2
1
5
.
5
5
.
5
2
1
.
0
0
.
5
5
.
0
0
.
3
1
.
0
3 2 1
1
9
.
4
m
i
n
3
.
6
m
a
x
15.8 0.5
3.5
+ 0.2
0.1
3.6 0.2
5.45 0.2
1.0
2.0
+ 0.25
0.15
0
.
6
+
0
.
2
5
0
.
1
5
3.15
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
1. Gate
2. Collector
3. Emitter
TO-220AB TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(N) TO-3P(LH)
15
7
Final-Phase and Obsolete Products
The following products are in stock but are being phased out of production. The recommended replacements that continue to
be available are listed in the right-hand column. However, the characteristics of the recommended replacements may not be
exactly the same as those of the final-phase and obsolete products. Before using a recommended replacement, be sure to
check that it is suitable for use under the intended operating conditions.
Audio amps Package Package
Final-Phase or
Obsolete Product
Recommended
Obsolete Replacements
Absolute Maximum Ratings
VCES (V) IC (A) DC
Absolute Maximum Ratings
VCES (V) IC (A) DC
MG30T1AL1
MG60M1AL1
GT40M101
GT40M301
GT40Q322
GT40Q323
GT40T101
GT40T301
GT50L101
GT50M101
GT50Q101
GT50S101
GT50T101
GT60J101
GT60J322
GT60M101
GT60M102
GT60M103
GT60M104
GT60M105
GT60M301
GT60M302
GT60M305
GT60M322
GT60N323
GT80J101
GT80J101A
GT8J101
GT8J102
GT8N101
GT8Q101
GT8Q102
GT10Q311
GT15J101
GT15J102
GT15J103
GT15N101
GT15Q101
GT15Q311
GT20J311
GT25H101
GT25J101
GT25J102
GT25Q101
GT30J311
GT50J101
GT5G101
GT5G102
GT5G103
GT8G101
GT8G102
GT8G103
GT10G101
GT10G102
GT15G101
GT20G101
GT20G102
GT25G101
GT25G102
GT50G101
GT50G102
GT75G101
GT20D101
GT20D201
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT40Q321
GT40Q321
GT40T302
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT80J101B
GT60J321
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60M303
GT60N321
GT60N322
GT80J101B
GT80J101B
GT10J303
GT10J312
GT10Q101
GT10Q101
GT20J101
GT15J301
GT15J311
GT15Q102
GT15Q102
GT30J121
GT30J121
GT30J126
GT25Q102
GT50J121
IH
IH
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
IH
IH
IH
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-220SM
TO-3P(SM)
TO-3P(N)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(SM)
TO-3P(SM)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)IS
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(SM)
TO-3P(L)
NPM
DP
DP
NPM
NPM
DP
TO-220NIS
TO-220NIS
TO-220NIS
TO-220FL
TO-220FL
TO-220FL
TO-220FL
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(L)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-220NIS
TO-220SM
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(N)
TO-3P(LH)
TO-3P(LH)
1500
900
900
900
1200
1200
1500
1500
800
900
1200
1400
1500
600
600
900
900
900
900
900
900
900
900
950
1050
600
600
600
600
1000
1200
1200
1200
600
600
600
1000
1200
1200
600
500
600
600
1200
600
600
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
400
250
250
30
60
40
40
39
39
40
40
50
50
50
50
50
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
80
80
8
8
8
8
8
10
15
15
15
15
15
15
20
25
25
25
25
30
50
130 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
150 (pulsed)
150 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
170 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
130 (pulsed)
170 (pulsed)
150 (pulsed)
100 (pulsed)
100 (pulsed)
150 (pulsed)
20
20
60
60
42
42
40
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
60
57
80
80
10
10
10
10
20
15
15
15
15
30
30
30
25
50
900
900
1200
1200
1500
900
900
600
600
900
900
900
900
900
900
900
900
1000
1000
600
600
600
600
1200
1200
600
600
600
1200
1200
600
600
600
1200
600
Soft switching
Resonant switching
General-purpose
motors
General-purpose
inverters
Strobe flashes
Audio amps
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
TOSHIBA is continually working to improve the quality and reliability of its products. Nevertheless, semiconductor devices in general can malfunction or fail due to their inherent electrical
sensitivity and vulnerability to physical stress. It is the responsibility of the buyer, when utilizing TOSHIBA products, to comply with the standards of safety in making a safe design for the entire
system, and to avoid situations in which a malfunction or failure of such TOSHIBA products could cause loss of human life, bodily injury or damage to property. In developing your designs,
please ensure that TOSHIBA products are used within specified operating ranges as set forth in the most recent TOSHIBA products specifications. Also, please keep in mind the precautions
and conditions set forth in the Handling Guide for Semiconductor Devices, or TOSHIBA Semiconductor Reliability Handbook etc.
The TOSHIBA products listed in this document are intended for usage in general electronics applications (computer, personal equipment, office equipment, measuring equipment, industrial
robotics, domestic appliances, etc.). These TOSHIBA products are neither intended nor warranted for usage in equipment that requires extraordinarily high quality and/or reliability or a
malfunction or failure of which may cause loss of human life or bodily injury (Unintended Usage). Unintended Usage include atomic energy control instruments, airplane or spaceship
instruments, transportation instruments, traffic signal instruments, combustion control instruments, medical instruments, all types of safety devices, etc. Unintended Usage of TOSHIBA
products listed in this document shall be made at the customers own risk.
The products described in this document shall not be used or embedded to any downstream products of which manufacture, use and/or sale are prohibited under any applicable laws and
regulations.
The information contained herein is presented only as a guide for the applications of our products. No responsibility is assumed by TOSHIBA for any infringements of patents or other rights of
the third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other rights of TOSHIBA or the third parties.
Please contact your sales representative for product-by-product details in this document regarding RoHS compatibility. Please use these products in this document in compliance with all
applicable laws and regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of controlled substances. Toshiba assumes no liability for damage or losses occurring as a result of noncompliance with
applicable laws and regulations.
BCE0010F
Previous edition: BCE0010E
2009-3(2k)PC-DQ
2009
D
i
s
c
r
e
t
e
I
G
B
T
s
2009-3
Website: http://www.semicon.toshiba.co.jp/eng
Semiconductor Company
(As of October 01, 2008) OVERSEAS SUBSIDIARIES AND AFFILIATES
Toshiba America
Electronic Components, Inc.
Headquarters-Irvine, CA
19900 MacArthur Boulevard,
Suite 400, Irvine, CA 92612, U.S.A.
Tel: (949)623-2900 Fax: (949)474-1330
Buffalo Grove (Chicago)
2150 E. Lake Cook Road, Suite 310,
Buffalo Grove, IL 60089, U.S.A.
Tel: (847)484-2400 Fax: (847)541-7287
Duluth, GA (Atlanta)
3700 Crestwood Pkwy, #160,
Duluth, GA 30096, U.S.A.
Tel: (770)931-3363 Fax: (770)931-7602
San Jose Engineering Center, CA
2590 Orchard Parkway San Jose,
CA 95131, U.S.A.
Tel: (408)526-2400 Fax:(408)526-2410
Wixom (Detroit)
48679 Alpha Drive, Suite 120, Wixom,
MI 48393 U.S.A.
Tel: (248)347-2607 Fax: (248)347-2602
Toshiba Electronics do Brasil Ltda.
Rua Machado Bittencourt, 361, CJ, 1102,
Bairro Vila Clementino, San Paulo, SP,
CEP 04044-001, Brasil
Tel: (011)5085-5990 Fax: (011)5085-5995
Toshiba India Private Ltd.
6F DR. Gopal Das Bhawan 28,
Barakhamba Road, New Delhi, 110001, India
Tel: (011)2331-8422 Fax: (011)2371-4603
Toshiba Electronics Europe GmbH
Dsseldorf Head Office
Hansaallee 181, D-40549 Dsseldorf,
Germany
Tel: (0211)5296-0 Fax: (0211)5296-400
France Branch
Les Jardins du Golf 6 rue de Rome F-93561,
Rosny-Sous-Bois, Cedex, France
Tel: (1)48-12-48-12 Fax: (1)48-94-51-15
Italy Branch
Centro Direzionale Colleoni,
Palazzo Perseo 3,
I-20041 Agrate Brianza, (Milan), Italy
Tel: (039)68701 Fax: (039)6870205
Spain Branch
Parque Empresarial, San Fernando, Edificio Europa,
1
a
Planta, E-28831 Madrid, Spain
Tel: (91)660-6798 Fax:(91)660-6799
U.K. Branch
Delta House, The Crescent Southwood Business Park
Farnborough, Hampshire GU14 ONL, U.K.
Tel: (0870)060-2370 Fax: (01252)53-0250
Sweden Branch
Gustavslundsvgen 18, 5th Floor,
S-167 15 Bromma, Sweden
Tel: (08)704-0900 Fax: (08)80-8459
Toshiba Electronics Asia
(Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
438B Alexandra Road, #06-08/12 Alexandra
Technopark, Singapore 119968
Tel: (6278)5252 Fax: (6271)5155
Toshiba Electronics Service
(Thailand) Co., Ltd.
135 Moo 5, Bangkadi Industrial Park, Tivanon Road,
Pathumthani, 12000, Thailand
Tel: (02)501-1635 Fax: (02)501-1638
Toshiba Electronics Trading
(Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd.
Kuala Lumpur Head Office
Suite W1203, Wisma Consplant, No.2,
Jalan SS 16/4, Subang Jaya, 47500 Petaling Jaya,
Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
Tel: (03)5631-6311 Fax: (03)5631-6307
Penang Office
Suite 13-1, 13th Floor, Menara Penang Garden,
42-A, Jalan Sultan Ahmad Shah,
10050 Penang, Malaysia
Tel: (04)226-8523 Fax: (04)226-8515
Toshiba Electronics Philippines, Inc.
26th Floor, Citibank Tower, Valero Street, Makati,
Manila, Philippines
Tel: (02)750-5510 Fax: (02)750-5511
Toshiba Electronics Asia, Ltd.
Hong Kong Head Office
Level 11, Tower 2, Grand Century Place, No.193,
Prince Edward Road West, Mongkok, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: 2375-6111 Fax: 2375-0969
Beijing Office
Room 814, Beijing Fortune Building, No.5 Dong San Huan Bei-Lu,
Chao Yang District, Beijing, 100004, China
Tel: (010)6590-8796 Fax: (010)6590-8791
Chengdu Office
Room 2508A, 2 Zongfu Street, Times Plaza,
Chengdu 610016 Sichuan, China
Tel: (028)8675-1773 Fax: (028)8675-1065
Qingdao Office
Room 4(D-E), 24F, International Financial Center,
59 Xiang Gang Zhong Road, Qingdao 266071, Shandong, China
Tel: (532)8579-3328 Fax: (532)8579-3329
Toshiba Electronics Shenzhen Co., Ltd.
28/F, Excellence Times Square Building, 4068 Yi Tian Road,
Fu Tian District, Shenzhen 518048, China
Tel: (0755)2399-6897 Fax: (0755)2399-5573
Toshiba Electronics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Shanghai Head Office
11F, HSBC Tower, 1000 Lujiazui Ring Road,
Pudong New Area, Shanghai 200120, China
Tel: (021)6841-0666 Fax: (021)6841-5002
Hangzhou Office
502 JiaHua International Business Center,
No.28 HangDa Road, Hangzhou, 310007, China
Tel: (0571)8717-5004 Fax: (0571)8717-5013
Nanjing Office
23F Shiji Shangmao Plaza,
No.49 Zhong Shan South Road, Nanjing, 210005, China
Tel: (025)8689-0070 Fax: (025)8689-0125
Toshiba Electronics (Dalian) Co., Ltd.
14/F, Senmao Building, 147, Zhongshan Road,
Xigang Dist., Dalian, 116011, China
Tel: (0411)8368-6882 Fax: (0411)8369-0822
Tsurong Xiamen Xiangyu Trading Co., Ltd.
14G, International Bank BLDG., No.8 Lujiang Road,
Xiamen, 361001, China
Tel: (0592)226-1398 Fax: (0592)226-1399
Toshiba Electronics Korea Corporation
Seoul Head Office
891, Samsung Life Insurance Daechi Tower 20F, Daechi-dong,
Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 135-738, Korea
Tel: (02)3484-4334 Fax: (02)3484-4302
Daegu Office
16F, Hosoo Bldg. 50-3 Dongin-Dong 2(i)-GA,
Jung-gu, Daegu, Korea 700-732
Tel: (053)428-7610 Fax: (053)428-7617
Toshiba Electronics Taiwan Corporation
Taipei Head Office
10F., No.10, Sec.3, Minsheng E.Rd., Taipei City 10480, Taiwan
Tel: (02)2508-9988 Fax: (02)2508-9999
Kaohsiung Office
16F-A, Chung-Cheng Building, 2, Chung-Cheng 3Road,
Kaohsiung, 80027, Taiwan
Tel: (07)237-0826 Fax: (07)236-0046
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsFrom EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNo ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Mosfet Igbt BJT Difference and ApplicationDocument5 pagesMosfet Igbt BJT Difference and ApplicationSangammeshwra AbNo ratings yet
- 84 - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (Igbts)Document2 pages84 - Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (Igbts)Guillermo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- CA3080Document12 pagesCA3080yusufwpNo ratings yet
- IGBT TransistorsDocument16 pagesIGBT TransistorsMiodragNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Kemppi Master Mastertig 1400 1500 2200 2800 3500Document31 pagesKemppi Master Mastertig 1400 1500 2200 2800 3500Acubas0% (1)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Nippon PDFDocument96 pagesNippon PDFEugen BratuNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Circuit Breacker 1Document156 pagesCircuit Breacker 1Paulo Cesar100% (1)
- Photovoltaic TechnologyDocument181 pagesPhotovoltaic TechnologyMUKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Guia Igbt Toshiba 2011Document16 pagesGuia Igbt Toshiba 2011Francisco Orozco100% (1)
- Igbt PDFDocument16 pagesIgbt PDFPablo AllosiaNo ratings yet
- Igb 0001Document15 pagesIgb 0001Дејан МркајаNo ratings yet
- Latest Technology PT Igbts vs. Power Mosfets: Application Note Apt0302 Rev. A April 4, 2003Document6 pagesLatest Technology PT Igbts vs. Power Mosfets: Application Note Apt0302 Rev. A April 4, 2003Jyothsna VayyalaNo ratings yet
- MK 2 PiDocument7 pagesMK 2 PiA Whick Bumbum TralalaNo ratings yet
- Insulate D Gate Bipolart Ransisto R (Igbt) : IGBT Is A Voltage Controlled Device. It Has High Input Impedance Like ADocument67 pagesInsulate D Gate Bipolart Ransisto R (Igbt) : IGBT Is A Voltage Controlled Device. It Has High Input Impedance Like AIssam ZeidanNo ratings yet
- IGCTDocument6 pagesIGCTsuresh5254No ratings yet
- An 9742Document12 pagesAn 9742Alejandra SeguraNo ratings yet
- IGBT Module Series For Advanced-NPC Circuits: Kosuke Komatsu Takahito Harada Yoshiyuki KusunokiDocument6 pagesIGBT Module Series For Advanced-NPC Circuits: Kosuke Komatsu Takahito Harada Yoshiyuki KusunokivinaykumaarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IGBT and GTO For High Power Inverters PDFDocument9 pagesComparison of IGBT and GTO For High Power Inverters PDFLuis Eduardo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Inversor Abb 20kwDocument4 pagesInversor Abb 20kwapi-290643326No ratings yet
- 600/1200V Igbts Set Benchmark Performance in High Switching Speed ApplicationsDocument4 pages600/1200V Igbts Set Benchmark Performance in High Switching Speed Applicationsthienvuong90No ratings yet
- CMOS Implemented VDTA Based Colpitt OscillatorDocument4 pagesCMOS Implemented VDTA Based Colpitt OscillatorijsretNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Voltage TransformerDocument12 pagesCapacitor Voltage TransformerThangco HutNo ratings yet
- Advancements in P.esDocument30 pagesAdvancements in P.esSifar TeenNo ratings yet
- An 9020Document25 pagesAn 9020Reshmi Parikal RaghavanNo ratings yet
- A1230 DatasheetDocument17 pagesA1230 DatasheetBruno Koch SchmittNo ratings yet
- An 9742Document12 pagesAn 9742EmersonMagnoMoraesNo ratings yet
- CA3102Document11 pagesCA3102bonaparteCWBNo ratings yet
- 24v CFL BallastDocument8 pages24v CFL BallastAkshaya SVNo ratings yet
- IGBT or MOSFET: Choose Wisely: by Carl Blake and Chris Bull, International RectifierDocument5 pagesIGBT or MOSFET: Choose Wisely: by Carl Blake and Chris Bull, International RectifiergubiliNo ratings yet
- 984-480 SystemspecsDocument12 pages984-480 SystemspecsJoao CarlosNo ratings yet
- Abb High Power SemiconductorsDocument36 pagesAbb High Power SemiconductorskarakuloNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor DrivesDocument30 pagesInduction Motor DrivesAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- LM3080 Operational Transconductance Amplifier: General Description FeaturesDocument7 pagesLM3080 Operational Transconductance Amplifier: General Description FeaturesJohn PachecoNo ratings yet
- Air Circuit Breaker Product Catalogue and ACB Price List - ShopelectDocument4 pagesAir Circuit Breaker Product Catalogue and ACB Price List - ShopelectShopElectNo ratings yet
- Reles de Proteccion T60 & T35Document53 pagesReles de Proteccion T60 & T35Carlos MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lm386 DatasheetDocument7 pagesLm386 DatasheetJM Carrasco HottmanNo ratings yet
- Features Description: FM IF SystemDocument7 pagesFeatures Description: FM IF Systemlu1agpNo ratings yet
- TRN Spec SheetDocument2 pagesTRN Spec Sheetapi-170472102No ratings yet
- 5101 Motor DriverDocument11 pages5101 Motor DriverMoise CristinaNo ratings yet
- Igbt BasicsDocument16 pagesIgbt BasicsRahul SoniNo ratings yet
- Choosing Power Switching Devices For SMPS Designs: Mosfets or Igbts?Document6 pagesChoosing Power Switching Devices For SMPS Designs: Mosfets or Igbts?RubenG200No ratings yet
- CA3140Document20 pagesCA3140Brzata PticaNo ratings yet
- New High Power Semiconductors: High Voltage Igbts and GctsDocument7 pagesNew High Power Semiconductors: High Voltage Igbts and GctsSinan PravadaliogluNo ratings yet
- Application Note 9017 Manufacturing Technology of A Small Capacity Inverter Using A Fairchild IGBTDocument28 pagesApplication Note 9017 Manufacturing Technology of A Small Capacity Inverter Using A Fairchild IGBTRajesh VyasNo ratings yet
- Functionarea IGCT Si IGBTDocument58 pagesFunctionarea IGCT Si IGBTFaqRONo ratings yet
- AS15GDocument12 pagesAS15Gjailton1958No ratings yet
- Voltage-Controlled Oscillator: ... The Analog Plus CompanyDocument24 pagesVoltage-Controlled Oscillator: ... The Analog Plus CompanyMoltrevNo ratings yet
- CA3140Document19 pagesCA3140samNo ratings yet
- SolarADEPT Workshop NxtGenPwr Singh PDFDocument19 pagesSolarADEPT Workshop NxtGenPwr Singh PDFPaola MantillaNo ratings yet
- Irgb4055Pbf: PDP Trench IgbtDocument7 pagesIrgb4055Pbf: PDP Trench IgbtdbayeahNo ratings yet
- p340-h340 OptronDocument19 pagesp340-h340 Optronfyusupov882No ratings yet
- DSA91000 E-Series ManualDocument32 pagesDSA91000 E-Series Manualabdullahnisar92No ratings yet
- Irg 7 SC 28 UpbfDocument8 pagesIrg 7 SC 28 UpbfEdgar OcantoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ToshibaDocument43 pagesCatalogo Toshibapepitito22100% (1)
- 3 Hints For Application: 3.1 Dimensioning and Selection of Mosfet, Igbt and Skiippack ModulesDocument7 pages3 Hints For Application: 3.1 Dimensioning and Selection of Mosfet, Igbt and Skiippack ModulesDan DanubiusNo ratings yet
- Corporate Profile: 00A2-E-0003a Printed in Japan 2013.7Document15 pagesCorporate Profile: 00A2-E-0003a Printed in Japan 2013.7surojit99No ratings yet
- The Best Example of Rectifier That Is Used in Our Daily Life Is in The Mobile Phone Charger andDocument3 pagesThe Best Example of Rectifier That Is Used in Our Daily Life Is in The Mobile Phone Charger andENTERTAINMENT TUBENo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ch-1 PDFDocument50 pagesPower Electronics ch-1 PDFbelayneh ayichewNo ratings yet
- CM100DY-24NF MitsubishiElectricSemiconductorDocument4 pagesCM100DY-24NF MitsubishiElectricSemiconductorJerry LeeNo ratings yet
- COT-01 NewDocument2 pagesCOT-01 NewamitcrathodNo ratings yet
- Power SytemsDocument6 pagesPower SytemsAshwin RaghavanNo ratings yet
- STGB18N40LZT4, STGD18N40LZ, STGP18N40LZ: Automotive-Grade 390 V Internally Clamped IGBT E 180 MJDocument25 pagesSTGB18N40LZT4, STGD18N40LZ, STGP18N40LZ: Automotive-Grade 390 V Internally Clamped IGBT E 180 MJJoakin BcNo ratings yet
- 01 EMC EMI InverterDocument40 pages01 EMC EMI Inverterkaviarasu1990No ratings yet
- T - Type 1Document11 pagesT - Type 1Jhonatan Leandro Clavijo TrochesNo ratings yet
- Energy Saving in Induction MotorsDocument11 pagesEnergy Saving in Induction MotorsS Bharadwaj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices ClassificationDocument9 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices ClassificationdevchandarNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet IGBTDocument12 pagesData Sheet IGBTAndrés David Martínez MarteloNo ratings yet
- High and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryDocument14 pagesHigh and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryLuis ToledoNo ratings yet
- Devices Part TwoDocument19 pagesDevices Part Twohabte gebreial shrashrNo ratings yet
- IGBT BasicsDocument20 pagesIGBT Basicsscrewyou2222No ratings yet
- The MOS Controlled Thyristor (MCT)Document4 pagesThe MOS Controlled Thyristor (MCT)Debayan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesEce-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFAdarsh S Shettigar100% (1)
- SiC Power Devices On QUASIC and SiCOI Smart-CutDocument7 pagesSiC Power Devices On QUASIC and SiCOI Smart-CutTeststeNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Using IGBT Modules 4.1 Structure and Operation of IGBT ModuleDocument27 pages4.0 Using IGBT Modules 4.1 Structure and Operation of IGBT Modulerodruren01No ratings yet
- Fmea Power ElctronicsDocument79 pagesFmea Power ElctronicsNipun DahraNo ratings yet
- Vincotech Layout 1Document5 pagesVincotech Layout 1Rajani Kumar ThirukoluriNo ratings yet