Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elte SGD b8 Genital
Uploaded by
GWKNANDAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elte SGD b8 Genital
Uploaded by
GWKNANDACopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy of Female Genital System
SGD B8
Day 2
Case 1 : A 42 year-old woman is referred for vaginal sonography to rule out luteal cyst. The sonic probe is
placed in the anterior vaginal fornix and aimed anteriorly
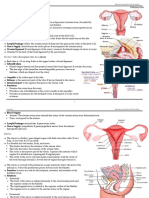
1. hat is the normal position of the uterus and its relation to other structure in pelvic cavity!
The non-gravid "non-pregnant# uterus usually lies in the lesser pelvis$ with its body lying on the urinary
bladder and its cervix between the urinary bladder and rectum. Adult uterus is usually anteverted "tipped
anterosuperiorly relative to the axis of the vagina# and anteflexed "flexed or bent anteriorly relative to the
cervix$ creating the angle of flexion# so that its mass lies over the bladder
%elation of uterus :
Anteriorly "anteroinferiorly in its normal anteverted position#: the vesicouterine pouch and superior
surface of the bladder& the supravaginal part of the cervix is related to the bladder and is separated
from it by only fibrous connective tissue.
'osteriorly: the rectouterine pouch and the anterior surface of rectum&
(aterally: the peritoneal broad ligament and the fascial cardinal ligaments& the ureters
2. )ow much of the uterus can be felt per rectum!
*t normaly cannot palpable rectaly$ +ust can felt its wall to examine if there is any abnormality in there.
,. hat is the normal support of the uterus!
The principal supports of the uterus holding it in this position are both passive and active or dynamic.
-ynamic support of the uterus is provided by the pelvic diaphragm. *ts tone during sitting and standing and
active contraction during periods of increased intra-abdominal pressure "snee.ing$ coughing$ etc.# is
transmitted through the surrounding pelvic organs and the endopelvic fascia in which they are embedded.
'assive support of the uterus is provided by its position/the way in which the normally anteverted and
anteflexed uterus rests on top of the bladder. hen intra-abdominal pressure is increased$ the uterus is
pressed against the bladder
4. hy do you thin0 the uterus is in that position!
1. -escribe the ovaries$ uterine tubes$ uterus and broad ligaments!
Ovaries : The ovaries are almond-shaped and -si.ed female gonads in which the oocytes "female
gametes or germ cells# develop. They are also endocrine glands that produce reproductive
hormones. 2ach ovary is suspended by a short peritoneal fold or mesentery
Uterine tubes : The uterine tubes "formerly called oviducts or fallopian tubes# conduct the oocyte.
They are approximately 13 cm long and lie in a narrow mesentry called the mesosalpinx. They are
divided into 4 parts& infundibulum$ ampula. *sthmus$ uterine part
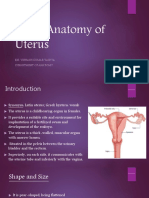
Uterus : The uterus "womb# is a thic0-walled$ pear-shaped$ hollow muscular organ. *t is located in
the lesser pelvis. Adult uterus is usually anteverted and anteflexed so that it les over the bladder.
Broad ligaments : The broad ligament of the uterus is a double layer of peritoneum "mesentery#
that extends from the sides of the uterus to the lateral walls and floor of the pelvis.This ligament
Anatomy of Female Genital System
SGD B8
Day 2
assists in 0eeping the uterus in position. The two layers of the broad ligament are continuous with
each other at a free edge that surrounds the uterine tube
4. -escribe the peritoneal relationship of the ovary and the uterine tubes
2ach ovary is suspended by a short peritoneal fold or mesentery$ the mesovarium. The
mesovarium is a subdivision of a larger mesentery of the uterus$ the broad ligament
The uterine lie in a narrow mesentery$ the mesosalpinx$ forming the free anterosuperior edges of
the broad ligaments
*t extend laterally from the uterine horns and open into the peritoneal cavity near the ovaries. *n
ovaries$ it is suspended in peritoneal cavity 5 not covered by peritoneum.
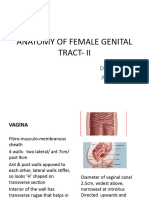
6. -escribe the walls$ fornices and immediate visceral relations of the vagina
The vagina is usually collapsed. The orifice is usually collapsed toward the midline so that its
lateral walls are in contact on each side of an anteroposterior slit. 7uperior to the orifice$ however$
the anterior and posterior walls are in contact on each side of a transverse potential cavity$ )-
shaped in cross section
The vaginal fornix$ the recess around the cervix$ has anterior$ posterior$ and lateral parts
Anteriorly to the fundus of the urinary bladder and urethra& laterally to the levator ani$ visceral pelvic
fascia$ and ureters& and posteriorly "from inferior to superior# to the anal canal$ rectum$ and
rectouterine pouch
8. To describe the blood supply and lymph drainage of the female genital tract
Ovaries and uterine tubules : receive a double "collateral# blood supply from the abdominal aorta
via the ovarian arteries and from the internal iliac arteries via the uterine arteries.
Uterus : receive blood from from the uterine arteries$ and collateral supply from the ovarian
arteries .The uterine veins enter the broad ligaments with the arteries and form a uterine venous
plexus on each side of the cervix. 9eins from the uterine plexus drain into the internal iliac veins.
Vagina : blood for superior part of the vagina derive from the uterine arteries. The arteries
supplying the middle and inferior parts of the vagina derive from the vaginal and internal pudendal
arteries. The vaginal veins form vaginal venous plexuses along the sides of the vagina and within
the vaginal mucosa .These veins are continuous with the uterine venous plexus as the uterovaginal
venous plexus and drain into the internal iliac veins through the uterine vein
:. To describe general anatomy$ vasculari.ation$ and lymphatic system of breast
The breasts "(. mammae# consist of glandular and supporting fibrous tissue embedded within a
fatty matrix$ together with blood vessels$ lymphatics$ and nerves. At the greatest prominence of the
breast is the nipple$ surrounded by a circular pigmented area of s0in$ the areola "(. small area#.
Arterial supply : ;edial mammary branches of perforating branches and anterior intercostal
Anatomy of Female Genital System
SGD B8
Day 2
branches of the internal thoracic artery$ (ateral thoracic and thoracoacromial arteries$ branches of
the axillary artery& 'osterior intercostal arteries$ branches of the thoracic aorta in the 2nd$ ,rd$ and
4th intercostal spaces.
Venous drainage : The venous drainage of the breast is mainly to the axillary vein$ but there is
some drainage to the internal thoracic vein
Lymph system : (ymph passes from the nipple$ areola$ and lobules of the gland to the subareolar
lymphatic plexus. Then 61<"lateral# of this plexus will drain into the axillary lymph nodes$ while the
remaining"medial# will drain into the parasternal lymph node&the opposite breast and for the inferior
=uadrants$ to the abdominal lymph node.
13. -escribe the anatomical feature of the female pelvis and its difference with the male pelvis
>ony 'elvis ;ale ?emale
@eneral structure Thic0 and heavy Thin and light
@reater pelvis "pelvis ma+or# -eep 7hallow
(esser pelvis "pelvis minor# Aarrow and deep$ tapering ide and shallow$ cylindrical
'elvic inlet "superior pelvic aperture# )eart-shaped$ narrow Bval and rounded& wide
'elvic outlet "inferior pelvic aperture# Comparatively small Comparatively large
'ubic arch and subpubic angle Aarrow "D63E# ide "F83E#
Bbturator foramen %ound Bval
Acetabulum (arge 7mall
@reater sciatic notch Aarrow "G63E#& inverted 9 Almost :3E
11. -escribe the pelvic diaphragm and perineum
The perineum refers to a shallow compartment of the body "perineal compartment# bounded by the
pelvic outlet and separated from the pelvic cavity by the fascia covering the inferior aspect of the
pelvic diaphragm$ formed by the levator ani and coccygeus muscles
The pelvic floor is formed by the bowl- or funnel-shaped pelvic diaphragm$ which consists of the
coccygeus and levator ani muscles and the fascias "(. fasciae# covering the superior and inferior
aspects of these muscles.The pelvic diaphragm lies within the lesser pelvis$ separating the pelvic
cavity from the perineum$ for which it forms the roof
The floor of the pelvis is formed by the pelvic diaphragm$ encircled by and suspended in part from
the pubic symphysis and pubic bones anteriorly$ the ilia laterally$ and the sacrum and coccyx
Anatomy of Female Genital System
SGD B8
Day 2
posteriorly
You might also like
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledDania Ibraheem100% (1)
- Anatomy Screeningcervix by DR. VACHASPATIDocument52 pagesAnatomy Screeningcervix by DR. VACHASPATIOshydh PojnNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The UterusDocument21 pagesAnatomy of The UterusSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- PELVIS AND PERINEUM Session 4 - 2022Document53 pagesPELVIS AND PERINEUM Session 4 - 2022zealotwisdom0No ratings yet
- Maternal Anatomy WilliamsDocument60 pagesMaternal Anatomy WilliamsZari Novela100% (2)
- 7pelvic CavityDocument71 pages7pelvic CavityDan MupenziNo ratings yet
- 11th - The Female Reproductive SystemDocument21 pages11th - The Female Reproductive Systemprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of GIT For PCII Students..Document106 pagesAnatomy of GIT For PCII Students..AMANUEL HABTEWOLDNo ratings yet
- Uterus and Ovary UltrasoundDocument144 pagesUterus and Ovary Ultrasoundisicheipraise3No ratings yet
- P. Cavity: (Female Reproductive Organs)Document38 pagesP. Cavity: (Female Reproductive Organs)SAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- CBL 2Document20 pagesCBL 2Hammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- ÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇDocument18 pagesÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇÇsostegnawNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyDocument25 pagesGross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyAhsan TariqNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAzza100% (11)
- Intro Lab Anatomi Rps (2024)Document117 pagesIntro Lab Anatomi Rps (2024)Jason Maxwell mcguireNo ratings yet
- 07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, OvariesDocument52 pages07 - Uterus, Uterine Tubes, Ovariesck4realNo ratings yet
- UterusDocument34 pagesUterushammad992No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female ReproductionDocument108 pagesAnatomy of The Female ReproductionDaisy HamdaliNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Human ReproductiveDocument68 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproductivesavita hanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryDocument89 pagesAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Genital Tract - IiDocument44 pagesAnatomy of Female Genital Tract - Iigksah711No ratings yet
- Urinary Bladder, Rectum and Anal CanalDocument34 pagesUrinary Bladder, Rectum and Anal CanalIbe ClementNo ratings yet
- Female Genital OrgansDocument40 pagesFemale Genital OrgansShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Revisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDocument50 pagesRevisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDr. AyshaNo ratings yet
- Uterus Fallopian Tube and OvaryDocument35 pagesUterus Fallopian Tube and Ovaryvijaya pranaviNo ratings yet
- Normal Anatomy and Physiology of Female PelvisDocument58 pagesNormal Anatomy and Physiology of Female PelvisVic RobovskiNo ratings yet
- 41 Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument14 pages41 Female Reproductive Anatomyruaa firasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall and HerniaDocument35 pagesAbdominal Wall and HerniaMohammad BanisalmanNo ratings yet
- Lec.1.Anatomy of PregnancyDocument53 pagesLec.1.Anatomy of PregnancyManal AsadNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 1 Repro VivianDocument119 pagesPemicu 1 Repro VivianVivian SaputraNo ratings yet
- 23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Document206 pages23 Female Reproductive System 1213116557688874 8Rodel AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BladderDocument10 pagesAnatomy of BladderKiran tyraNo ratings yet
- ANATOMIDocument43 pagesANATOMIWidayuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument62 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerNo ratings yet
- Urinary BladderDocument35 pagesUrinary Bladderfabunmiopeyemiv23No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- 1) Femal Pelvis&fetal SkullDocument36 pages1) Femal Pelvis&fetal SkullHayder MuthanaNo ratings yet
- Curs 2 - 3 Histoanatomy of COW Ovaries and Uterus FW Si CLDocument93 pagesCurs 2 - 3 Histoanatomy of COW Ovaries and Uterus FW Si CLB.L.C.SNo ratings yet
- Perineal Tear: Presented by - Mayuri Zanwar Guided By-Dr. Sheetal Ma'AmDocument20 pagesPerineal Tear: Presented by - Mayuri Zanwar Guided By-Dr. Sheetal Ma'Ammayuri zanwarNo ratings yet
- Female Genital Organs.Document18 pagesFemale Genital Organs.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- The Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFDocument9 pagesThe Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Female PerineumDocument27 pagesFemale Perineumkaartikey dubeNo ratings yet
- Microscopic OF THE E.: University Kansas School MedicineDocument16 pagesMicroscopic OF THE E.: University Kansas School MedicineYousra HadjNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The VaginaDocument74 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The VaginaRacquel BurrowesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Uterus and Vagina and PudendumDocument38 pagesAnatomy of Uterus and Vagina and Pudendumgugus aminaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemMahad Maxamed AxmedNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Diaphragm & Pelvic FasciaDocument22 pagesPelvic Diaphragm & Pelvic Fasciafarwafurqan1No ratings yet
- UterusDocument3 pagesUterusBernadette FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology of Bladder: Dr. Deepesh Kalra Institute of Urology Madras Medical College, ChennaiDocument33 pagesAnatomy and Embryology of Bladder: Dr. Deepesh Kalra Institute of Urology Madras Medical College, ChennaiFatima Zahra Rahim ArchiNo ratings yet
- The PerineumDocument3 pagesThe PerineumSanjay KishoreNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System (Week 17)Document95 pagesReproductive System (Week 17)Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Ligaments of Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesLigaments of Reproductive SystemHarini ThiruNo ratings yet
- 2-Anatomy of Reproductive SystemDocument53 pages2-Anatomy of Reproductive SystemMustafa SHawkiNo ratings yet
- Perineal TearsDocument49 pagesPerineal TearsvisakhaNo ratings yet
- 1 InroductionDocument44 pages1 Inroductiondemeke andebetNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum & Peritoneal Cavity PresentationDocument59 pagesPeritoneum & Peritoneal Cavity Presentationsaint thuggerNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (20)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)