Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide
Uploaded by
Kuu KiiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide
Uploaded by
Kuu KiiCopyright:
Available Formats
www.actix.
com
November 2005
UMTS
Analysis Guide
www.actix.com
2
The content of this manual is provided for information only, is subject to change without
notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by Actix. Actix assumes no
responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that appear in this documentation.
Copyright Actix 2005-2008. All rights reserved. All trademarks are hereby acknowledged.
www.actix.com
2
Contents
1 INTRODUCTION.........................................................................................4
2 OPERATIONAL TASKS AND PROCESSES .............................................................5
2.1 SITE INTEGRATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE TESTING .................................................... 7
2.2 DETAILED CALL SEQUENCE ANALYSIS .................................................................... 8
2.3 BENCHMARKING AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS............................................................ 9
2.4 RADIO LINK PERFORMANCE TROUBLESHOOTING........................................................10
3 FEATURE OVERVIEW................................................................................. 12
3.1 ACTIX ANALYZER...........................................................................................12
3.2 APPLICATION LAYERS ......................................................................................13
3.2.1 Neighbor List Analysis Module ...............................................................14
3.2.2 CPICH Pollution Analysis Module............................................................17
3.2.3 Handoff State Analysis Module (for scanner) ...........................................19
3.2.4 Emulated Active Set Module..................................................................22
3.2.5 CPICH before RRC Connection Request Module ........................................23
3.2.6 CPICH before call end or drop Module.....................................................24
3.2.7 CPICH during call Module......................................................................25
3.2.8 CPICH after call end or drop Module.......................................................26
3.2.9 Call Setup Status Module......................................................................27
3.2.10 Call Sequence Analysis Module ............................................................28
3.2.11 Call Statistics Module (CS or PS)..........................................................29
3.2.12 Call Sustainability Module ...................................................................30
3.2.13 Call Timing Analysis Module ................................................................31
3.2.14 File Summary Module.........................................................................32
3.2.15 Coverage Summary Module ................................................................33
3.2.16 Handoff Breakdown Analysis Module (Handset) ......................................34
3.2.17 SHO per event 1a-1b-1c Module ..........................................................35
3.2.18 Overall BLER Module ..........................................................................36
3.2.19 BLER Per call Module..........................................................................36
3.2.20 BLER during SHO Module....................................................................37
3.3 FILTERS .....................................................................................................37
3.4 STATEFORMS................................................................................................38
3.4.1 UMTS Data Event Navigator ..................................................................38
3.4.2 UMTS Data Session .............................................................................39
3.4.3 UMTS Throughput ...............................................................................40
3.4.4 UMTS Top 10 Scan Measurements .........................................................41
3.4.5 UMTS UE Active + Monitored Set ...........................................................42
3.4.6 UMTS UE Call Information.....................................................................43
3.4.7 UMTS UE Measurements Charts.............................................................44
3.4.8 UMTS UE Radio Parameters ..................................................................45
3.4.9 UMTS UE Transport Channel Info...........................................................46
3.4.10 UMTS Voice Event Navigator (CS Only) .................................................47
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Introduction 4
www.actix.com
2
1 Introduction
It is widely recognized that increasing productivity fuelled much of the global economic
expansion of the 1990s. Technological advances in software and hardware usually enable
these productivity improvements, although there is often a lag between the availability of
the new technology, and its widespread acceptance and deployment by industry. This gap
is sometimes called the productivity lag factor.
Some examples of this include the introduction of automated bank teller technology in the
1980s in the US. When the technology initially became available, it was only sparingly
deployed, and the units were often placed inside bank buildings where the productivity
enhancements they offered were limited. Likewise, unattended gasoline pump technology
has been slow to roll out in Europe, but as the technology has become widely adapted,
huge efficiency gains have been realized.
The wireless industry is now at a similar point. It understands that the traditional labor-
intensive techniques for maximizing performance and capacity in wireless infrastructure
are fundamentally limited by a lack of structured algorithms to determine improvements.
Actix Analyzer offers the possibility to look at drive test data and scanner data to fully
optimize a UMTS network. It allows the engineer to understand the causes and reasons for
drop calls and access failures.
Analyzer offers an unprecedented capability to execute a detailed examination of message
flows and automating statistical analyses of performance. Analyzer significantly accelerates
the rollout, troubleshooting and optimization of the UMTS network. Actix has embedded
intelligence in the software to allow the RF engineer to visualize specific events and
understand real problems occurring in the network.
Analyzer embodies our extensive experience as the market leader in optimization solutions
for CDMA, UMTS and GSM. All of the lessons learned and the techniques developed over a
10-year period have been incorporated into these powerful, vendor-independent solutions
for UMTS infrastructure.
This document provides an overview of the key benefits, applications and features of
Analyzer. For additional information, including white papers and other literature, please
refer to www.actix.com.
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 5
www.actix.com
2
2 Operational Tasks and Processes
Actix Solutions embody our extensive experience as the market leader in optimization
solutions for CDMA, UMTS and GSM. All of the lessons learned and the techniques
developed over a 10-year period have been incorporated into these powerful, vendor-
independent solutions for cdma2000, GPRS and UMTS infrastructure.
Analyzers Rollout Verification is a novel solution to the challenge of rolling out,
troubleshooting and optimizing real UMTS networks. Analyzer may be used in field trial,
benchmarking and operational settings to automate the process of quantifying network
performance, thereby mitigating the risk of performance problems during commercial
operation.
Analyzer offers an unprecedented capability to execute a detailed examination of message
flows and automating statistical analyses of performance. Analyzer significantly accelerates
the rollout, troubleshooting and optimization of the UMTS network. Actix has embedded
intelligence in the software to allow the RF engineer to visualize specific events and
understand real problems occurring in the network.
Applications addressed by Analyzer first become pertinent during the new technology
rollout, as shown in Figure 1. Then, as first-generation technology is rolled out for soft or
commercial launches, Analyzer continues to address a number of critical challenges. As
new sites are coming on air and more customers are accessing the network, the real
challenge for the RF engineer is to maximize the coverage, capacity and quality of service.
Analyzer offers a number of applications applicable to these ongoing challenges.
Figure 1: Applicability of Analyzer begins in the Initial Rollout and continues throughout the lifecycle of
the network deployment
Analyzer is a powerful tool designed to help the RF engineer analyze data from scanner
and handset sources. It gives a detailed analysis during the whole drive route. From
missing neighbor to pilot pollution detection, the different embedded events give an
absolute advantage to the RF engineer in understanding the source of different problems.
Figure 2 depicts some of the major processes performed by engineering teams during the
initial rollout, immature buildout and mature growth phases; and indicates the key radio-
link configuration tasks that are common across these processes. The following sections
provide an outline (plus additional details) of the processes and tasks typically performed
during those phases.
R&D
Trials
Initial
Rollout
Immature
Buildout
Mature
Growth
Rollout
Verification
S l
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 6
www.actix.com
2
Figure 2: Scanner and Drive tests analysis, Site Integration and Optimization are performed as part of
critical processes in the Initial Rollout, Immature Buildout and Mature Growth phases
Analyzer allows the user to focus on the following tasks for site integration and testing,
coverage analysis, troubleshooting and optimization:
Site Integration and Infrastructure Testing
Detailed Call Sequence Analysis
Benchmarking and Statistical Analysis
Radio Link Performance Troubleshooting
Event Detection and Drive Test Analysis
The following sections describe the high-level capabilities of Analyzer for each of these
applications. Because Analyzer is based on an open architecture platformwhich includes
Benchmarking
R&D / Trials
& Planning
Initial
Rollout
Immature
Buildout
Mature
Growth
Scanner and
Drive Tests
Analysis
Event
Detections
Service
Coverage
Availability
Site Calibration
Initial Testing
Throughput
and Rates
Calculation
Initial Coverage
Analysis
Processes
Phases
Tasks
Subscriber-Perceived
Performance
Radio Link
Performance
On-going
Optimization
Network
Growth
Power
Measurements
Site Integration
and
Optimization
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 7
www.actix.com
2
user-definable query and open data import capabilitiesit may be used for many ad-hoc
troubleshooting and performance analysis tasks beyond those covered in this document.
2.1 Site Integration and Infrastructure Testing
Part of the process in rolling out a network is to be able to test and integrate new sites.
Analyzer provides the following features for site integration and infrastructure testing:
The file summary report allows the engineer to have a quick look at the overall
performance during the entire drive test.
Embedded charts and graphs help to visualize key parameters like Ec/No or RSCP
in the active set.
Detailed reports on call statistics on cell by cell basis
User-definable queries allow creation of customized statistical analysis
Automated report generation containing statistical summaries of key performance
indicator
Figure 3: Charts and graphs for UMTS site integration and infrastructure testing
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 8
www.actix.com
2
2.2 Detailed Call Sequence Analysis
Analyzer provides these analyses of call sequence and call setup procedures:
Detailed call sequence analysis on a message by message basis
Automated report generation for visualization of call sequence messages
Automated report generation statistical summaries of call setup problems
Figure 4: Statistical summaries of call setup procedures and failure causes
Figure 5: Detailed call sequence analysis
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 9
www.actix.com
2
2.3 Benchmarking and Statistical Analysis
Analyzer provides the following features for benchmarking and statistical analysis:
Automated report generation for quick visualization of call statistics such as drop
calls, access failures, call sustainability, etc.
Working with different sources of data to create homogeneous set of reports for
benchmarking
User-defined queries allowing easy access to different statistics
Figure 6: Charts and graphs representing different call statistics
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 10
www.actix.com
2
Figure 7: Various call statistics filtered by cells
2.4 Radio Link Performance Troubleshooting
Analyzer may be used to diagnose and determine remedial action for key radio-link
configuration problems, including:
Distant servers
Too many servers
Unnecessarily large neighbor lists
Excessive soft handoff area
Figure 8: Identify problems for UMTS radio networks by visualizing
pilot signals as lines drawn to serving cells on a map
Radio Link Performance Metrics available from Analyzer will include the following
attributes, depending on the specific vendor and specific source (handset or scanner):
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Operational Tasks and Processes 11
www.actix.com
2
Mobile Transmit Power, Mobile Receive Power, BLER
CPICH Ec/No, Ec/Io and RSCP per scrambling code
Chip Offset and Delay Spread per SC
Ec/Io, RSCP and Pathloss for Nth best SCs
CPICH Ec/No and SC in Active and Monitored set
Handoff State, Call ID
Figure 9: Charts and graphs for a handoff state analysis
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 12
www.actix.com
2
3 Feature Overview
3.1 Actix Analyzer
Depending on the licenses available to you, Analyzer is able to analyze cdma2000, GSM,
GPRS and EDGE, as well as UMTS data. Analyzer provides a core set of capabilities to
analyze network performance data:
Interfaces to a large number of network performance data sources
Support for a wide variety of wireless protocols from the air-interface to the core
network
Filtering and binning module
Finite state event detection engine
Time-series and multi-dimensional statistical query module
Data merging and synchronization / correlation module
Mapping, charting, and reporting modules
Messaging and protocol stack browsers
Network element database
Open data import and export module
Analyzers flexibility allows it to be configured for a wide range of network performance-
data analysis tasks.
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 13
www.actix.com
2
3.2 Application Layers
Application Layers can be added to Analyzer to implement task or application specific
functionality. Analyzer includes the following application layers:
UMTS Accelerated Network Rollout Solution
Neighbor List Analysis Module
Handoff State Analysis Module
CPICH Pollution Module
Emulated Active Set Module
UMTS CPICH Level Analysis
CPICH before RRC Connection Request Module
CPICH before call end or drop Module
CPICH during call Module
CPICH after call end or drop Module
UMTS Call Setup Analysis
Call Setup Status Module
Call Sequence Analysis Module
UMTS Call Statistics
Call Statistics Module
Call Statistics PS Module
Call Sustainability Module
Call Timing Analysis Module
UMTS Drive Test Summary
File Summary Module
Coverage Summary Module
UMTS Handoff Analysis
Handoff Breakdown Analysis Module
SHO per event 1a-1b-1c Module
UMTS Quality Analysis
Overall BLER Module
BLER Per call Module
BLER during SHO Module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 14
www.actix.com
2
3.2.1 Neighbor List Analysis Module
The Neighbor List Analysis provides an automated approach for generating optimal
neighbor lists and overcoming major service-degrading problems such as missing
neighbors.
The key components of the neighbor-list analysis module are:
Generation of recommendations for optimal neighbor list settings based on UMTS/WCDMA
scanner drive test data.
Integration with Network Element Database to audit existing neighbor lists and suggest
changes, and to correlate non-unique measured data attributes such as Scrambling Code
with unique identifiers such as Sector ID.
The Neighbor List Module implements the following algorithm:
Ec/Io measurements below a noise floor are filtered out of the data set before analysis.
User definable binning is used to reduce the number of measurements points in each bin to
create one value per bin optionally, no binning at all can be applied and the analysis will
run on the full data set.
At each point along the drive test, a list of prospective neighbors is accumulated as
indicated in Figure 19. If a neighbor signal is within a user-definable threshold of the best
server in the active set, then it is considered as a potential neighbor.
Using the geographic information in the log file and the SC, the network element database
is searched to identify the Sector and Cell IDs of the SC.
A symmetrical neighbor array is created in memory which records the number of times
each sector ID is seen as a prospective neighbor of another sector ID as shown in Table 1.
Once all bins in the log file have been compiled into the symmetrical matrix, the results
are compared against actual neighbor lists contained in the network element database and
the following are calculated:
a list of sector IDs included in the matrix, but not the actual neighbor list
a list of sector IDs included in the actual list but not in the matrix
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 15
www.actix.com
2
Figure 19: Cell A is the best server by CPICH Ec/Io. Cells B and C are within a user-specified threshold
of Cell As Ec/Io, and so are counted as potential neighbors of A. Cell D is not within the required
threshold and so is not counted as a prospective neighbor, nor is Cell E which did not have a
measurable signal contribution at this point in the drive test.
A B C D
A N/A 10 2 15
B 10 N/A 40 0
C 2 40 N/A 12
D 15 0 12 N/A
Table 1: A sample symmetric prospective neighbor array using sector IDs A, B, C, and D
Limitations of the algorithm:
Results are only produced in areas that have been tested, so the test areas should be
carefully considered before removing any Sectors from the neighbor lists
Drive tests do not necessarily emulate the radio environment encountered by pedestrian
and in-building users; however, walk tests and in-building tests may be included in the
analysis as desired
Results are presented in the following application reports:
Neighbor List Summary
Drive Test
Route
A
Best Server
B
Neighbour 1
C
Neighbour 2
D
Not a Neighbour
E
Excluded from Analysis
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 16
www.actix.com
2
Neighbor List Audit
Recommended Neighbor Lists
Figure 20: A sample Recommended Neighbor Lists report
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 17
www.actix.com
2
3.2.2 CPICH Pollution Analysis Module
The CPICH or Pilot Pollution Analysis uses an emulated Active Set to estimate which pilots
would have been actively demodulated by the UE, and then detects other pilots above a
user-definable threshold that cause excessive interference. Please see the Emulated Active
Set Module section for more details on how the Active Set is estimated based on WCDMA
scanner measurements.
The pilot pollution algorithm has these components:
Ec/Io measurements below a noise floor are filtered out of the data set prior to
analysis.
User definable binning is used to reduce the number of measurements points in
each bin to create one value per bin optionally, no binning at all can be applied
and the analysis will run on the full data set.
At each point along the drive test, CPICH Ec/Io data for each Scrambling Code is
used to assign SCs to an Active Set or a Pollution Set (please see the Emulated
Active Set Module section for more details).
The Pollution Set consists of all SCs that are not in the Active Set, and have a
CPICH Ec/Io within a user specified pollution threshold of the strongest CPICH
Ec/Io in the Active Set (see Figure 21).
Using the geographic information in the log file and the SC, the network element
database is searched to identify the Sector and Cell IDs of the SC.
A pollution array is created in memory which records the number of times each
sector ID is seen as a source of pilot pollution as shown in Table 2
All bins in the log file are then processed into the pollution matrix.
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 18
www.actix.com
2
Figure 21: Cell A, B and C are part of the Active Set, as determined by the Emulated Active Set
module. Cell D has a CPICH Ec/Io within a user-specified pollution threshold of the Active Sets best
server Ec/Io, and so is counted as a contributor to pilot pollution at this point in the drive test. Cell E
has a CPICH Ec/Io that is not within this threshold and so is not a pollution source.
Sector ID Pollution
Count
A 0
B 150
C 45
D 12
Table 2: A sample pollution array indicating the number of points at which each sector caused pilot
pollution for sector IDs A, B, C, and D
Results are presented in the Pilot Pollution Analysis application report as shown in Figure
22. In addition, Pilot Pollution may be geographically analyzed for each SC by accessing
the Pollution_for_SC attribute in the workspace view.
D
Pollution Source
A
Active Set
B
Active Set
C
Active Set
Drive Test
Route
E
Not a Pollution Source, or in
Active Set
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 19
www.actix.com
2
Figure 22: The Pilot Pollution Analysis report indicates the worst interferers sorted by Scrambling Code
3.2.3 Handoff State Analysis Module (for scanner)
The Handoff State Analysis module uses the emulated Active Set to determine the handoff
state at each point along a drive test. Statistics on handoff state may then be calculated
and presented in a report format. Excessive handoff state reduces capacity and increase
infrastructure costs for a given traffic level. Please see the Emulated Active Set Module
section for more details on how the Active Set is estimated based on WCDMA scanner
measurements.
The handoff state algorithm has the following components:
The Active Set of pilots is determined using the Emulated Active Set module
Using the geographic information in the log file and the SC, the network element
database is searched to identify the Sector and Cell IDs of the SC
Handoff state is calculated by determining the configuration of the sectors in the
Active Set as shown in Figure 23
All bins in the log file are then processed into the handoff state matrix
Reports showing the percentage of handoff state for each sector and for the total drive test
may then be calculated as shown in Figure 24.
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 20
www.actix.com
2
Figure 23: The Handoff State Analysis examines Sector IDs involved in call at a given drive test point
and determines which of the above states applies, based on UMTS scanner data
Single-sector
Softer Soft
3-way Softer
3 sectors
same node B
Soft-softer
2 sectors
same node B
3-way soft
2 sectors
same node B
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 21
www.actix.com
2
Figure 24: A report showing the percentage of drive test in each handoff state for scanner data
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 22
www.actix.com
2
3.2.4 Emulated Active Set Module
CPICH Pollution Analysis and Handoff Analysis are both based on a calculated Active Set,
which is determined by the Emulated Active Set module. The Emulated Active Set module
implements the 3GPP handoff algorithm and uses scanner Ec/Io measurements in
conjunction with user-specific 3GPP handoff thresholds to emulate the Active Set at each
point along a drive test. Figure 25 shows a sample set of scanner data for three individual
SCs with color and vertical lines indicating transitions of pilots into and out of the Active
Set.
Figure 25: Using Scanner Ec/Io measurements to implement 3GPP handoff algorithms for the Active
Set
Figure 26 shows the list of attributes available for modification by the user, as indicated in
the 3GPP specifications:
Figure 26: Setting 3GPP handoff algorithm attributes including Reporting Range: Hysteresis Event and
Time to Trigger Event
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 23
www.actix.com
2
3.2.5 CPICH before RRC Connection Request Module
The CPICH before RRC Connection Request module helps the engineer to understand the
environment right before the call started or to be more precise, before the first RRC
connection request happens. For every call in the log file, the report can show the
following parameters:
Call Identification, based on the attribute Uu_Call_id
Time of the first RRC Connection Request for a specific call
Site the call was placed, based on the attribute ServingCellid
Scrambling Code the call originated on, based on the attribute
Uu_ActiveSet_SC_0
Ec/Io of that same Scrambling Code, based on the attribute
Uu_ActiveSet_EcNo_0
RSCP of that same Scrambling Code, based on the attribute
Uu_ActiveSet_RSCP_0 or the calculated RSCP if the regular RSCP values are not
present or were not logged.
Site, SC, Ec/Io and RSCP of the Monitored Set if applicable
End result of that particular call
For any of these parameters, the module searches 5 seconds before the first RRC
Connection Request for the specific details. If it cannot find the parameters during those 5
seconds, the value No Data is shown.
Figure 27 shows a typical analysis executed by the CPICH before RRC Connection Request
module. For the engineer, it is an easy way to look at the conditions before the call started
and the end result.
Figure 27: Example of a log file analyzed by the CPICH before RRC Connection Request module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 24
www.actix.com
2
3.2.6 CPICH before call end or drop Module
The CPICH before call end or drop module helps the engineer to understand the
environment right before the call ended or dropped. For every call in the log file, the report
can show the following parameters:
Call Identification, based on the attribute Uu_Call_id
Time when the call ended or dropped (see event definitions)
Site ID of the active site when the call ended or dropped (attribute ServingCellid)
Scrambling Code of the 1
st
finger in the Active Set
Ec/Io of that same Scrambling Code
RSCP of that same Scrambling Code
Site, SC, Ec/Io and RSCP of the Monitored Set if applicable
End result of that particular call
Figure 28 shows a typical analysis executed by the CPICH before call end or drop module.
For the engineer, it is an easy way to look at the conditions right before the call ended.
Figure 28: Example of a log file analyzed by the CPICH before call end or drop module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 25
www.actix.com
2
3.2.7 CPICH during call Module
The CPICH during call module helps the engineer to understand the environment during a
particular call. For every call in the log file, the report can show the following parameters:
Call Identification
Site ID of the most common active site (site associated with the scrambling code
of the first finger in the active set)
Most common Scrambling Code of 1
st
finger in the Active Set
Average Ec/Io during the entire call
Average RSCP during the entire call
Site ID of the most common monitored site (site associated with the scrambling
code of the first finger in the monitored set)
Most common Scrambling Code in the Monitored Set
Average Ec/Io during the entire call
Average RSCP during the entire call
End result of that particular call
Figure 29 shows a typical analysis executed by the CPICH during call module. For the
engineer, it is an easy way to look at the average conditions during the call.
Figure 29: Example of a log file analyzed by the CPICH during call module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 26
www.actix.com
2
3.2.8 CPICH after call end or drop Module
The CPICH after call end or drop module helps the engineer to understand the environment
right after the call ended or dropped. For every call in the log file, the report can show the
following parameters:
Call Identification
Time when the call ended or dropped
Site ID of the active site when the call ended or dropped
Scrambling Code of the 1
st
finger in the Active Set
Ec/Io of that same Scrambling Code
RSCP of that same Scrambling Code
Site, SC, Ec/Io and RSCP of the Monitored Set if applicable
End result of that particular call
Figure 30 shows a typical analysis executed by the CPICH after call end or drop module.
For the engineer, it is an easy way to look at the conditions right after the call ended.
Figure 30: Example of a log file analyzed by the CPICH after call end or drop module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 27
www.actix.com
2
3.2.9 Call Setup Status Module
The Call Setup Status module offers a general overview on how and when the call failed.
The normal call sequence should go like this:
RRC Connection Request (MOC)
or Paging Type1 (MTC)
RRC Connection Setup
RRC Connection Complete
MM CM Service Request (MOC) or
Paging Response (MTC)
MM CM Service Accept
Authentication Request
Authentication Accept
Security Mode Command
Security Mode Complete
CC Setup
CC Call Proceeding
Radio Bearer Setup
Radio Bearer Setup Complete
CC Alert
CC Connect
If all messages are received properly, the call is a success. If it fails to reach the CC
Connect, it should be pegged as a call failure and this module should give the reason for it.
Refer to section 3.2 Event Definitions for more details.
Figure 31 shows a typical analysis executed by the call setup status module.
Figure 31: Example of a log file analyzed by the call setup status module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 28
www.actix.com
2
3.2.10 Call Sequence Analysis Module
The Call Sequence Analysis module offers a general overview on how call failed and when
they failed. This module has the same structure and analysis as the call setup status
module except for a few differences. It doesnt summarize as what is the cause of the
failure. On the other hand, it gives the call sequence with detailed information on every
call and the outcome of it. It gives the engineer the possibility to look at individual calls on
a message-by-message basis.
Figure 32: Example of a log file analyzed by the call sequence analysis module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 29
www.actix.com
2
3.2.11 Call Statistics Module (CS or PS)
The Call Statistics Module helps the engineer to have a quick look at the overall
performance during a specific drive test. The following parameters' statistics are defined in
each file:
Total Number of calls: Number of Mobile Originated Calls (MOC) + Number of Mobile
Terminated Calls (MTC). This includes all calls, even failures.
Successful Incoming Calls: Number of successful Mobile Terminated Calls (MTC). To be
successful, a call needs to follow the call sequence as mentioned in section 3.2
Successful Outgoing Calls: Number of successful Mobile Originated Calls (MOC). To be
successful, a call needs to follow the call sequence as mentioned in section 3.2
Total Successful Calls:
Successful Incoming Calls +
Successful Outgoing Calls
Connected Percentage: Total
Successful Calls/Total number
of calls * 100
Call Failures Incoming:
Access Failure for a Mobile
Terminated Call (MTC) as
defined in section 3.2
Call Failures Outgoing:
Access Failure for a Mobile
Originated Call (MOC) as
defined in section 3.2
Access Failure Rate: Total
Access Failures/Total number
of calls * 100
Total Drops: Total number of
dropped calls. A dropped call is
defined as one of the
following:
Drop Rate percentage: Total
Drops/Total Successful Calls *
100
Total Completed Calls: Total
number of completed calls. A
completed call is defined as
the following:
Success Rate: Total completed
calls/Total Successful Calls *
100
Figure 33: Example of a log file analyzed by the
Call Statistics Module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 30
www.actix.com
2
3.2.12 Call Sustainability Module
The call sustainability
module helps the
engineer to have a
quick view at the call
duration for all calls
during the drive route.
The statistic is
calculated on a per call
basis and is the
difference in time
when the call ends and
when the call starts.
More precisely:
Call Sustainability =
Time when RRC
Connection request
happens (or paging
type 1) Time when
call drops or ends.
Figure 34 shows the
call sustainability
statistics and the call
duration distribution.
Figure 34: Example of a log file analyzed by the
call sustainability module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 31
www.actix.com
2
3.2.13 Call Timing Analysis Module
The Call Timing Analysis gives various time statistics on differences between specific
messages. In cases where the RRC Connection Request terminology is used, it relates to
the first RRC Connection Request message transmitted.
Figure 35: Example of a log file analyzed by the call timing analysis module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 32
www.actix.com
2
3.2.14 File Summary Module
The file summary module helps the
engineer to visualize quickly the
content of a file. The thresholds for
the coverage and quality charts are:
Coverage:
Good: RSCP > -80 dBm
Fair: -80 dBm >= RSCP >= -95 dBm
Poor: -95 dBm > RSCP
Quality:
Good: Ec/Io > -8 dB
Fair: -8 dB >= Ec/Io >= -15 dB
Poor: -15 dB > Ec/Io
Figure 36: Example of a log file analyzed
by the file summary module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 33
www.actix.com
2
3.2.15 Coverage Summary Module
The file summary module helps the engineer to visualize quickly the statistics related to
the strongest RSCP and the strongest Ec/No for a particular file.
Figure 37: Example of a log file analyzed by the
coverage summary module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 34
www.actix.com
2
3.2.16 Handoff Breakdown Analysis Module (Handset)
The Handoff State Analysis
module for handset uses the Real
Active Set from the handset to
determine the handoff state at
each point along a drive test.
Statistics on handoff state may
then be calculated and presented
in a report format. Excessive
handoff state reduces capacity
and increase infrastructure costs
for a given traffic level. Please see
section 3.2.3 for more details on
the Handoff State Analysis for
scanner.
The handoff state algorithm has
the following components:
Using the geographic information
in the log file and the SC, the
network element database is
searched to identify the Sector
and Cell IDs of the SC
Handoff state is calculated by
determining the configuration of
the sectors in the Active Set as
shown in Figure 23 Section
3.3.3
All bins in the log file are then
processed into the handoff state
matrix
The Actual SHO Overhead
represents the sum of all soft-
handoff configurations
Reports showing the percentage
of handoff state for each sector
and for the total drive test may
then be calculated as shown in
Figure 38.
Figure 38: Example of a log file analyzed by the
handoff state analysis for handset
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 35
www.actix.com
2
3.2.17 SHO per event 1a-1b-1c Module
The SHO per event 1a-1b-1c module gives a brief summary about the different types of
handoff that occur in a file. It shows quickly the number of:
Addition: Event 1a
Removal: Event 1b
Replacement: Event 1c
Also, it reports the number of completion for each of those events and calculates a
percentage of success.
Figure 39: Example of a log file analyzed by the
soft-handover performance module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 36
www.actix.com
2
3.2.18 Overall BLER Module
The overall BLER (Block Error
Rate) module gives a brief
summary about the
distribution and statistical
analysis of BLER for an entire
file.
Figure 40: Example of a log file analyzed by the Overall
BLER module
3.2.19 BLER Per call Module
The BLER per call module
gives a summary of the main
statistics associated with the
BLER on a call-by-call basis.
The maximum value
The minimum value
The average value for that
particular call
Figure 41: Example of a log file analyzed by the BLER per
call module
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 37
www.actix.com
2
3.2.20 BLER during SHO Module
The BLER during SHO (soft handover) module provides statistics on the downlink transport
channel BLER aggregated across all SHOs and on a call-by-call basis (note that only the
calls with BLER measurements during the SHO procedure will be included in this report.
Figure 42: Example of a log file analyzed by the
BLER during SHO module
3.3 Filters
Filters can be added to Analyzer to implement task or application-specific functionality.
Analyzer includes the following pre-defined filters:
Poor Mobile Receive Power
CPICH_RSCP_in_ActiveSet[0] < -95 dBm
High Mobile Transmit Power
UeTransmittedPower > 0 dBm
Low Mobile Transmit Power
UeTransmittedPower < -30 dBm
High Mobile Receive Power
CPICH_RSCP_in_ActiveSet[0] > -80 dBm
Poor Ec/No
CPICH_EcNo_in_ActiveSet[0] < -15 dB
High Ec/No
CPICH_EcNo_in_ActiveSet[0] > -8 dB
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 38
www.actix.com
2
3.4 Stateforms
Stateforms can be added to Analyzer to implement task or application-specific
functionality. Analyzer includes the following stateforms:
UMTS Data Event
Navigator
UMTS Data Session
UMTS Throughput
UMTS Top 10 Scan
Measurements
UMTS UE Active + Monitored Set
UMTS UE Call Information
UMTS UE Measurements Charts
UMTS UE Radio Parameters
UMTS UE Transport Channel Info
UMTS Voice
Event Navigator
3.4.1 UMTS Data Event Navigator
The UMTS Data Event Navigator stateform allows the engineer to view the entire drive test
with just one quick look. During a data session, it is possible to keep track of the following
events:
GPRS_PDPContextAct_Successful
GPRS_PDPContextDeact_Successful
GPRS_Attach_Successful
GPRS_Detach_Successful
GPRS_PDPContextAct_Failure
GPRS_RAU_Successful
Event_Task_Start
While keeping track of the current SC in the active set. Figure 42 shows an example of
those different events at different moments in time with the track at the top showing the
SC.
Figure 43: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS Data Event Navigator Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 39
www.actix.com
2
3.4.2 UMTS Data Session
The UMTS Data Session stateform allows the engineer to view the data testing information
collected during a data session.
Figure 44: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS Data Session Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 40
www.actix.com
2
3.4.3 UMTS Throughput
The UMTS Throughput stateform chart allows the engineer to view the application and IP
downlink throughput graphically for the entire drive test. This information comes from the
data testing information collected during the drive test.
Figure 45: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS Throughput Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 41
www.actix.com
2
3.4.4 UMTS Top 10 Scan Measurements
The UMTS Top 10 Scan Measurements stateform allows the engineer to view important
details regarding the scanner measurements. The following parameters are displayed at
any specific moment during the drive test replay:
Top 10 Scrambling Code based on their Ec/Io
Top 10 Ec/Io for these respective SC
Top 10 RSCP for these respective SC
Global RSSI
Figure 46: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS Top 10 Scan Measurements Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 42
www.actix.com
2
3.4.5 UMTS UE Active + Monitored Set
The UMTS UE Active + Monitored Set stateform allows the engineer to visualize rapidly the
content of the active and monitored sets at any specific moment during the drive test. The
following parameters are represented for both the active and the monitored sets.
The Scrambling Code
The Ec/No for each of those scrambling code
The RSCP for each of those scrambling code
The Pathloss if applicable
It is a very quick way for the engineer to follow the active and monitored sets. Using the
replay tool, the engineer can follow the drive test and analyze very quickly any particular
events.
Figure 47: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS UE Active + Monitored Set Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 43
www.actix.com
2
3.4.6 UMTS UE Call Information
The UMTS UE call information stateform allows the engineer to have a quick view at the
following events:
IMSI Mobiles Identification
number used for testing
Called Party Number called for
that particular test/call
Calling Party In case of mobile
terminated calls, the number of
the party that called
Call id The call identification
based on the UMTS call tracker
Call State The state the mobile
is on. Different states are:
Init
Idle
RRC Con Request
RRC Con Setup
RRC Setup Complete
Outgoing Call Setup
Incoming Call Setup
Paging
In Call
Security Mode Command
Security Complete
CC Setup
Authentication Request
Authentication Response
CC Call Proceeding
RAB Setup
RAB Complete
Channel Reconfig
Radio Bearer Reconfig
GSM Mode
LAC
RAC
Figure 48: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS UE Call Information Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 44
www.actix.com
2
3.4.7 UMTS UE Measurements Charts
The UMTS UE Measurements Charts stateform allows the engineer to look at the most
important information in a log file. It is very easy to visualize rapidly the following
parameters:
EcNo Uu_ActiveSet_EcNo
RSSI UTRA_UE_CarrierRSSI
TxPower UE_TxPow
SIR Uu_SIR
SIR_Target Uu_TargetSIR
Figure 49: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS UE Measurements Charts Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 45
www.actix.com
2
3.4.8 UMTS UE Radio Parameters
The UMTS UE Radio Parameters stateform allows the engineer to view radio parameters at
a specific moment during the drive test. The available parameters are:
TxPower
RSSI
SIR
SIR Target
UTRA_ARFCN_DL
Figure 50: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS UE Radio Parameters Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 46
www.actix.com
2
3.4.9 UMTS UE Transport Channel Info
The UMTS UE Transport Channel Info allows the engineer to visualize the BLER per channel
and also the aggregate BLER.
Figure 51: Example of a log file analyzed by the
UMTS UE Transport Channel Info Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 47
www.actix.com
2
3.4.10 UMTS Voice Event Navigator (CS Only)
The UMTS Voice Event Navigator stateform allows the engineer to view the entire drive
test with just one quick look. During a session, it is possible to keep track of the following
events:
Uu_OutgoingCallOK
Uu_IncomingCallOK
Uu_OutgoingCallSetupFail
Uu_IncomingCallSetupFail
Uu_CallDropped
Uu_CallCompleted
While keeping track of the current SC in the active set. Figure 51 shows an example of
those different events at different moments in time with the colored track at the top
showing the SC.
Figure 52: Example of a log file analyzed by the UMTS Voice Event Navigator Stateform
Actix Analyzer UMTS Analysis Guide November 2005 Feature Overview 48
www.actix.com
2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Genex Discovery TutorialDocument60 pagesGenex Discovery Tutorialwildan100% (2)
- Netspan Counters and KPIs Reference Guide - SR15.00 - Rev 7.1Document278 pagesNetspan Counters and KPIs Reference Guide - SR15.00 - Rev 7.1Mohd AliNo ratings yet
- InfoVista Xeus Pro 5 TMR Quick GuideDocument76 pagesInfoVista Xeus Pro 5 TMR Quick GuideNguyen Dang KhanhNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Handover Control Feature Guide - V8 5 - 201312 - 548013Document434 pagesZTE UMTS Handover Control Feature Guide - V8 5 - 201312 - 548013Đỗ Ngọc Tân100% (1)
- GSM TimersDocument26 pagesGSM Timersharithcg100% (1)
- Lecture 5Document49 pagesLecture 5Nurul AtikahNo ratings yet
- Vijay Kumar CVDocument3 pagesVijay Kumar CVAhmad ShamsulNo ratings yet
- 1.15 Ho PDFDocument6 pages1.15 Ho PDFMuhammad HarisNo ratings yet
- LR VolteDocument144 pagesLR Voltealemayehu tefferaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulario para Las Especificaciones de 3GPPDocument68 pagesVocabulario para Las Especificaciones de 3GPPRodolfo VelozNo ratings yet
- GBSS15.0 Basic Feature DescriptionDocument256 pagesGBSS15.0 Basic Feature DescriptionSokrates100% (1)
- 2G Ericsson Nokia MappingDocument139 pages2G Ericsson Nokia MappingRinaldi AzharNo ratings yet
- Nokia 2G Parameters: Prepared by Nishant Gaurav 1Document22 pagesNokia 2G Parameters: Prepared by Nishant Gaurav 1Denis100% (1)
- 3G Parameter LayeringDocument5 pages3G Parameter Layeringnoer1304No ratings yet
- Double BCCH AllocationDocument17 pagesDouble BCCH AllocationUmarFarooqNo ratings yet
- 06) GSM Radio ParametersDocument56 pages06) GSM Radio Parameterskamal waniNo ratings yet
- Interoperability Between UMTS and LTE (RAN16.0 - Draft A)Document1,534 pagesInteroperability Between UMTS and LTE (RAN16.0 - Draft A)Sam FicherNo ratings yet
- Huawei RNP User Manual v1.0Document324 pagesHuawei RNP User Manual v1.0b0r3l_01No ratings yet
- Mobile: CommunicationDocument363 pagesMobile: CommunicationGreeshma Deepak100% (1)
- GSM Tuning ParametersDocument31 pagesGSM Tuning ParametersPaul KabeyaNo ratings yet
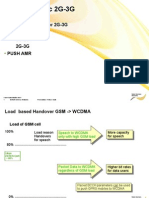
- 3G OPTI Crash CourseDocument13 pages3G OPTI Crash CourseoluwachintaNo ratings yet
- Admission Control in Frequency Hopping GSM SystemsDocument5 pagesAdmission Control in Frequency Hopping GSM SystemsShadowNo ratings yet
- Lte Icic Feature Issue 1.00Document50 pagesLte Icic Feature Issue 1.00Arief Hilman FauzanNo ratings yet
- Cdma Technology Seminar ReportDocument24 pagesCdma Technology Seminar ReportPriya DixitNo ratings yet
- GSM Design Validation and Quick AnalysisDocument6 pagesGSM Design Validation and Quick AnalysisAliSamariNo ratings yet
- Ran Kpi ReferenceDocument120 pagesRan Kpi ReferenceSamiNo ratings yet
- NSN 2G-3G Parameter SettingDocument17 pagesNSN 2G-3G Parameter SettingTOMTOB_123100% (5)
- SRLTE Optimization (ERAN11.1 01)Document28 pagesSRLTE Optimization (ERAN11.1 01)Sameh GalalNo ratings yet
- Calculator For LTE Mobility Events - Huawei - eRAN6Document31 pagesCalculator For LTE Mobility Events - Huawei - eRAN6erhan karadenizNo ratings yet
- Cellular Technology PDFDocument16 pagesCellular Technology PDFvengatrajaNo ratings yet