Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smaw Halimaw Teacher's Guide
Smaw Halimaw Teacher's Guide
Uploaded by
redant21ltdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smaw Halimaw Teacher's Guide
Smaw Halimaw Teacher's Guide
Uploaded by
redant21ltdCopyright:
Available Formats
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
Exploratory Course on
SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
Republic of the Philippines
DEPARTMENT OF EDCUATION
TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
TEACHERS GUIDE
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
Background Information
The Overall Goal of the K to 12 Curriculum ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
The Conceptual Framework of the Teaching of TLE .......................................................................................................................................... 3
The TLE Exploratory Courses ........................................................................................................................................................................... 5
The Learning Modules and Lessons ............................................................................................................................................................................ 6
New Feature of the Teaching of TLE ........................................................................................................................................................................... 6
About the Learning Module
Design of the Module ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
Parts of the Lesson ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Reflection .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Curriculum Guide ....................................................................................................................................................................................................... 12
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 3
Teachers Guide for TLE Exploratory Course on SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
Introduction
This Teachers Guide is intended for you, the TLE teacher, who teaches any of the more than 24 TLE exploratory courses in the Grades 7 and 8 of the
K to 12 curriculum. To ensure that you teach the TLE exploratory courses the way they were intended to be taught, you must see the big picture of the K to 12
curriculum and the teaching of TLE. Some background information is necessary.
Background Information
1. The Overall Goal of the K to 12 Curriculum
The K to 12 Curriculum has as its overarching goal the holistic development of every Filipino learner with 21
st
century skills who is adequately
prepared for work, entrepreneurship, middle level skills development and higher education. The over arching goal of the K to 12 curriculum, tells
you that the teaching of TLE plays a very important role in the realization of the overall goal of the curriculum. Whether or not the K to 12 graduate
is skilled and ready for work, entrepreneurship and middle skills development depend to a great extent on how effectively you taught TLE.
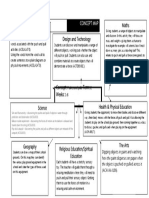
2. The Conceptual Framework of the Teaching of TLE
Below is a schematic diagram of Technology and Livelihood Education (TLE) framework in general secondary schools. This should guide you in
the teaching of the TLE exploratory courses.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 4
Figure 1.TLE Framework
The diagram shows that Technology and Livelihood Education encompasses the field of Home Economics, Industrial Arts, Agri-Fishery Arts and ICT. The 24
TLE courses can be categorized under any of these fields.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 5
TLE is geared towards the development of technological proficiency and is anchored on knowledge and information, entrepreneurial concepts,
process and delivery, work values and life skills. K to 12 TLE is
a. one that is built on adequate mastery of knowledge and information, skills and processes, acquisition of right work values and life skills;
b. one that equip students with skills for lifelong learning; and
c. one that is founded on cognitive, behavioral or psychomotor and affective dimensions of human development.
The diagram likewise shows that entrepreneurial concepts also form part of the foundation of quality TLE. It is expected that your TLE students,
after using the Learning Module on Entrepreneurship, imbibe the entrepreneurial spirit and consequently set up their own businesses in the areas
of Agri-Fishery Arts, Industrial Arts, Home Economics, and Information and Communication Technology.
TLE by its nature is dominantly a skill subject and so you must engage your students in an experiential, contextualized, and authentic teaching-
learning process. It is a subject where your students learn best by doing. It is integrative in approach. For instance, it integrates entrepreneurship
with all the areas of TLE. It integrates concepts, skills and values.
3. The TLE Exploratory Courses
TLE in Grades 7 and 8 are exploratory in nature. Your school will choose at least 4 from the list of 24 courses for which 23 Learning Modules have
been prepared.
1
Your schools choice is determined by the availability of its resources (faculty and facilities) as well as the local needs and
resources of the community.
The 24 TLE exploratory courses focus on four basic common competencies: 1) use and maintenance of tools and equipment; 2) mensuration and
calculation; 3) occupational health and safety procedures, and 4) preparation and interpretation of technical drawing. Why are these competencies
called basic? Because they are competencies that you must acquire in order that you can do higher level competencies. They are also described
common because these are true to all TR-based TLE courses.
1
There are 24 TLE courses but there are only 23 Learning Modules because there is one Learning Module for Tailoring and Dressmaking.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 6
The Learning Modules and Lessons
There is a Learning Module for each exploratory course. If there are 24 exploratory courses then you have 24 Learning Modules in your hands. But
you will use 4 Modules only for the entire year in Grade 7(plus a fifth one on Entrepreneurship) and another 4 Modules in Grade 8 (plus a fifth one on
Entrepreneurship).
Each Learning Module consists of 4 to 5 Lessons
2
. The Lessons are focused on the 4 to 5 basic competencies. To avoid meaningless repetition of the
teaching of the 5 common competencies, you have to teach them in the context of the TLE course. For example, you teach use and maintenance of tools in
beauty care when you are teaching the course on Beauty Care. You teach the same competencies - use and maintenance of tools-in Horticulture but in the
context of Horticulture and so your tools will not be entirely the same.
New Feature on the Teaching of TLE
Whats new in the teaching of TLE in the K to 12 curriculum? In the K to 12 curriculum, the TLE courses are taught based on the learning
outcomes and performance criteria stated on the Training Regulations(TR)from Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA). They are TR-
based.
Why is this necessary? To prepare the K to 12 graduate for lucrative work, he/she must earn a National Certificate (NC)I, II or even an NC of higher
level that is required by industries. This he/she earns after passing an assessment given by TESDA.
How can you ensure that the K to 12 high school student (Grade 9 to 12) pass TESDA assessment and obtain an NC? By seeing to it that you
teach the TLE course in accordance with the performance criteria and learning outcomes laid down in the TESDA Training Regulations.
Do the exploratory courses enable the high school student to earn already an NC? Not yet. Completion of the exploratory courses may not yet
qualify a high school student to take an assessment for an NC. Instead, it helps him/her earn a Certificate of Competency (COC) at least in Grade 9 that will
lead eventually him/her to an NC. In short, the COC paves the way to the earning of an NC.
2
Some Learning Modules combined use and maintenance of tools to make one Lesson, so the number of Lessons amount to 4; others made separate Lessons for use of tools and for
maintenance of tools, thus the total is 5 Lessons.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 7
Students choice of TLE specialization begins in Grades 9.Afterhaving been exposed to an array of TLE courses during the exploratory phase in the
first two years, the student will be most benefited, if in Grades 10,11, or 12 he/she continues with a TLE course in which he/she already has a COC. In that
way, he/she will get an NC faster.
About the Learning Module
1. Design of the Module
a. The Module is designed to be a teacher-assisted learning kit or a self-learning kit on competencies that a Grade 7 TLE ought to possess. It
explores the course on Aquaculture which helps your student earn a Certificate of Competency in Grade 9which leads to a National Certificate
Level I / II (NCI / II)in Grades 10, 11 or 12.
b. The Learning Module is made up of 4 to 5 Lessons based on the competencies. Each Lesson contains the following:
1) Learning Outcomes
2) Performance Standards
3) Materials/Resources
4) Definition of Terms
5) What Do You Already Know?
6) What Do You Need to Know?
7) How Much Have You Learned?
8) How Do You Apply What You Learned?
9) What Is Your Score?
10) References
There are some TLE Modules which have a section on How Do You Extend Your Learning?, This section is meant for enrichment. It is usually
given as an assignment for not everything can be taught and done in the classroom given a limited time.
c. The Self-check can also serve as the posttest of the lesson.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 8
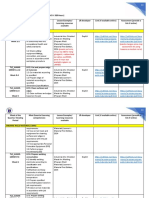
2. Parts of the Lesson. -The following explain the parts of each Lesson and describe what your students- as well as your tasks are.
Part of the Lesson Students Task Teachers Task
1. Learning outcomes are what your TLE
student is supposed to know and be able
to do after using the module. Since our
TLE courses are TR-based, all learning
outcomes are lifted from the TESDA TR. In
the Curriculum Guide (the matrix which
contains Content Standard, Performance
Standard, Learning Competencies,
Projects/Activities, Assessment, Duration),
the identified Learning Outcomes are
written in the column of Learning
Competencies.
Students acquaint themselves with the learning
outcomes and performance standards and
make them their personal goals.
You introduce the learning outcomes to your
students and make sure that they understand
them and make these learning targets their
own.
Make these your goals for instruction.
2. Performance Standards are referred to
as performance criteria in the TESDA TR.
They are more specific descriptions of the
students behavior that serve as evidence
that the expected learning outcomes have
been realized with the expected level of
proficiency or in accordance with
established standards.
The learning outcomes and performance
standards set the direction of your lessons.
These are what you should teach and, in
turn, what you should assess. They are
identified and are written for you in the
Students clearly understand the performance
standards and make them their own learning
goals.
You introduce the performance standards to
your students and make sure that they
understand them and make these performance
standards their own.
Let these standards give your lesson its specific
direction.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 9
Curriculum Guide.
3. Materials/Resources and References
To teach effectively, you need materials
and references. Materials may include
equipment, hand tools or consumables.
The references are the books, magazines,
articles, websites you yourself and your
students will read or refer to in order to
gain greater understanding of the lesson.
They are either in soft copy or hard copy.
Get to know the materials. They are part of the
Lesson.
By all means, read the references for lesson
mastery.
Prepare the materials you need in advance. For
gadget, tool or equipment, it is always wise to
prepare, check and try them in advance to
ensure that they function when you use them.
As the saying goes forewarned is forearmed.
Be resourceful in the preparation of materials.
You are strongly encouraged to use appropriate
local materials as substitute for listed materials
that are not available.
For effective teaching, your lesson preparation
should include reading the list of references.
Do not limit yourself to the list of references. If
you discover good reference material/s, add to
the list of references.
Introduce the references to your students.
Motivate them to read these references as they
go through the module for mastery of the
lesson.
4. The definition of terms and acronyms
will help you understand the meaning of
key words in your lesson. Defining key
words as they are used in your lesson will
ensure that the key terms in your lesson
mean one and the same for everyone in
class and so avoid misunderstanding.
Refer to the definition of terms for greater
understanding of the lesson.
Remind your students to refer to the definition
of terms and acronyms for clearer
understanding of the lesson.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 10
5. The section What Do You Already
Know is intended to determine entry
knowledge and skills of your students to
find out if you have to teach the lesson,
teach some parts of the lesson or skip it
entirely because your students already
know it. This is done by way of a pretest.
Take the test honestly.
Check answers against the answer key
provided.
Tell your students to accomplish the pretest.
Explain that the purpose of the pretest is to find
out how much they already know about the
lesson in order to determine your next steps. It
is, therefore, necessary that they take the test
honestly, if they want to learn or want to be
helped.
Make it clear to them that their scores will not
be recorded for grading purposes and will not
be taken against them.
If you find out that your students already know
what you are about to teach, logic dictates that
you do not need to teach it anymore. You may
as well proceed to the next lesson. If, however,
you find out that they do not yet know what you
are about to teach, then by all means teach. Or
if you discover that your students have some
erroneous concepts, then teach and correct
their misconceptions. To know what your
students already know and do not yet know will
guide you in adjusting your instruction.
6. What Do You Need To Know?- This
section contains one or more Information
Sheets and for some modules an
Operation Sheet. These are important
notes for the TLE student to read after
which he/she is asked to do a Self-check to
determine how much he/she has learned.
Read and understand the Information Sheet/s
and /or Operation Sheet.
Be prepared For a Self-check which serves as
a posttest.
Correct answers by referring to the answer key.
Make sure students are engaged in reading the
Information Sheet/Observation Sheet and in
answering the self-check.
Give assistance to your students where
needed.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 11
The self-check functions as a pretest.
7. How Do You Apply What You
Learned? In this section, you give your
student the opportunity to transfer what
he/she has learned in another activity or in
real life situation. Ideally, this should be a
performance test, what you usually call
practical test. If the proof of the pudding is
in the eating, then your student must be
able to apply what she/he learned in real-
life setting or must be able to come up with
a product as an evidence of learning.
Do the Activity.
To determine level of performance, use the
scoring rubrics or check answers against the
answer key, which ever is applicable.
Reflect on assessment results.
Find a way to test real life application of what
your students have learned.
Do not hesitate to use ways of determining how
your students can apply learned facts and
concepts which are more authentic and realistic
than that/those given in the Module.
Reflect on assessment results. Use
assessment results in planning your instruction.
8. How Do You Extend Your Learning?
As the word implies, this activity is done
outside class hours for enrichment
purposes. This can reinforce lesson
mastery.
Do the task assigned outside class hours. Motivate the students to do the task by making
clear what the enrichment activity is about why
it is given, how it is done, how it relates to the
class lesson .
Reflection
It is a good habit to reflect on your teaching for the day what went well, what did not go well, why this activity went well with this group, why it didnt
work well with the other group. What are your realizations? What are lessons learned? Jot them down in your diary. Commit them to your memory. If you do
this consistently, you will find your delivery improve substantially.
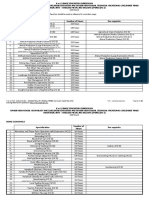
Curriculum Guide for the Exploratory Course on SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
For you to get a complete picture of the complete TLE exploratory course on Computer Hardware Servicing, you are hereby provided with the
Curriculum Guide on Computer Hardware Servicing.
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 12
Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competencies Project/ Activities Assessment Duration
LESSON 1: USE BASIC HAND TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
Demonstrate understanding
of/on:
Hand tools and their uses
Defective and non-
defective hand tools
1. Hand tools selected are
appropriate to the requirements
of the task.
2. Unsafe or defective tools are
identified and marked for repair
according to procedure.
LO1. Select and classify
hand tools and
equipment
Written exam
Performance
test
6 hours
Performing tasks
o Adjusting
o Dismantling
o Assembling
o Finishing of item or
components
Procedure on using
different hand tools and
equipment
1. Task is performed in accordance
with company or industry safety
procedure.
LO2. Use hand tools and
equipment
1. Students
demonstration on
the proper use
and care of tools
Written Exam
Routine maintenance
o Lubricating
o Tightening
o Repairing simple tool
o Hand sharpening
o Cleaning
Proper storage of hand
tools equipment
1. Routine maintenance of hand
tools is undertaken according to
standard operating procedures,
principles and techniques.
2. Hand tools are stored in
designated location in
accordance with manufacturers
instruction/standard operating
procedure.
LO3. Maintain hand tools. Written Exam
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 13
Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competencies Project/ Activities Assessment Duration
LESSON 2: PERFORM MENSURATION AND CALCULATION
Demonstrate understanding
of/on:
Fundamental Operations
o Subtraction
o Addition
o Multiplication
o Division
1. Simple calculations involving
whole numbers, mixed numbers,
fraction and decimal are
performed using the four
fundamental operations.
LO1. Perform four
fundamental
operations.
1. Computation
involving the four
fundamental
operations (2-3
digits)
Written/oral
Performance
test
Conversion of English to
metric (vice versa)
o English and metric
system of
measurements
Measurement Systems
Unit conversion
1. Units are converted to the
required figure using the given
formulae.
2. English measurements are
converted to metric
measurements according to
procedure.
LO2. Convert English
Unit of
measurement to
Metric System
Written Exam
Ratio and proportion
Area and volume
1. Percentages are computed
using appropriate formula.
2. Precise and accurate formulas
for computing area needed in
metal trade are used.
LO3. Perform basic
ration and
proportion area
and volume
calculations
Written Exam
LESSON 3: APPLY SAFETY PRACTICES
Demonstrate understanding
of/on:
Identifying hazard to be
1. Hazards are identified correctly
LO1. Identify hazardous
Written exam
6 hours
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 14
Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competencies Project/ Activities Assessment Duration
avoided in welding
safety signs and symbols
types of hazards
occupational safety and
health standards
in accordance with
OHS(occupational health and
safety) procedures.
2. Safety signs and symbols are
identified and adhered to in
accordance with workplace
safety procedure.
area.
Using personal protective
equipment (PPE) and its
proper uses
1. Personal protective
clothing/equipment (PPE) as per
job requirements are identified.
2. Proper wearing of PPE is
properly observed in accordance
with workplace safety policies.
LO2. Use personal
protective clothing
and devices.
Written exam
Pre-use inspection and
checking procedures
1. Safe handling of tools,
equipment and materials is
properly observed in accordance
with OHS requirements and
industry/ company policies.
2. Safety label and tag of tools and
equipment are strictly followed.
LO3. Identify safety and
health
requirements and
policy
1. Proper use and
care of power
tools
Written exam
LESSON 4: INTERPRETING PLANS AND DRAWINGS
Demonstrate understanding
of/on:
Alphabet of lines
1. Alphabet of lines are identified
according to ISO(International
Standard Organization).
LO1. Identify standard
alphabet of lines.
Written Exam
Performance
test
6 hours
Supplementary symbols 1. Welding joints and symbols are LO2. Interpret standard Written Exam
K to 12 TECHNOLOGY AND LIVELIHOOD EDUCATION
INDUSTRIAL ARTS SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
(Exploratory)
*TWG on K to 12 Curriculum Guide version January 31, 2012 15
Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competencies Project/ Activities Assessment Duration
interpreted according to drawing
standard
drawing symbols.
By three methods we may learn wisdom: First, by reflection, which is noblest; second, by imitation, which is
easiest; and third by experience, which is the bitterest.
- Confucius
You might also like
- TLE-ICT-Contact Center Services Grade 10 LMDocument301 pagesTLE-ICT-Contact Center Services Grade 10 LMHari Ng Sablay81% (91)
- TLE-ICT-Contact Center Services Grade 10 TGDocument94 pagesTLE-ICT-Contact Center Services Grade 10 TGHari Ng Sablay97% (34)
- CB-PAST Forms For TeachersDocument38 pagesCB-PAST Forms For TeachersHari Ng Sablay93% (29)
- TLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 9Document262 pagesTLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 9Hari Ng Sablay87% (410)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Math2-RankingDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Math2-RankingPaula Anjelica Rivera86% (21)
- Ia - Smaw - Prepare Weld Materials PDFDocument36 pagesIa - Smaw - Prepare Weld Materials PDFJanus Salinas85% (20)
- TLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 10 LMDocument334 pagesTLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 10 LMHari Ng Sablay93% (241)
- Department of Education: Candugay High SchoolDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Candugay High SchoolISAGANI80% (5)
- SMAW Pretest1Document2 pagesSMAW Pretest1Arnelson Derecho75% (4)
- Smaw August 1, 2019 Thursday 730 To 930 CotDocument3 pagesSmaw August 1, 2019 Thursday 730 To 930 Cotronald curayag100% (2)
- TLE-ICT-Technical Drafting Grade 10 LMDocument175 pagesTLE-ICT-Technical Drafting Grade 10 LMHari Ng Sablay87% (114)
- K To 12 Fish Processing Learning ModuleDocument190 pagesK To 12 Fish Processing Learning ModuleSan Vicente Integrated80% (15)
- Family Life Education PhilosophyDocument3 pagesFamily Life Education Philosophyapi-30085186950% (2)
- Session Plan in Smaw PipesDocument7 pagesSession Plan in Smaw PipesGuada Lupe100% (1)
- Grade 9 SMAW NC I SECOND QUARTER PERIODICAL by JIGGER MANCAWAN TALAKAG NHSDocument4 pagesGrade 9 SMAW NC I SECOND QUARTER PERIODICAL by JIGGER MANCAWAN TALAKAG NHSjigger b. mancawan100% (1)
- Tos Smaw 1ST QuarterDocument2 pagesTos Smaw 1ST Quarterjigger b. mancawan80% (5)
- Grade 10 - Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument3 pagesGrade 10 - Shielded Metal Arc WeldingLiezl Sabado79% (33)
- SMAW FinalsDocument4 pagesSMAW FinalsIan Asperga100% (1)
- Smaw g11 1st ExamDocument3 pagesSmaw g11 1st ExamNeil Alcantara Masangcay91% (33)
- K To 12 Dressmaking and Tailoring Teacher's GuideDocument15 pagesK To 12 Dressmaking and Tailoring Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay88% (43)
- E-CHS LM Module4 Q3-Q4decDocument130 pagesE-CHS LM Module4 Q3-Q4decHari Ng Sablay91% (11)
- K To 12 - MATHEMATIC Curriculum Guide - Grade 1Document28 pagesK To 12 - MATHEMATIC Curriculum Guide - Grade 1Hari Ng Sablay100% (6)
- K To 12 Crop Production Learning ModulesDocument124 pagesK To 12 Crop Production Learning ModulesHari Ng Sablay98% (53)
- Joan Hunt Final Documentv1Document17 pagesJoan Hunt Final Documentv1Nancy OliverNo ratings yet
- Memo Self IntroDocument1 pageMemo Self IntroAwais SohailNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN SMAW (Explicit-Based Learning)Document6 pagesLESSON PLAN SMAW (Explicit-Based Learning)juza mia ministerio100% (1)
- Final Tle - Ia - Smaw Grades 11-12 01.09.2014Document9 pagesFinal Tle - Ia - Smaw Grades 11-12 01.09.2014Renante Deseo60% (5)
- Smaw 12 DLLDocument3 pagesSmaw 12 DLLSally Java Senayo100% (5)
- Smaw 9 Prepare Weld Materials LC 123Document3 pagesSmaw 9 Prepare Weld Materials LC 123RoanBronolaSumalinog0% (1)
- SMAW TestDocument4 pagesSMAW TestBapunNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding NC Ii 3 Final ExaminationDocument2 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding NC Ii 3 Final ExaminationJessa AquitanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Summative TestDocument8 pages2nd Summative TestSally Java Senayo100% (3)
- Shs Grade 11 - TVL SmawDocument34 pagesShs Grade 11 - TVL SmawLara Jeane Losbañes100% (3)
- MODULE 8 SMAW 11 12 Q2 X 1Document29 pagesMODULE 8 SMAW 11 12 Q2 X 1Marc Cadalin100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheets (LAS) For SMAW NC II: Weld Carbon Steel Plates in Flat Position (1G) andDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheets (LAS) For SMAW NC II: Weld Carbon Steel Plates in Flat Position (1G) andKler Daradar100% (2)
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) Grades 7-10Document20 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding (Smaw) Grades 7-10Claire Absin Pastelero100% (2)
- SMAW NC I Set C - 50 ItemsDocument9 pagesSMAW NC I Set C - 50 Itemslouie gerasmiaNo ratings yet
- TVL-SMAW 12 - Week 5 - Lesson 3 - Weld Defects, Causes, and RemediesDocument11 pagesTVL-SMAW 12 - Week 5 - Lesson 3 - Weld Defects, Causes, and RemediesNelPalalonNo ratings yet
- Q1 TLE Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) NC II Module 1Document30 pagesQ1 TLE Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) NC II Module 1Pladie Salomon100% (1)
- TLE - Shielded Metal Arc Welding 10 ThirdDocument5 pagesTLE - Shielded Metal Arc Welding 10 ThirdLyn Valles100% (1)
- Grade 10 Smaw Exam 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Smaw Exam 1st QuarterJymaer Geromo80% (5)
- SMAW 11 - Q1-Module-1-Lesson4Document11 pagesSMAW 11 - Q1-Module-1-Lesson4Jerome A. Gomez100% (2)
- Grade 12: Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument10 pagesGrade 12: Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDarry BlanciaNo ratings yet
- TVL-SMAW 12 - Week 5 - Lesson 1 - Acceptable Weld ProfilesDocument11 pagesTVL-SMAW 12 - Week 5 - Lesson 1 - Acceptable Weld ProfilesNelPalalon100% (3)
- Luray Ii Barangay High School Luray II, Toledo City, Cebu Quarter Exam in SMAW 8Document4 pagesLuray Ii Barangay High School Luray II, Toledo City, Cebu Quarter Exam in SMAW 8Krizzie Jade CailingNo ratings yet
- Performance Criteria ChecklistDocument2 pagesPerformance Criteria ChecklistShallimar AlcarionNo ratings yet
- Signed Off SMAW11 q1 m4 Fit-Up Welds Material v3Document33 pagesSigned Off SMAW11 q1 m4 Fit-Up Welds Material v3Christian Jake Respicio100% (1)
- Q3, Module 2, Lesson 3Document9 pagesQ3, Module 2, Lesson 3Jerome A. Gomez100% (2)
- Tle - Ia - Smaw: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Marking/Locating Weld DefectsDocument12 pagesTle - Ia - Smaw: Quarter 4 - Module 1 Marking/Locating Weld DefectsJessel Mejia OnzaNo ratings yet
- Tos 2nd Quarter SmawDocument6 pagesTos 2nd Quarter SmawArnelson Derecho100% (10)
- Reb TM1Document87 pagesReb TM1Weird Nahuman0% (1)
- 11 SMAW Q4 Module 4Document13 pages11 SMAW Q4 Module 4Mark Johnson VillaronNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding NC II: Quarter 2 - Module 2Document22 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding NC II: Quarter 2 - Module 2Genesis Dollison75% (4)
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding NC I CGDocument26 pagesShielded Metal Arc Welding NC I CGJoven Francisco100% (4)
- Grade 9 12 SMAWDocument10 pagesGrade 9 12 SMAWFlor Gagasa100% (4)
- SHS - SLK - Inudstrial Arts Smaw Marking or Locating Weld DefectsDocument20 pagesSHS - SLK - Inudstrial Arts Smaw Marking or Locating Weld Defectsiammhon100% (1)
- Q1, Module 1, Lesson3Document8 pagesQ1, Module 1, Lesson3Jerome A. Gomez100% (1)
- Shielded Metal Arc Works (SMAW) : Technology and Livelihood EducationDocument19 pagesShielded Metal Arc Works (SMAW) : Technology and Livelihood EducationLyn VallesNo ratings yet
- CBLM Smaw Plates 1g-4gDocument39 pagesCBLM Smaw Plates 1g-4gMarlon Ty Manalo85% (27)
- RATING SHEET FOR DEMONSTRATION SmawDocument3 pagesRATING SHEET FOR DEMONSTRATION SmawLudivino Toto Ledesma Condalor100% (2)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region IIIDocument12 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region IIIglordan758100% (6)
- Final Exam Tle 8 (Exploratory-Smaw) : Table of SpecificationsDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Tle 8 (Exploratory-Smaw) : Table of SpecificationsKrizzie Jade Cailing100% (1)
- CBLMDocument50 pagesCBLMLowen Tabance Simbit100% (2)
- Core Smaw NC IDocument13 pagesCore Smaw NC INICOSAT CollegesNo ratings yet
- DLL - SMAW - 1st Sem - Week 11Document3 pagesDLL - SMAW - 1st Sem - Week 11Mary Antoinette Magallanes100% (1)
- FINAL SMAW-12-Quarter-3-module 4 PDFDocument20 pagesFINAL SMAW-12-Quarter-3-module 4 PDFRandy Sacatani100% (1)
- Periodical Test 2018 in TVL SMAWDocument9 pagesPeriodical Test 2018 in TVL SMAWArnelson Derecho93% (14)
- 3rd Periodical Examination SMAWDocument30 pages3rd Periodical Examination SMAWFroilan MatutinoNo ratings yet
- Technical Vocational Livelihood: Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument7 pagesTechnical Vocational Livelihood: Shielded Metal Arc Weldingtibo bursioNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Carpentry Teacher's GuideDocument18 pagesK To 12 Carpentry Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay91% (11)
- K To 12 Mechanical Drafting Teacher's GuideDocument16 pagesK To 12 Mechanical Drafting Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay100% (11)
- K To 12 Tiles Setting Teacher's GuideDocument21 pagesK To 12 Tiles Setting Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay80% (5)
- K To 12 Rac ServicingDocument19 pagesK To 12 Rac ServicingBlessed Mary33% (3)
- K To 12 Electronics Teacher's GuideDocument17 pagesK To 12 Electronics Teacher's GuideHari Ng Sablay0% (1)
- TLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 10 TGDocument119 pagesTLE-ICT-Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 10 TGHari Ng Sablay83% (143)
- Online Research Activity: Click or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter TextDocument3 pagesOnline Research Activity: Click or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter TextHari Ng SablayNo ratings yet
- TLE-ICT-Technical Drafting Grade 10 TGDocument42 pagesTLE-ICT-Technical Drafting Grade 10 TGHari Ng Sablay90% (39)
- D Chs LM Module3 q1 q2 DecDocument151 pagesD Chs LM Module3 q1 q2 DecHari Ng Sablay89% (9)
- C-CHS LM Module 1 PECs and Module2 EMDocument35 pagesC-CHS LM Module 1 PECs and Module2 EMHari Ng Sablay95% (21)
- Language - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLanguage - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- K To 12 MUSIC Curriculum Guide GRADE 1Document47 pagesK To 12 MUSIC Curriculum Guide GRADE 1Hari Ng Sablay100% (2)
- B-CHS LM Table of ContentsDocument12 pagesB-CHS LM Table of ContentsHari Ng SablayNo ratings yet
- HTML Introduction: Structure and Formatting TagsDocument17 pagesHTML Introduction: Structure and Formatting TagsHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- Assessment System K-2Document47 pagesAssessment System K-2Hari Ng SablayNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Mother Tongue Curriculum Guide 1-3Document13 pagesK To 12 Mother Tongue Curriculum Guide 1-3Hari Ng Sablay100% (4)
- K To 12 Physical Education Curriculum Guide - Grade 1Document37 pagesK To 12 Physical Education Curriculum Guide - Grade 1Hari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- K To 12 Aquaculture Teacher's GuideDocument17 pagesK To 12 Aquaculture Teacher's Guidejaphethbersales83% (6)
- K To 12 - ART Curriculum Guide GRADE 1Document26 pagesK To 12 - ART Curriculum Guide GRADE 1Hari Ng Sablay100% (3)
- Grade 7 ToT Fil and Eng MLE OrientationDocument86 pagesGrade 7 ToT Fil and Eng MLE OrientationHari Ng SablayNo ratings yet
- K To 12 - Health Curriculum Grade 1Document12 pagesK To 12 - Health Curriculum Grade 1Hari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- Grade 7 ToT Fil and Eng MLE OrientationDocument86 pagesGrade 7 ToT Fil and Eng MLE OrientationHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- K To 12 Crop Production Teaching GuidesDocument20 pagesK To 12 Crop Production Teaching GuidesrhodoradevillamanaloNo ratings yet
- K To 12 Food (Fish) ProcessingDocument20 pagesK To 12 Food (Fish) Processingjagelido83% (23)
- K To 12 Aquaculture Learning ModuleDocument180 pagesK To 12 Aquaculture Learning ModuleHari Ng Sablay100% (2)
- Teachers Vocation and Students Attitudes TowardsDocument11 pagesTeachers Vocation and Students Attitudes TowardsValcorza KarenNo ratings yet
- Rahillah Shafahi: Key SkillsDocument2 pagesRahillah Shafahi: Key SkillsAstoriaNo ratings yet
- Evidence 7 Worshop Assessing The KPI For The Supply ChainDocument3 pagesEvidence 7 Worshop Assessing The KPI For The Supply ChainSolucarga Jyc0% (2)
- Motivation Power Point PresentationDocument34 pagesMotivation Power Point PresentationRichardAmuokNo ratings yet
- Nnest Vs NestDocument15 pagesNnest Vs NestVenezuela TESOL (VenTESOL)No ratings yet
- Homeroom Guidance ActivityDocument2 pagesHomeroom Guidance ActivityMs. Rizza Magno100% (1)
- Caregiver Resume ExamplesDocument7 pagesCaregiver Resume Examplesphewzeajd100% (2)
- The Opportunity To Obtain A Position As An Elementary Educator That Will Utilize My Strong Dedication To Children's DevelopmentDocument5 pagesThe Opportunity To Obtain A Position As An Elementary Educator That Will Utilize My Strong Dedication To Children's DevelopmentJoslyn BomgaarsNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 10Document8 pagesLesson Plan in English 10ArchessNo ratings yet
- Teaching Grammar CommunicativelyDocument15 pagesTeaching Grammar CommunicativelyKhairul WalidNo ratings yet
- fs1 The Learners DevelopmentDocument49 pagesfs1 The Learners DevelopmentGrace Joy Mascariñas MahusayNo ratings yet
- Test - 4 (English) Board TestDocument10 pagesTest - 4 (English) Board TestAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- January 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Document2 pagesJanuary 2013 Igcse Timetable 22-06-2012Rizwanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Home Visitation FormDocument1 pageHome Visitation FormMarilou SorianoNo ratings yet
- Admit Card 20003504193Document2 pagesAdmit Card 20003504193ShivangiNo ratings yet
- Behavior Specialist Rubric 6-01-14Document24 pagesBehavior Specialist Rubric 6-01-14Innovative Educational Services, CCIU100% (1)
- Lesson Plan and Rubric: Dance of The Scary HoleDocument9 pagesLesson Plan and Rubric: Dance of The Scary HoledfwdNo ratings yet
- Conversation WorksheetsDocument4 pagesConversation WorksheetslucianabianchiniNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Collective NounsDocument4 pagesActivity 1: Collective NounsReshantini RajendranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document9 pagesLesson 4api-371196243No ratings yet
- Religion Leaving Cert Coursework 2017Document5 pagesReligion Leaving Cert Coursework 2017zug0badej0n2100% (2)
- 3Q Mapeh 10 DLLDocument66 pages3Q Mapeh 10 DLLMaria isabel DicoNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-502692006No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 4Document8 pagesLesson Plan in English 4PATRICIA MAE AMADORANo ratings yet
- Module 5-7Document13 pagesModule 5-7Celema LazoNo ratings yet
- 13-04-21 Assignment The Ron Clark Story 992 Staff Teacher 19 1Document2 pages13-04-21 Assignment The Ron Clark Story 992 Staff Teacher 19 1Karleymar NievesNo ratings yet