Professional Documents
Culture Documents
There Are Three General Categories of Fits
There Are Three General Categories of Fits
Uploaded by
anon_9028355720 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesFitting refers to assembling mechanical components together by mating parts like shafts and holes. There are three categories of fits: clearance fits which allow rotation or sliding, interference fits which securely hold parts together, and transition fits which securely hold parts but still allow disassembly. The specific class of fit within each category is chosen based on the intended use and manufacturability of the parts.
Original Description:
Original Title
3.Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFitting refers to assembling mechanical components together by mating parts like shafts and holes. There are three categories of fits: clearance fits which allow rotation or sliding, interference fits which securely hold parts together, and transition fits which securely hold parts but still allow disassembly. The specific class of fit within each category is chosen based on the intended use and manufacturability of the parts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThere Are Three General Categories of Fits
There Are Three General Categories of Fits
Uploaded by
anon_902835572Fitting refers to assembling mechanical components together by mating parts like shafts and holes. There are three categories of fits: clearance fits which allow rotation or sliding, interference fits which securely hold parts together, and transition fits which securely hold parts but still allow disassembly. The specific class of fit within each category is chosen based on the intended use and manufacturability of the parts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Introduction
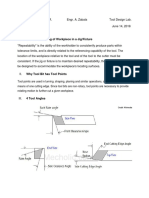
Fitting refers to the mating of two mechanical
components it is also refers to assembling of parts
together and removing metals to secure necessary
fit.Manufactured parts are very frequently required
to mate with one another. They may be designed to slide
freely against one another or they may be designed to
bind together to form a single unit. The most common fit
found in the machine shop is that of a shaft in a hole. This
operation include measuring, marking, chipping and filing
There are three general categories of fits:
1) Clearance fits for when it may be desirable for the
shaft to rotateor slide freely within the hole, this is
usually referred to as a"sliding fit."
2) Interference fits for when it is desirable for the shaft
to besecurely held within the hole, this is usually referred
to as an interference fit and
3) Transition fits for when it is desirable that the shaft
to be held securely, yet not so securely that it cannot be
disassembled, this is usually referred to as a Location or
Transition fit. Within each category of fit there
are several classes ranging from high precision and
narrow tolerance (allowance) to lower precision and
wider tolerance. The choice of fit is dictated first by the
use and secondly by the manufacturability of the parts
You might also like
- Semitub DesignDocument2 pagesSemitub DesignWero579No ratings yet
- Boeing Fastener TypesDocument2 pagesBoeing Fastener TypesBazán DanielNo ratings yet
- Home About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting InfoDocument9 pagesHome About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting Infopaeg6512No ratings yet
- Automotive Gaskets and FastenersDocument42 pagesAutomotive Gaskets and FastenersRhenzCarloLeonatoNo ratings yet
- FixturesDocument12 pagesFixturesakshay2761No ratings yet
- Project Title: Study and Design of A Mechanical SealDocument19 pagesProject Title: Study and Design of A Mechanical Sealsyed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Jig and FixturesDocument25 pagesJig and FixturesFadhli LieNo ratings yet
- CSNG Centralizers PaperDocument5 pagesCSNG Centralizers PaperAlexNo ratings yet
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsFrom EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsFrom EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsNo ratings yet
- Recommended FitsDocument10 pagesRecommended FitsZiad AkmalNo ratings yet
- Struc Steel Erection AidsDocument3 pagesStruc Steel Erection AidsSridhar MaharajaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical FasteningDocument17 pagesMechanical FasteningNurhuda HayatiNo ratings yet
- RivetDocument15 pagesRivetEllyYanaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt Design PhilosophyDocument6 pagesAnchor Bolt Design Philosophyprabhu81100% (1)
- Roller Chain GuideDocument5 pagesRoller Chain GuidechikoopandaNo ratings yet
- تقريييييرDocument8 pagesتقريييييرSaleh KettanNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - CouplingDocument10 pagesCH 7 - Couplingantoniogaetan.rakNo ratings yet
- What Are Limits and FitsDocument9 pagesWhat Are Limits and FitsKashif RasheedNo ratings yet
- ME TECH - Types of Fabricated PartsDocument4 pagesME TECH - Types of Fabricated PartsRobertRoyImmanuelBat-ogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Different Types of FixturesDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Different Types of FixturesaragawNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Damage, Repair and Types of Non Destructive TestingDocument11 pagesSheet Metal Damage, Repair and Types of Non Destructive TestingVasan VasanNo ratings yet
- DG - 1147313041 - Body in White 2Document19 pagesDG - 1147313041 - Body in White 2K S RANJITH ランジットNo ratings yet
- Just How Flexible Is Your Flexible Coupling in Reality?Document8 pagesJust How Flexible Is Your Flexible Coupling in Reality?peach5No ratings yet
- BEARINGDocument13 pagesBEARINGhariprasad.mmechregd1No ratings yet
- Rivet: What Is A Rivet?Document4 pagesRivet: What Is A Rivet?Karan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 PresentationDocument44 pagesModule 6-5 Fasteners Pt3 Presentationabdullahqureshi789456No ratings yet
- Fastener Materials and NomenclatureDocument16 pagesFastener Materials and NomenclatureabhiNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument57 pagesBearingsSayyid UkashaNo ratings yet
- Fastener FailureDocument4 pagesFastener FailureriysallNo ratings yet
- Elements of Machine DesignDocument8 pagesElements of Machine DesignYash PatilNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Assembly-RAIDocument48 pagesMechanical Assembly-RAIfinnandzestzuNo ratings yet
- Types of Fits: Engineering TolerancingDocument2 pagesTypes of Fits: Engineering TolerancingRandima GajanayakaNo ratings yet
- CouplingDocument9 pagesCouplingPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Thrust Bearings To Reduce Friction and Support Axial LoadsDocument13 pagesThrust Bearings To Reduce Friction and Support Axial LoadsThejaswiniNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mechanical Joint 22Document16 pagesWhat Is A Mechanical Joint 22Arjhay GironellaNo ratings yet
- Collet ChuckDocument4 pagesCollet ChuckAndrei IftincaNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2022 82714630Document7 pagesMUCLecture 2022 82714630Muthoni EliasNo ratings yet
- Coupling: This Article Is About A Mechanical Connection Between Two Objects. For Other Uses, SeeDocument24 pagesCoupling: This Article Is About A Mechanical Connection Between Two Objects. For Other Uses, Seerupesh8989No ratings yet
- Tool Bodies (Jigs & Fixtures)Document8 pagesTool Bodies (Jigs & Fixtures)nilam0% (1)
- Work 13Document17 pagesWork 13engineeradel2No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing - Fastening Devices Research PaperDocument16 pagesEngineering Drawing - Fastening Devices Research PaperMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Design of FixtureDocument4 pagesDesign of Fixtureapi-26046805No ratings yet
- Assembly in AerospaceDocument2 pagesAssembly in AerospaceoussamaNo ratings yet
- EMat 2 Catch-Up Module 5Document4 pagesEMat 2 Catch-Up Module 5Ej VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Collet Chuck: / Kɒlɪt/ Chuck Tapered Cylindrical ConicalDocument4 pagesCollet Chuck: / Kɒlɪt/ Chuck Tapered Cylindrical ConicalAndrei IftincaNo ratings yet
- Collet Chuck: / Kɒlɪt/ Chuck Tapered Cylindrical ConicalDocument4 pagesCollet Chuck: / Kɒlɪt/ Chuck Tapered Cylindrical ConicalAndrei IftincaNo ratings yet
- Removal of Broken HardwareDocument8 pagesRemoval of Broken Hardwarecronoss21No ratings yet
- Advanced Programming Methods of CNC Machine ToolsDocument8 pagesAdvanced Programming Methods of CNC Machine Toolsomar tahaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Locating and Clamping PrinciplesDocument15 pagesUnit I Locating and Clamping PrinciplesMECHANICAL DESIGNSNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Assembly Technology: Shenyang Aerospace UniversityDocument21 pagesAircraft Assembly Technology: Shenyang Aerospace Universityalokmotivation99No ratings yet
- Couplings: 1.0Document15 pagesCouplings: 1.0NyandaMadili MalashiNo ratings yet
- I. Repetitive Nesting of Workpiece in A Jig/FixtureDocument8 pagesI. Repetitive Nesting of Workpiece in A Jig/FixtureJeremy NicanorNo ratings yet
- Bolt and Nut Proposal ResearchDocument13 pagesBolt and Nut Proposal ResearchTavi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Implants in Vogue: Dr.D.J. ArwadeDocument15 pagesSelection of Implants in Vogue: Dr.D.J. Arwadedoctorsuril9108No ratings yet
- 1.0 CHP 1 Introduction DM&MEsDocument17 pages1.0 CHP 1 Introduction DM&MEsbutukiprop68372No ratings yet
- Jig and Fixtures 1Document3 pagesJig and Fixtures 1pjpatel5999No ratings yet
- Module 6-5 Fasteners Pt4 PresentationDocument46 pagesModule 6-5 Fasteners Pt4 Presentationabdullahqureshi789456No ratings yet
- Fits and ToleranceDocument5 pagesFits and ToleranceAbdullrahman ElkhatebNo ratings yet