Professional Documents
Culture Documents
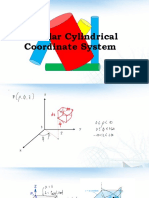
11.7 Day 1 Cylindrical Coordianates
Uploaded by
Bruce Wayne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pagesInto material for electrical engineers
Original Title
11.7 Day 1 Cylindrical Coordianates (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInto material for electrical engineers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views19 pages11.7 Day 1 Cylindrical Coordianates
Uploaded by
Bruce WayneInto material for electrical engineers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
11.
7 Day 1 Cylindrical Coordinates
Comparing Cartesian and cylindrical coordinates
Note: these are just polar coordinates with a
z coordinate (z is a vertical component)
Conversion formulas from
cylindrical to rectangular
coordinates
Converting between
cylindrical coordinates and
rectangular (Cartesian)
Note: these formulas must be memorized
Example 1
Convert the point (r, , z) = (4, 5/6, 3)
to rectangular coordinates.
Solution to
example 1
Example 2
_
Convert the point (x, y, z) = (1, 3 , 2)
to cylindrical coordinates.
Cylindrical coordinates are usually more
convenient for representing cylindrical
surfaces as they often result in simpler
equations.
Vertical planes containing the z-axis and
horizontal planes also have simple
cylindrical coordinate equations
Example 3 a
Find an equation in cylindrical coordinates for the
surfaces represented by the rectangular equation:
Solution to 3a
Example 3b
Find an equation in cylindrical coordinates for the
surfaces represented by the rectangular
equation:
Example 4
Find an equation in rectangular coordinates for the surface
represented by the cylindrical equation:
Identify the surface
r
2
cos2 +z
2
+1 = 0
Changing between coordinates on
the TI 89
Press 2
nd
5 (math) 4 matrices L Vecor ops
To polar, to cynd To convert rectangular to
Polar (2 D) or cylindrical (3D)
[1,2] to Polar (to expressed with a triangle)
[1,2,3] to Cylind
Homework
p. 825 1-11 odd, 21-27 odd,
97 104 odd (part a only)
105,107
You might also like
- Lecture - 2 - AV-231 - Cartesian Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDocument28 pagesLecture - 2 - AV-231 - Cartesian Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesHamza Salah-Ud-DinNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET7e - 15 - 08coordenadas CilíndricasDocument20 pagesStewartCalcET7e - 15 - 08coordenadas CilíndricasAndres F LeguizamonNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET8 15 07Document20 pagesStewartCalcET8 15 07OhoodKAlesayiNo ratings yet
- Math 220 Supplemental Notes 7 Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDocument10 pagesMath 220 Supplemental Notes 7 Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Week10 Lect3 HandoutsDocument3 pagesWeek10 Lect3 HandoutsManuel Xavier RajeshNo ratings yet
- AnGeom Bridging FinalDocument9 pagesAnGeom Bridging FinalAkira ToudouNo ratings yet
- Circles in Polar Coordinates. Graphing The Cardiod. Graphing The LemniscateDocument8 pagesCircles in Polar Coordinates. Graphing The Cardiod. Graphing The LemniscatePablitox84No ratings yet
- Studies in Geometry: 1 TesselatorsDocument12 pagesStudies in Geometry: 1 Tesselatorsjantarmantar12No ratings yet
- 17 - 2mm KKDocument17 pages17 - 2mm KKkazi wahexNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDocument18 pagesCylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesSankar KaruppaiahNo ratings yet
- 15.7 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates Integration in Cylindrical Coordinates Definition: Cylindrical CoordinatesDocument8 pages15.7 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates Integration in Cylindrical Coordinates Definition: Cylindrical CoordinatesPraviin JayakumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Geometric Coordinate SystemsDocument20 pages1 Geometric Coordinate SystemsVickyVenkataramanNo ratings yet
- 1.calculus III (Math211) - Week 1, 2 & 3Document65 pages1.calculus III (Math211) - Week 1, 2 & 3Khaled FaisalNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyDocument49 pagesComputer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Section 16.7 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates: Z (R, Theta)Document5 pagesSection 16.7 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates: Z (R, Theta)Alex TanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document17 pagesModule 2John RivasNo ratings yet
- Intro To Polar Coordinates: Lesson 6.5ADocument17 pagesIntro To Polar Coordinates: Lesson 6.5Asigma70egNo ratings yet
- HW Feb 4Document2 pagesHW Feb 4AparaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Functions and Relations: Precalculus, 1st EdDocument49 pagesChapter 1: Functions and Relations: Precalculus, 1st EdjakyNo ratings yet
- L21Document12 pagesL21kienkienNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument16 pagesOrthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesstriaukasNo ratings yet
- StewartCalc8 15 08Document25 pagesStewartCalc8 15 08Md HasanNo ratings yet
- 4-Vertex Theorems, Sturm Theory and Lagrangian SingularitiesDocument16 pages4-Vertex Theorems, Sturm Theory and Lagrangian SingularitiesSëñorithäMëlNo ratings yet
- HttpsDocument38 pagesHttpssmileforeverNo ratings yet
- Ford Circles and Spheres: Sam NorthshieldDocument34 pagesFord Circles and Spheres: Sam NorthshieldBal Bahadur TamangNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 HandoutDocument11 pagesLecture5 HandoutRowan RootNo ratings yet
- Macdougall Jim HeronapgpDocument7 pagesMacdougall Jim HeronapgpPerepePereNo ratings yet
- A Module On ConicsDocument6 pagesA Module On ConicsAna Marie ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial v1Document5 pagesTutorial v1Ram KumarNo ratings yet
- Trig Ch8Document14 pagesTrig Ch8BenedictVillaminPolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah Ke - 6Document46 pagesMateri Kuliah Ke - 6Jahfal JunarlinNo ratings yet
- REPORT-ED-MATH2 (Autosaved)Document16 pagesREPORT-ED-MATH2 (Autosaved)LAMA, ABEGAIL K. BSED-MATH 3No ratings yet
- Calculus NilDocument7 pagesCalculus NilPushpak ShewaleNo ratings yet
- Assignment 101Document9 pagesAssignment 101JOE JoJoNo ratings yet
- 2D Circular Cylidrical Coordinate SystemDocument23 pages2D Circular Cylidrical Coordinate SystemLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- التحويل بين الاحداثياتDocument31 pagesالتحويل بين الاحداثياتShaheen Al YafayNo ratings yet
- Additional Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesAdditional Exam QuestionsLaura MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates: We Live On A SphereDocument20 pagesPolar Coordinates: We Live On A SphereKurt HerreraNo ratings yet
- EEE 201 Engineering Mathematics Assoc - Prof. Dr. Ertuğrul AKSOY Cartesian and Cylindrical Coordinate SystemsDocument56 pagesEEE 201 Engineering Mathematics Assoc - Prof. Dr. Ertuğrul AKSOY Cartesian and Cylindrical Coordinate Systems357911No ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument35 pagesConic SectionsGina Fe S. LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Surface IntegralsDocument15 pagesSurface IntegralsTushar Gupta100% (1)
- Unit-10 by Cambridge University Learning LessonDocument21 pagesUnit-10 by Cambridge University Learning Lessondragonthegreat214No ratings yet
- HenonDocument22 pagesHenonArtur MinasyanNo ratings yet
- Cengage Study Vectors Imp Physics Volume VectorDocument52 pagesCengage Study Vectors Imp Physics Volume VectorTECH-A -TRONICSNo ratings yet
- Del in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates - WikipediaDocument15 pagesDel in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates - WikipediaSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- APPLICATION 1 Area Bounded by CurvesRectangular Polar Coordinates PDFDocument31 pagesAPPLICATION 1 Area Bounded by CurvesRectangular Polar Coordinates PDFJingWeybzNo ratings yet
- Conformal MappingDocument8 pagesConformal MappingSudharsan ThiruvenkadamNo ratings yet
- Notes - Circles (Another Copy)Document9 pagesNotes - Circles (Another Copy)mintuwondeNo ratings yet
- StewartCalcET7e 15 09ejeDocument27 pagesStewartCalcET7e 15 09ejeAndres F LeguizamonNo ratings yet
- Polar Forms of Conic Sections: Lesson 9-4Document35 pagesPolar Forms of Conic Sections: Lesson 9-4Fran LeeNo ratings yet
- Anna's AssignmentDocument16 pagesAnna's Assignmenttumaini murrayNo ratings yet
- Q2-Coordinate GeometryDocument33 pagesQ2-Coordinate GeometryAkshat ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ford Circles and Spheres: March 2015Document35 pagesFord Circles and Spheres: March 2015Lucas JoaquimNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Coordinates Arfken 5th EdDocument14 pagesCurvilinear Coordinates Arfken 5th EdManoj SNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q2 - Wk8 - Center Radius Form of The Equation of A Circle EvaluatedDocument12 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Wk8 - Center Radius Form of The Equation of A Circle EvaluatedBryce PandaanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document12 pagesModule 2rosejallores28No ratings yet
- Hex Circle PackingsDocument4 pagesHex Circle PackingsnospoonNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument8 pagesBasic GeometrymorrenbonnieNo ratings yet
- How and Why Did Hatshepsut Invent The Im PDFDocument100 pagesHow and Why Did Hatshepsut Invent The Im PDFBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Texas Property Tax ExemptionsDocument23 pagesTexas Property Tax ExemptionsBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- African History and Culture Study GuideDocument45 pagesAfrican History and Culture Study GuideBruce Wayne100% (1)
- Before The PreWordBriefDocument6 pagesBefore The PreWordBriefBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Religious Influences On The EarDocument37 pagesEgyptian Religious Influences On The EarBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Before The PreWordBriefDocument6 pagesBefore The PreWordBriefBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Calculus I Calculations On The TI-89: X 2x X 4 2xDocument1 pageCalculus I Calculations On The TI-89: X 2x X 4 2xBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Dictionaries Immutable - PyDocument1 pageDictionaries Immutable - PyBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Xbox OneDocument12 pagesXbox OneBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Cress Theory PDFDocument13 pagesCress Theory PDFBruce Wayne100% (1)
- KreoDocument3 pagesKreoBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- FBI Documents On Marcus Garvey Part 1-The-Afrikan-Library-M-Category-7268 PDFDocument1,154 pagesFBI Documents On Marcus Garvey Part 1-The-Afrikan-Library-M-Category-7268 PDFBruce Wayne100% (3)
- ReliablityDocument1 pageReliablityBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Quiz 5Document2 pagesElectromagnetics Quiz 5Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Manual Toshiba HDD 2TBDocument36 pagesManual Toshiba HDD 2TBLuis Eduardo JacomeNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Inference NotesDocument7 pagesBayesian Inference NotesNguyễn Văn QuỹNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Quiz 3Document2 pagesElectromagnetics Quiz 3Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Project 2Document6 pagesElectromagnetics Project 2Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Project 2Document6 pagesElectromagnetics Project 2Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Jesus and What He SaidDocument108 pagesJesus and What He SaidStvmapNo ratings yet
- Houston Channel LineupDocument2 pagesHouston Channel LineupBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Slavery and JusticeDocument107 pagesSlavery and JusticeKerri Turner100% (3)
- Electromagnetics Project 1Document3 pagesElectromagnetics Project 1Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetics Quiz 4Document3 pagesElectromagnetics Quiz 4Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- The Temples of Karnak - Schwaller de LubiczDocument28 pagesThe Temples of Karnak - Schwaller de LubiczDorian Taddei100% (4)
- Who Betrayed The African World Revolution John Henrik ClarkeDocument91 pagesWho Betrayed The African World Revolution John Henrik ClarkeBruce Wayne100% (5)
- The Teachings of Ptahhotep The Oldest Book in The WorldDocument29 pagesThe Teachings of Ptahhotep The Oldest Book in The Worldisis_anastasia100% (14)
- Houston Channel LineupDocument2 pagesHouston Channel LineupBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Detailed Diagram of SlaveryDocument17 pagesDetailed Diagram of SlaveryBruce WayneNo ratings yet