Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insulin Presentation
Uploaded by
api-2600535200 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views14 pagesOriginal Title
insulin presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views14 pagesInsulin Presentation
Uploaded by
api-260053520Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
By: Brittaney Bures
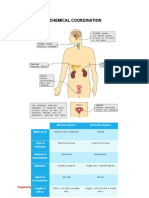
Glucose is one of the bodys most essential
molecules.
The body prefers to use glucose as its
primary energy source.
The brain relies almost exclusively on glucose
for its energy needs.
Important for blood glucose levels to remain
relatively constant throughout the day.
The pancreas recognizes rising blood glucose
level and releases insulin.
Insulin acts to decrease blood glucose levels.
Without insulin, glucose stays in the
bloodstream and is not able to enter cells of
the body. Cells may be surrounded by
glucose but they are not able to use it until
insulin arrives.
Insulin as a gatekeeper.
Lock and key the door of the cell is locked
and the insulin has the key to let the glucose in.
The fundamental principle to remember
about insulin therapy the right amount of
insulin must be available to cells when
glucose is present in the blood.
Characteristics
Types
Insulin has 3 characteristics:
Onset
Peak
Duration
Onset
The length of time before insulin reaches the
bloodstream and begins lowering blood glucose.
Peak
The time during which insulin is at maximum
strength in terms of lowering blood glucose.
Duration
How long insulin continues to lower blood
glucose.
Rapid-acting insulin
Regular or Short-acting insulin
Intermediate-acting insulin
Long-acting insulin
Rapid-acting insulin, begins to work about
15 minutes after injection, peaks in about 1
hour, and continues to work for 3 to 5 hours.
Regular or Short-acting insulin usually
reaches the bloodstream within 30 minutes
after injection, peaks anywhere from 2 to 4
hours after injection, and is effective for
approximately 5 to 7 hours.
Intermediate-acting insulin generally
reaches the bloodstream about 1 to 2 hours
after injection, peaks 4 to 12 hours later, and
is effective for about 18 to 24 hours.
Long-acting insulin reaches the bloodstream
several hours after injection and tends to
lower glucose levels fairly evenly over a 24-
hour period.
Adams, M., & Holland, L. N. (2011).
Pharmacology for nurses: a pathophysiologic
approach (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.:
Pearson Education.
You might also like
- Leadership and Management in The NicuDocument7 pagesLeadership and Management in The Nicuapi-260053520100% (1)
- Capstone PaperDocument8 pagesCapstone Paperapi-260053520No ratings yet
- An Overview of InsulinDocument4 pagesAn Overview of InsulinRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Readings (Insulin) - RetuyaDocument20 pagesReadings (Insulin) - RetuyaFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Insulin Is A Hormone Central To Regulating Carbohydrate and Fat MetabolismDocument4 pagesInsulin Insulin Is A Hormone Central To Regulating Carbohydrate and Fat Metabolismmaeca101No ratings yet
- Insulin: Deciding How Much Insulin To TakeDocument12 pagesInsulin: Deciding How Much Insulin To Takeராபர்ட் ஆன்றோ ரெனி100% (1)
- Everything You Need To Know About InsulinDocument6 pagesEverything You Need To Know About InsulinRodolfo CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Insulin Administration Revised 1Document43 pagesInsulin Administration Revised 1Cheryl Tabañag TalledoNo ratings yet
- Long-Acting Insulin - How It WorksDocument9 pagesLong-Acting Insulin - How It Workstoontoons092No ratings yet
- Brands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreDocument3 pagesBrands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreNanda Asyura RizkyaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentDocument2 pagesTypes of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentKrystale Mae ValdezNo ratings yet
- Insulin: T Ypes and Activit yDocument0 pagesInsulin: T Ypes and Activit yClara DohudeNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin: NOTE: Exact Onset, Action, and Duration Are Dependent On The Generic/brand UsedDocument3 pagesTypes of Insulin: NOTE: Exact Onset, Action, and Duration Are Dependent On The Generic/brand Usedask1400No ratings yet
- What Are The Things You Need To Know When Receiving A Patient From ER?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Things You Need To Know When Receiving A Patient From ER?Earl Joseph DezaNo ratings yet
- Insulin TypesDocument3 pagesInsulin TypesAbdullah A. ElgazarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY PROJECT. HomeostasisDocument13 pagesBIOLOGY PROJECT. HomeostasisJAYLEN TRACEYNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinsitapuNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Insulin PDFRetno WulanNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy Is A Critical Part of Treatment For People Who Have Type 1 Diabetes and For Many Who Have Type 2 DiabetesDocument3 pagesInsulin Therapy Is A Critical Part of Treatment For People Who Have Type 1 Diabetes and For Many Who Have Type 2 DiabetesRebeccah Abrazaldo100% (1)
- Lantus UsageDocument10 pagesLantus UsageSyed Masood AliNo ratings yet
- Pamplet Regarding InsulinDocument3 pagesPamplet Regarding InsulinGayatriJenaNo ratings yet
- Insulin TypesDocument4 pagesInsulin TypesMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesThe Endocrine SystemMaisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Explain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTDocument2 pagesExplain The Mechanism Involved During OGTTLumaho Greg Mikael DulawanNo ratings yet
- TX Insulina IncretinasDocument5 pagesTX Insulina IncretinasFabiola Pantoja ViorNo ratings yet
- Hayatt Univesity College. Faculty of Medicine. Family Medicine. Mohamed Gassim Mohamed. Insulin ManagementDocument14 pagesHayatt Univesity College. Faculty of Medicine. Family Medicine. Mohamed Gassim Mohamed. Insulin ManagementMohammed GassimNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Study GuideDocument4 pagesDiabetes Study GuideNicole Brassington0% (1)
- Insulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32Document16 pagesInsulin: Mert Aygüler 13O2O2O32deryaaaNo ratings yet
- INSULINDocument2 pagesINSULINremjith rajendranNo ratings yet
- Insulin EditedDocument3 pagesInsulin EditedMakauNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument4 pagesInsulinHa Zizzle100% (1)
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinAshan BopitiyaNo ratings yet
- Long Acting Insulin Is A Type of Insulin That Begins To Work Within 1Document1 pageLong Acting Insulin Is A Type of Insulin That Begins To Work Within 1Abdul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Insulin: BY Dental Student Mahmoud Kamal Mohammed SaeedDocument10 pagesInsulin: BY Dental Student Mahmoud Kamal Mohammed SaeedMahmood SaeedNo ratings yet
- Using Insulin: What Is Insulin? Types of InsulinDocument4 pagesUsing Insulin: What Is Insulin? Types of InsulinRyo RyozNo ratings yet
- The Nutrition Principle EbookDocument28 pagesThe Nutrition Principle EbookRx.MindsetNo ratings yet
- Anti-Diabetic Drugs InsulinDocument26 pagesAnti-Diabetic Drugs Insulinwissam salimNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmar_ouqNo ratings yet
- The Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte3Document20 pagesThe Diabetes Handbook by DK - Parte3CarlosPutnamNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanDocument21 pagesSubmitted By: Bartolata, Greyna Mercado RegeanRegean MercadoNo ratings yet
- How Diabetes Works: Click HereDocument13 pagesHow Diabetes Works: Click HereVishal Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument6 pagesInsulinkg5457663No ratings yet
- DInsulin Types 1Document22 pagesDInsulin Types 1zahrabokerNo ratings yet
- Insulin ShockDocument9 pagesInsulin ShockMarina CiburciuNo ratings yet
- MetabolicDocument1 pageMetabolicAnand SwamiNo ratings yet
- Insulin and How To Use It Safely - LeafletDocument2 pagesInsulin and How To Use It Safely - LeafletneurologytseeneNo ratings yet
- Insulin An Undeserved Bad Reputation 1Document13 pagesInsulin An Undeserved Bad Reputation 1Jonathan AvilesNo ratings yet
- Insulin Overview Lowers Blood Glucose Levels Rapid Acting Insulin Aspart Lispro GlulisineDocument5 pagesInsulin Overview Lowers Blood Glucose Levels Rapid Acting Insulin Aspart Lispro GlulisineLola LeNo ratings yet
- 6007 PDFDocument1 page6007 PDFAngga Aryo LukmantoNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Humans NotesDocument8 pagesHormones in Humans NotesSchool ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Insulin Handout 2Document2 pagesInsulin Handout 2tommy taylor084No ratings yet
- What Is DiabetesDocument9 pagesWhat Is Diabeteskdubb90No ratings yet
- Rapid Acting Terhadap Penurunan Glukosa Darah MencitDocument6 pagesRapid Acting Terhadap Penurunan Glukosa Darah MencitDany RamdhaniNo ratings yet
- What Is Diabetes?Document1 pageWhat Is Diabetes?debabrata5976No ratings yet
- Hormones NotesDocument14 pagesHormones NotesTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- Endo Lect InsulinDocument24 pagesEndo Lect InsulindoctorrfarrukhNo ratings yet
- Glucose Homestasis and Diabetes PresentationDocument23 pagesGlucose Homestasis and Diabetes Presentationapi-320112884No ratings yet
- The Insulin Factor: Can’t Lose Weight? Can’t Concentrate? Can’t Resist Sugar? Could Syndrome X Be Your Problem?From EverandThe Insulin Factor: Can’t Lose Weight? Can’t Concentrate? Can’t Resist Sugar? Could Syndrome X Be Your Problem?Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- For PRESENTATIONpancreatichormones 130526052114 Phpapp02Document54 pagesFor PRESENTATIONpancreatichormones 130526052114 Phpapp02Jayniel Erys MollenoNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety Synthesis PaperDocument6 pagesQuality and Safety Synthesis Paperapi-260053520No ratings yet
- DC Planning ProjectDocument4 pagesDC Planning Projectapi-260053520No ratings yet
- Pat2 MsiiDocument20 pagesPat2 Msiiapi-260053520No ratings yet