Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gastrointestinal System
Gastrointestinal System
Uploaded by
Binyo BioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gastrointestinal System
Gastrointestinal System
Uploaded by
Binyo BioCopyright:
Available Formats
Mila Citrawati
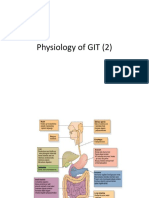
Function of GIS
Ingestion
Mechanical processing
Digestion
Secretion
Absorption
Excretion
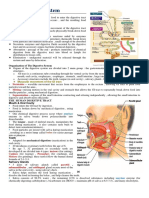
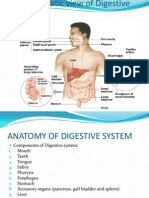
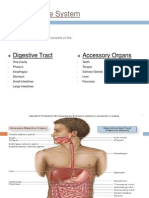
Components of GIS
Oral cavity, teeth, tongue
Salivary glands
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Large intestine
The Oral Cavity
Sensory analysis
Mechanical process
Lubrication
Limited digestion
6
The Tongue
Mechanical process
Assist chewing and prepare swallowing
Sensory analysis
Secretion
8
Salivary Glands
Parotid salivary glands (Stensens duct)
Sublingual salivary glands (Rivinus duct)
Submandibular salivary glands (Whartons duct)
Lubricating, moistening, dissolving
1,0 1,5 L/day (99,4% water, electrolytes, buffer,
glycoprotein, antibodies, enzymes, waste products)
10
The Teeth
Incisors, cuspids, bicuspids, molars
Mastications
12
The Pharynx
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx
Common passage way
Swallowing (deglutition):
1. Buccal phase (voluntary)
2. Pharyngeal phase (medulla oblongata, N. V, N. IX)
3. Esophageal phase (peristaltic wave) 9
14
The Esophagus
25 cm with diameter of about 2 cm (C6 T7)
Conveys solid food and liquids to the stomach
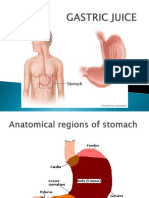
The Stomach
Function :
1. Storage
2. Mechanical breakdown
3. Disruption of chemical bonds
4. Production of intrinsic factor
T7 L3
Cardia, fundus, body, pylorus
Capacity : 1 1,5 L
17
Gastric glands :
1. Mucus cells (mucus)
2. Parietal cells (intrinsic factor, HCl)
3. Chief cells (pepsinogen)
4. G cells (gastrin) and D cells (somatostatin)
1500 ml/day of gastric juice
pH 1,5 2,0
1. Kills microorganisms
2. Denatures protein and inactivates enzymes in food
3. Breakdown plant cell walls and connective tissue in meat
4. Activation pepsinogen
Regulation of gastric activity
1. CNS
2. Enteric nervous system
3. Hormones
Phase
1. Cephalic phase
2. Gastric phase
3. Intestinal phase
Cephalic phase
Sight, smell, taste, thoughts CNS __> sub mucosal plexus
mucus, parietal, chief, G cells
Gastric phase
- Neural response : stretch and chemoreceptor
- Hormonal response : gastrin
- Local response : distention histamine
Intestinal phase
- Neural response : stretch and chemoreceptor
enterogastric reflex
- Hormonal response : CCK, GIP, Secretin
The Small Intestine
1. Duodenum
2. Jejenum
3. Ileum
Plicae, villi, micro villi ( 600 folds, 300 m
2
)
Intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkuhn, Brunners
glands, duodenal glands)
Intestinal juice 1,8 L/day (moistens, buffer,
enzymes)
Peyers patches
23
Regulation of intestinal glands :
1. Local reflex
2. Hormonal
3. Neural (cephalic phase)
Intestinal movements
1. Gastroenteric reflex
2. Gastroileal reflex
3. Enterogastric reflex
The Pancreas
Pancreatic juice (enzymes, water, ions, bicarbonat,
phosphate) 1000 ml
Triggered by secretin watery buffer of pH 7,5 8,8
Triggered by CCK pancreatic enzymes (amylase,
lipase, nuclease, protease, peptidase)
Proenzymes : trypsinogen (activated by enterokinase),
chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, proelastase
The Liver
Left, right, caudate, quadrate lobes
100,000 liver lobules, hepatocytes, central vein, Kupffer
cells
Function :
1. Metabolic regulation
2. Hematological regulation
3. Bile production
Metabolic regulation :
1. Carbohydrate metabolism (glycolysis,
gluconeogenesis, glikogenesis)
2. Lipid metabolism (triglycerides, fatty acids,
cholesterol)
3. Amino acids metabolism (protein, lipid, glucose)
4. Waste product removal (ammonia urea)
5. Vitamin storage (fat soluble and B
12
)
6. Mineral storage (feritin)
7. Drug inactivation
Hematological regulation
1. Phagocytosis and APC (Kupffer cells)
2. Synthesis plasma proteins
3. Removal of circulating hormones and
absorbs+converts
4. Removal of antibodies
5. Removal or storage of toxin (lipid soluble and others)
6. Synthesis and secretion of bile
Bile production
1 L/day
Consist of water, ions, bilirubin, cholesterol, bile salts
Synthesized in the liver
Excreted into duodenum lumen
90% reabsorbed by enterohepatic circulation
Function
Emulsification of lipid droplets
Facilitates interaction between lipid and lipid-digesting
enzymes
The gallbladder
Function as bile storage and bile modification
Released under stimulation of CCK
The Large Intestine
Function :
1. Reabsorption of water
2. Feces formation
3. Absorption of vitamin (K, Biotin, B
5
)
4. Storage of fecal material
Cecum, colon, rectum
Defecation reflex
TO
BE
CONTINUED,
GUYS!
You might also like
- Key Concepts of Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesKey Concepts of Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyMarcus, RN100% (1)
- How To Warm Up On Sunday Morning WorkbookDocument9 pagesHow To Warm Up On Sunday Morning WorkbookErin Doramis RomanNo ratings yet
- Intro To EPDocument48 pagesIntro To EPusfcards100% (2)
- DigestionDocument187 pagesDigestionJane Andrea Christiano Djianzonie100% (1)
- The Digestive System MODULEDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- The Battle For Your MindDocument16 pagesThe Battle For Your MindSon of Rizq100% (1)
- Osce 2Document5 pagesOsce 2George ahoy100% (1)
- The Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DDocument54 pagesThe Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DAchmadPrihadianto100% (1)
- 1.biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument55 pages1.biochemistry of Digestive SystemNor Izhharuddin Zainy60% (10)
- IB Style Exam Questions: Cell Detective Activity: Multiple Choice Questions MODEL ANSWERSDocument2 pagesIB Style Exam Questions: Cell Detective Activity: Multiple Choice Questions MODEL ANSWERSdomNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal HormonesDocument46 pagesGastrointestinal HormonesTaufiq Singgih BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- Gastric JuiceDocument21 pagesGastric JuiceSohail AhamdNo ratings yet
- Robbins Chapter 3 DiagramsDocument16 pagesRobbins Chapter 3 DiagramsjeffaguilarNo ratings yet
- Git HandoutsDocument49 pagesGit HandoutsCharlz Zipagan100% (1)
- Treatment of Cardiac Arrest in The Hyperbaric Environment - Key Steps On The Sequence of Care - Case ReportsDocument8 pagesTreatment of Cardiac Arrest in The Hyperbaric Environment - Key Steps On The Sequence of Care - Case Reportstonylee24No ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeJamaica Louise Quetua MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Colon CancerDocument8 pagesCase Study Colon CancerVecky Tolentino80% (5)
- Physiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)Document67 pagesPhysiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)RISALATUL KHOIROTUNISANo ratings yet
- Newborn Hypothermia and Hyperthermia (Final Copy)Document30 pagesNewborn Hypothermia and Hyperthermia (Final Copy)Shizuka Marycris Amane67% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Typhoid FeverCharise Ligores67% (6)
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocument92 pagesGastrointestinal SystemdhafaarifanoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal (Alimentary) System 01Document31 pagesGastrointestinal (Alimentary) System 01udayasudharakaNo ratings yet
- 6MD GI EnglishDocument86 pages6MD GI EnglishAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentDocument14 pagesBiopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentRA TanvirNo ratings yet
- Sistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDocument30 pagesSistim Pencernakan: Zaenal M. SOFRO Bagian Ilmu Faal FK - UGMDesi Dwi CahyantiNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022Document59 pagesBasic Nutrition Chapt 1 2022a.joshuaNo ratings yet
- Git PhysioDocument102 pagesGit PhysioPahw BaluisNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Document41 pagesDigestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Divya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pencernaan Dan Gatah PencernaanDocument53 pagesSistem Pencernaan Dan Gatah PencernaanLaila NrzntNo ratings yet
- DigestDocument84 pagesDigestBella FebrianNo ratings yet
- GIT Physiology: Powered by ATPDocument53 pagesGIT Physiology: Powered by ATPNashir MahmudNo ratings yet
- GROUP 11 Problem 1-2Document85 pagesGROUP 11 Problem 1-2Shitta InayahNo ratings yet
- Pages From Physio Term 2Document453 pagesPages From Physio Term 2Deshi SportsNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BODY Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesHUMAN BODY Digestive SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument55 pagesDigestive SystemPradeep KonduriNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Dr. Bipin Shrestha MBBS, MD 1Document50 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Dr. Bipin Shrestha MBBS, MD 1Prepladder ChyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument123 pagesPhysiology of Digestive Systemkidusabeje7No ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument95 pagesUnit 8 - Gastrointestinal Physiologykrystal1994No ratings yet
- The Digestive System: S.Kep, NS., M.KepDocument10 pagesThe Digestive System: S.Kep, NS., M.KepAuliya AlfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Introduction To The Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 24 - Introduction To The Digestive Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine and PancreasDocument52 pagesSmall Intestine and PancreasLutfi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument63 pagesDigestive SystemFiqri NovianNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pencernaan d3 KepDocument56 pagesSistem Pencernaan d3 KepSura MaduNo ratings yet
- PencernaanDocument39 pagesPencernaanVina Zavira NizarNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunTeeNo ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Sistem PencernaanDocument49 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Sistem PencernaanNurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Gastrointestinal IDocument31 pagesFisiologi Gastrointestinal IAvlya ZelykaNo ratings yet
- Digest Alimentary SYSTEM Medical Nov 2016Document45 pagesDigest Alimentary SYSTEM Medical Nov 2016Surya SaladaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Sekresi & AbsorpsiDocument67 pagesFisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Sekresi & AbsorpsiImmanuel Jeffri PaianNo ratings yet
- Lea 417 510 2011Document121 pagesLea 417 510 2011Oliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingDocument58 pagesPharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingRaveenmayiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRDocument64 pagesFisiologi Sistem Pencernaan: Kristanti, DRFeny Maharani100% (1)
- DigestiDocument56 pagesDigestiStephanie Putri FonatabaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestion 1Document55 pagesPhysiology of Digestion 1dicksonsamboNo ratings yet
- Pendahuluan Gi SystemDocument21 pagesPendahuluan Gi SystemdeasyahNo ratings yet
- Digestion Science Form 2Document25 pagesDigestion Science Form 2tengkusuhaidaNo ratings yet
- The Gastrointestinal TractDocument6 pagesThe Gastrointestinal Tractdarkgreen666No ratings yet
- 8th 1Document382 pages8th 1sandy candyNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument40 pagesAnatomyMichael GustiloNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Heces CompletoDocument10 pagesAnalisis de Heces CompletoIvonne SVNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 LectureDocument34 pagesNCMB 316 LecturePatrisha May MahinayNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument69 pagesDigestive SystemDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 ReviewDocument15 pagesExam 2 Reviewalana stoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - Digestive SystemDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- Digestion: - Processing of Food - TypesDocument28 pagesDigestion: - Processing of Food - TypesXheena WeberNo ratings yet
- Gastro 4Document537 pagesGastro 4Andrei ManeaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Jen Aragon, MD November 2015Document87 pagesThe Digestive System: Jen Aragon, MD November 2015Zyrick Laurence Eslao TimmangoNo ratings yet
- C. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 11: Vascular Trauma Chapter 11.1: Principles and Management J. V. RobbsDocument36 pagesC. J. Mieny, U. Mennen: Principles of Surgical Patient Care - Volume II Chapter 11: Vascular Trauma Chapter 11.1: Principles and Management J. V. RobbsGordana UzelacNo ratings yet
- Msds InhibitorDocument6 pagesMsds InhibitorBen Yudha SatriaNo ratings yet
- Deep Breathing For KidsDocument2 pagesDeep Breathing For KidsGilang Faisal AndrianNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5 KaisyahDocument36 pagesBiology Chapter 5 KaisyahKaisyah Rizqiin Mohamed KamaludeenNo ratings yet
- Eee-061: Power Quality LTP 3 1 0 Unit-I Introduction To Power QualityDocument6 pagesEee-061: Power Quality LTP 3 1 0 Unit-I Introduction To Power QualityMohammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- PG BOTANY Plant Physiology Question Bank CompleteDocument10 pagesPG BOTANY Plant Physiology Question Bank CompleteAbid ShowketNo ratings yet
- 7G SW Buffers 2Document20 pages7G SW Buffers 2barettNo ratings yet
- I. Physical Exam: Poor Skin TurgorDocument8 pagesI. Physical Exam: Poor Skin TurgorEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Role of Condyle Jc1Document13 pagesRole of Condyle Jc1FourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Tyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology: Molecular SciencesDocument48 pagesTyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology: Molecular SciencesAnuradha Monga KapoorNo ratings yet
- The Name of The You Rose473499Document335 pagesThe Name of The You Rose473499takNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Assignment 2015Document4 pagesEnzyme Assignment 2015Nadia Ananda PuteriNo ratings yet
- Makalah Trauma KepalaDocument39 pagesMakalah Trauma KepalalaudyaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument57 pagesEpithelial TissuePreet Kaur100% (1)
- DownloadDocument11 pagesDownloadChristopher Chew Dian MingNo ratings yet
- L A Level Biology MS Jan 06Document180 pagesL A Level Biology MS Jan 06zetsubou-chanNo ratings yet
- Examination of Dental PatientDocument51 pagesExamination of Dental PatientClaritashaAdiendaNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Behavior and The Integration of Brain-Body ScienceDocument7 pagesHormones and Behavior and The Integration of Brain-Body SciencePerla Arguelles CastroNo ratings yet
- COORDINATIONDocument20 pagesCOORDINATIONJessica Jasmine MajestadNo ratings yet
- ch26 - RNA MetabolismDocument86 pagesch26 - RNA MetabolismAstri AldelinaNo ratings yet