Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Warehousing Management Final
Uploaded by
Sai Indrakaran Reddy CherabuddiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Warehousing Management Final
Uploaded by
Sai Indrakaran Reddy CherabuddiCopyright:
Available Formats
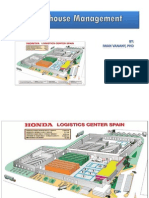
WAREHOUSING
MANAGEMENT
Gaurav Narkhede | Josue Servalis | Mike Macas |
Praneetha Boda
Part of firms logistics system that stores
products at and between point of origin and
point of consumption.
Term Warehousing is referred as
transportation at zero miles per hour
Warehousing provides time and place utility for
raw materials, industrial goods, and finished
products, allowing firms to use customer service
as a dynamic value-adding competitive tool.
THE ROLE OF THE WAREHOUSE IN
THE LOGISTICS SYSTEM
The warehouse is where the supply chain holds
or stores goods.
Functions of warehousing include
Transportation consolidation
Product mixing
Docking
Service
Protection against contingencies
TYPE OF WAREHOUSING
Public Warehousing
Private Warehousing
Contract Warehousing
Multi-client Warehousing
DESIGN CONSIDERATION
Ideal Facility for Pure Supplier
Consolidation
(Full Pallet Movement)
Warehouse Space
Requirements
PRINCIPLES OF WAREHOUSE
LAYOUT DESIGN
Use one-story
facilities
Move goods in a
straight line
Use efficient
materials-
handling
equipment
Use an effective
storage plan
Minimize aisle
space
Use maximum
height of the
building
WAREHOUSE PROCESS
Put-away
Identify Product
Identify Product Location
Move Products
Update Records
Storage
Equipment
Stock Location
Popularity
Unit Size
Cube
Shipping Preparation
Packing
Labeling
Stacking
Order Picking
Information
Walk & Pick
Batch Picking
Shipping
Schedule Carrier
Load Vehicle
Bill of Loading
Record Update
RECEIVING
Schedule Carrier
Unload Vehicle
Inspect for damage
INP
UT
OUT
PUT
OBJECTIVES OF EFFICIENT
WAREHOUSE OPERATIONS
Provide timely customer service.
Keep track of items so they can be found readily &
correctly.
Minimize the total physical effort & thus the cost of
moving goods into & out of storage.
Provide communication links with customers
Benefits of Warehouse Management
Provide a place to store & protect inventory
Reduce transportation costs
Improve customer service levels
Complexity of warehouse operation depends on the
number of SKUs handled & the number of orders
received & filled.
Most activity in a warehouse is material handling.
Capital costs
Costs of space & materials handling
equipment
Operating costs
Cost of labor
Measure of labor productivity is the number of
units that an operator can move in a day
COSTS OF OPERATING A WAREHOUSE
WAREHOUSE ACTIVITIES
Receive goods
Identify the goods
Dispatch goods to
storage
Hold goods
Pick goods
Marshal shipment
Dispatch shipment
Operate an information
system
Accepts goods from
Outside transportation or attached factory &
accepts responsibility
Check the goods against an order & the bill of
loading
Check the quantities
Check for damage & fill out damage reports if
necessary
Inspect goods if required
Receive goods
items are identified with the appropriate stock-
keeping unit (SKU) number (part number) &
the quantity received recorded
Identify the goods
Dispatch goods to storage
goods are sorted & put away
Hold goods
goods are kept in storage & under proper
protection until needed
Pick goods
items required from stock must be selected
from storage & brought to a marshalling area
Marshal the shipment
goods making up a single order are brought
together & checked for omissions or errors; order
records are updated
Dispatch the shipment
orders are packaged, shipping documents are
prepared, & goods loaded on the vehicle
Operate an information system
a record must be maintained for each item in
stock showing the quantity on hand, quantity
received, quantity issued, & location in the
warehouse
Maximize productivity & minimize
cost, warehouse management must
work with the following
Maximize use of space
space is the largest capital cost
Effective use of labor & equipment
labor is the largest operating cost
material handling equipment is the second
largest capital cost
FACTORS INFLUENCING EFFECTIVE
USE OF WAREHOUSES
Cube utilization and accessibility
Stock location
Order picking and assembly
Physical Control & Security - Elements
Cube utilization and
accessibility
Goods stored not just on the floor, but in the
cubic space of the warehouse; warehouse
capacity depends on how high goods can be
stored
Accessibility means being able to get at the
goods wanted with a minimum amount of
work
Cube utilization and accessibility
continued
Stock Location
Objectives
To provide the required customer
service
To keep track of where items are stored
To minimize effort to receive, put away,
and retrieve items
Basic Stock Locating Systems
Group functionally related items
together
Group fast-moving items together
Group physically similar items together
Locate working stock and reserve stock
separately
Fixed Location
SKU assigned a permanent location, & no other
items are stored there
Fixed-location systems usually have poor cube
utilization
Usually used in small warehouses; throughput is
small, & there are few SKUs
Floating (Random) Location
Goods stored wherever there is appropriate
space
Advantage is improved cube utilization
It requires accurate and up-to-date information
Warehouses using floating-location systems are
usually computer-based
Stock Location
continued
Stock Location
continued
Two other systems sometimes used are
Point-of-use storage
Inventory stored close to where it will be
needed
Used in repetitive manufacturing & JIT
systems
Central storage
Contains all inventory in one central location
Advantages of Point-of-use Storage
Materials are readily accessible to users
Material handling is reduced or eliminated
Central storage costs are reduced
Material is accessible all the time
Stock Location
continued
Advantages of Central Storage
Ease of control
Inventory record accuracy is easier to
maintain
Specialized storage can be used
Reduced safety stock, since users do not
need to carry their own safety stock
Stock Location
continued
Order Picking and
Assembly
When an order is received, items must
be obtained from the warehouse,
grouped, & prepared for shipment,
systems used
Area system
Zone system
Multi-order system
Area system
Order picker circulates throughout
warehouse selecting items on an order --
order is ready to ship when order picker is
finished
Zone system
Warehouse is divided into zones, & each
picker works only in an assigned zone --
order is divided by zone, & the items from
each zone are sent to the marshaling
area
Order Picking and
Assembly continued
Multi-order system
Same as the zone system, except that
each picker collects items for a number of
orders at the same time
Order Picking and
Assembly continued
PHYSICAL CONTROL & SECURITY -
ELEMENTS
Good part numbering system
Simple, well-documented transaction system
Identify the item
Verify the quantity
Record the transaction
Physically execute the transaction
Limited access
Inventory must be kept in a safe, secure
(locked) place with limited general access
Well-trained workforce
VIDEO
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
Cbj2d_0w24E
Questio
ns ?
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- Warehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha BodaDocument31 pagesWarehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha Bodahr chemtek100% (1)
- Warehouse ManagementDocument31 pagesWarehouse ManagementASHOK SUTHARNo ratings yet
- 06.01.2021.warehouse ManagementDocument29 pages06.01.2021.warehouse ManagementArham OrbNo ratings yet
- 4.2.1warehouse ManagementDocument29 pages4.2.1warehouse ManagementhimmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Warehouse Operations & ManagementDocument69 pagesChapter 7 Warehouse Operations & ManagementKhánh Đoan Lê Đình100% (1)
- Warehousing Management FinalDocument31 pagesWarehousing Management FinalSalah AnayaNo ratings yet
- Warehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha BodaDocument31 pagesWarehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha BodaNataraja Sekhar Reddy VaddamaniNo ratings yet
- WAREHOUSING MANAGEMENT FinalDocument22 pagesWAREHOUSING MANAGEMENT FinalPulkit MarwahNo ratings yet
- TRISEM252023-24 BMT6188 ETH VL2023240300005 2024-01-09 Reference-Material-IDocument32 pagesTRISEM252023-24 BMT6188 ETH VL2023240300005 2024-01-09 Reference-Material-ImrinfiniousNo ratings yet
- Warehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha BodaDocument32 pagesWarehousing Management: Gaurav Narkhede - Josue Servalis - Mike Macas - Praneetha Bodashahzaib aghaNo ratings yet
- Warehousing Unit - 1Document41 pagesWarehousing Unit - 1pramav2411No ratings yet
- (Mr.P.V.Bapat) 731 SCM Warehouse Management-Converted-CompressedDocument28 pages(Mr.P.V.Bapat) 731 SCM Warehouse Management-Converted-CompressedTayseer EltayebNo ratings yet
- Warehousing Management FinalDocument30 pagesWarehousing Management FinalMritunjay YadavNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management Chapter 5 Warehouse and Supply Chain ManagementDocument78 pagesInventory Management Chapter 5 Warehouse and Supply Chain ManagementPhương DungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 WarehouseDocument76 pagesChapter 7 Warehousenkminh19082003No ratings yet
- Warehousing ManagementDocument22 pagesWarehousing Managementdeepthikundan100% (1)
- Warehouse Management & LogisticsDocument28 pagesWarehouse Management & LogisticsShamsa Noorallah BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument89 pagesWarehouse ManagementSadeep SasankaNo ratings yet
- Warehousing ManagementDocument8 pagesWarehousing ManagementPoornika AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument36 pagesWarehouse ManagementMochamad Sulaiman100% (5)
- Essentials of Warehouse ManagementDocument33 pagesEssentials of Warehouse ManagementXoanor Kluger100% (1)
- WarehousingDocument33 pagesWarehousingMervyn Joe Sebastian100% (2)
- Definition of WarehouseDocument14 pagesDefinition of WarehouseHímà SumânthNo ratings yet
- Angielski ZawodowyDocument35 pagesAngielski ZawodowyEgzoNNNNo ratings yet
- SAP EWM An IntroductionDocument26 pagesSAP EWM An Introductiondbabu7100% (2)
- Warehousing OperationsDocument24 pagesWarehousing OperationsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Warehousing ManagementDocument24 pagesWarehousing ManagementFrans N PandjaitanNo ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument28 pagesWarehouse ManagementRavi Singh100% (2)
- Warehousing & Storage Techniques - Lecture 5Document38 pagesWarehousing & Storage Techniques - Lecture 5Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Warehousing ConceptDocument68 pagesWarehousing ConceptJohana MiraflorNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Cont'd : Warehousing and Matériels ManagementDocument27 pagesChapter Five Cont'd : Warehousing and Matériels ManagementTamratAfeworkNo ratings yet
- Logistics & WarehousingDocument27 pagesLogistics & WarehousingManasi PatilNo ratings yet
- Good Warehousing Practices (GWP)Document36 pagesGood Warehousing Practices (GWP)erikaoktavianipurba100% (1)
- Warehouse Management - PIM 1dayDocument21 pagesWarehouse Management - PIM 1dayIbrahimshoaibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Firdaus LasnangNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MaerialDocument47 pagesCH 1 MaerialBacha AyanaNo ratings yet
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Document29 pagesWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Warehousing 2Document17 pagesWarehousing 2abubakar arshadNo ratings yet
- Warehouse SpaceplanningDocument16 pagesWarehouse SpaceplanningShahrukh Ghulam Nabi0% (1)
- Lecture 7 - WAREHOUSING MANAGEMENTDocument51 pagesLecture 7 - WAREHOUSING MANAGEMENTsamwel100% (1)
- WAREHOUSING & STORAGE TECHNIQUES - Lecture 2Document31 pagesWAREHOUSING & STORAGE TECHNIQUES - Lecture 2Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- C H A P T E R 9 Storage and Warehouse SystemsDocument114 pagesC H A P T E R 9 Storage and Warehouse SystemsKhaled SamaraNo ratings yet
- Store KeepingDocument60 pagesStore KeepingHaritha Mugunthan100% (2)
- Air Cargo Warehousing and Inventory ManagementDocument25 pagesAir Cargo Warehousing and Inventory Managementvageesha100% (1)
- Unit 2 Production MGTDocument63 pagesUnit 2 Production MGTVaish VarshNo ratings yet
- I I T T M: Warehousing ManagementDocument23 pagesI I T T M: Warehousing ManagementMoonka Ankit100% (1)
- Purchasing Plan Is Prepared As Per The Output From The MarketingDocument2 pagesPurchasing Plan Is Prepared As Per The Output From The MarketingArun SathyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - OPER8030Document44 pagesChapter 7 - OPER8030srinivas saiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesDocument54 pagesAn Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesGabriele LorussoNo ratings yet
- Manh Warehouse Management Brochure enDocument8 pagesManh Warehouse Management Brochure enTanweer AlamNo ratings yet
- Warehousing and Storage in Supply Chain Management: Group MembersDocument58 pagesWarehousing and Storage in Supply Chain Management: Group MembersMuhamad Abi HaykalNo ratings yet
- Warehousing and Storage in Supply Chain ManagementDocument58 pagesWarehousing and Storage in Supply Chain ManagementGilles100% (1)
- Odoo WMS - Warehouse Management SystemDocument19 pagesOdoo WMS - Warehouse Management Systemanton widodo100% (1)
- Inventory Control and Types of Inventery PDFDocument19 pagesInventory Control and Types of Inventery PDFsreekanth3185No ratings yet
- Ome 664: Project Procurement and Contracting: Lecture Three: Warehouse ManagementDocument35 pagesOme 664: Project Procurement and Contracting: Lecture Three: Warehouse ManagementYonas Alemayehu100% (1)
- Material Handling Systems:: Submitted By: SWATI DUBEY (PG2018-P053) Logistics and Warehousing ManagementDocument23 pagesMaterial Handling Systems:: Submitted By: SWATI DUBEY (PG2018-P053) Logistics and Warehousing ManagementSwati DubeyNo ratings yet
- 5S: A Practical Guide to Visualizing and Organizing Workplaces to Improve ProductivityFrom Everand5S: A Practical Guide to Visualizing and Organizing Workplaces to Improve ProductivityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dec 2022Document8 pagesDec 2022John CNo ratings yet
- Jun SMSDocument43 pagesJun SMSgallardo0121No ratings yet
- Rankel Engine.Document16 pagesRankel Engine.Divya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MET Till DEC 2018 PDFDocument171 pagesMET Till DEC 2018 PDFt.srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Manual Construction Standards Completo CorregidozDocument240 pagesManual Construction Standards Completo CorregidozJose DiazNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesDocument41 pagesANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesalexNo ratings yet
- VX-1700 Owners ManualDocument32 pagesVX-1700 Owners ManualVan ThaoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Audi q5 sq5 71153 PDFDocument302 pages2015 Audi q5 sq5 71153 PDFPraveen100% (1)
- Technical Data For Elevator Buckets - Bucket ElevatorDocument1 pageTechnical Data For Elevator Buckets - Bucket ElevatorFitra VertikalNo ratings yet
- VAPORISERDocument62 pagesVAPORISERAshish ChavanNo ratings yet
- 01 Cone Winding Study (Calculation)Document4 pages01 Cone Winding Study (Calculation)Hasan Istiaque Ahmed60% (5)
- REE Copy PDFDocument9 pagesREE Copy PDFJake ZozobradoNo ratings yet
- Ruckus Wired Accreditation ExamDocument15 pagesRuckus Wired Accreditation ExamDennis Dube25% (8)
- Black Invention MythsDocument16 pagesBlack Invention MythsjoetylorNo ratings yet
- En 12604 (2000) (E)Document7 pagesEn 12604 (2000) (E)Carlos LanzillottoNo ratings yet
- (Ebook - Electronics) - Principles of PLL - Tutorial (Kroupa 2000)Document66 pages(Ebook - Electronics) - Principles of PLL - Tutorial (Kroupa 2000)양종렬No ratings yet
- Droop Vs Iso Control Modes For Gas TurbinesDocument3 pagesDroop Vs Iso Control Modes For Gas TurbinesArdvark100% (1)
- Meitrack Gprs Protocol v1.6Document45 pagesMeitrack Gprs Protocol v1.6monillo123No ratings yet
- Quotation 98665Document5 pagesQuotation 98665Reda IsmailNo ratings yet
- PB Hydro en PDFDocument86 pagesPB Hydro en PDFWahyu Tirta NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Vertical Take Off and LandingDocument126 pagesVertical Take Off and LandingMukesh JindalNo ratings yet
- Error Number Mentor GraphicsDocument30 pagesError Number Mentor GraphicsMendesNo ratings yet
- VarPlus Can - BLRCH104A125B48Document2 pagesVarPlus Can - BLRCH104A125B48Achira DasanayakeNo ratings yet
- Alloc 150 DMDocument301 pagesAlloc 150 DMSheik Mohamed ImranNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Manuallib.com) - MOELLER EASY512&Minus AB&Minus RCDocument8 pages(WWW - Manuallib.com) - MOELLER EASY512&Minus AB&Minus RCErik VermaakNo ratings yet
- Elvax 460Document3 pagesElvax 460ingindjorimaNo ratings yet
- Transfer Action in Sap HRDocument3 pagesTransfer Action in Sap HRKarthi MrvkNo ratings yet
- Toyota Vios Ecu Wiring DiagramDocument4 pagesToyota Vios Ecu Wiring DiagramSri Yuniati17% (6)
- Wastewater Treatment Options For Paper Mills Using Waste Paper/imported Pulps As Raw Materials: Bangladesh PerspectiveDocument4 pagesWastewater Treatment Options For Paper Mills Using Waste Paper/imported Pulps As Raw Materials: Bangladesh PerspectiveKool LokeshNo ratings yet
- BEC198 (Finals)Document180 pagesBEC198 (Finals)Lorenz BerroyaNo ratings yet