Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Field Density Test by Core Cutter
Field Density Test by Core Cutter
Uploaded by
Jalaluddin Johan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesgood
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentgood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesField Density Test by Core Cutter
Field Density Test by Core Cutter
Uploaded by
Jalaluddin Johangood
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
DENSITY OF SOIL BY CORE CUTTER METHOD
Aim of the Experiment:
To determine the field or in-situ density or unit weight of soil by core cutter method
Apparatus Required:
a) Special:
i. Cylindrical core cutter
ii. Steel rammer
iii. Steel dolly
b) General:
i. Balance of capacity5 Kg and sensitivity 1 gm.
ii. Balance of capacity 200gms and sensitivity 0.01 gms.
iii. Scale
iv. Spade or pickaxe or crowbar
v. Trimming Knife
vi. Oven
vii. Water content containers
viii. Desiccator.
Theory:
Field density is defined as weight of unit volume of soil present in site. That is
Where, Density of soil
W = Total weight of soil
V = Total volume of soil
The soil weight consists of three phase system that is solids, water and air. The
voids may be filled up with both water and air, or only with air, or only with water.
Consequently the soil may be dry, saturated or partially saturated.
In soils, mass of air is considered to be negligible, and therefore the saturated
density is maximum, dry density is minimum and wet density is in between the two.
Dry density of the soil is calculated by using equation,
Where, dry density of soil
Wet density of soil
w = moisture content of soil.
Density or unit weight of soils may be determined by using the following method:
i. Core cutter method
ii. Sand replacement test
iii. Rubber balloon test
iv. Water displacement method
v. Gamma ray method
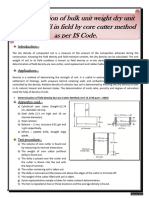
Hear we use core cutter method, the equipment arrangement is shown as fallows,
Application:
Field density is used in calculating the stress in the soil due to its overburden
pressure it is needed in estimating the bearing capacity of soil foundation system,
settlement of footing earth pressures behind the retaining walls and embankments.
Stability of natural slopes, dams, embankments and cuts is checked with the help of
density of those soils. It is the density that controls the field compaction of soils.
Permeability of soils depends upon its density. Relative density of cohesionless soils
is determined by knowing the dry density of soil in natural, loosest and densest
states. Void ratio, porosity and degree of saturation need the help of density of soil.
Core cutter method in particular, is suitable for soft to medium cohesive soils, in
which the cutter can be driven. It is not possible to drive the cutter into hard, boulder
or murrumy soils. In such case other methods are adopted.
Procedure:
i. Measure the height and internal diameter of the core cutter.
ii. Weight the clean core cutter.
iii. Clean and level the ground where the density is to be determined.
iv. Press the cylindrical cutter into the soil to its full depth with the help of steel
rammer.
v. Remove the soil around the cutter by spade.
vi. Lift up the cutter.
vii. Trim the top and bottom surfaces of the sample carefully.
viii. Clean the outside surface of the cutter.
ix. Weight the core cutter with the soil.
x. Remove the soil core from the cutter and take the representative sample in
the water content containers to determine the moisture content
Precautions:
i. Steel dolly should be placed on the top of the cutter before ramming it down
into the ground.
ii. Core cutter should not be used for gravels, boulders or any hard ground.
iii. Before removing the cutter, soil should be removed around the cutter to
minimize the disturbances.
iv. While lifting the cutter, no soil should drop down
Observation and Calculation Table:
Internal diameter of cutter (cm): _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Height of the cutter (cm): _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Cross sectional area of the cutter (cm2): _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Volume of the cutter, V (cm3): _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Water/Moisture content determination:
sample 1 sample 2 sample 3
Weight of can, W
1
(g)
Weight of can + wet soil W
2
(g)
Weight of can + dry soil W
3
(g)
Water/Moisture content
Calculation Table:
sample 1 sample 2 sample 3
Mass of core cutter, W
1
(gm)
Mass of cutter + soil from field, W
2
(gm)
Wet density, (gm/cm3)
Dry density , (gm/cm3)
QUESTIONNAIRE:
i. Out of wet density, dry density, and saturated density, which one of them is
maximum and minimum? Explain.
ii. What are the main factors which affect in-situ density of soil? Explain.
iii. Beside the density what other properties do you need to calculate the void
ratio and degree of saturation of soils?
iv. What are the other methods to calculate the field density of soil?
You might also like
- Ballistic Performance Evaluation of Ceramic Tiles With Respect To Projectile Velocity Against Hard Steel Projectile Using DOP TestDocument7 pagesBallistic Performance Evaluation of Ceramic Tiles With Respect To Projectile Velocity Against Hard Steel Projectile Using DOP TestAnonymous LYTNuHK9dsNo ratings yet
- B 29 - 14Document4 pagesB 29 - 14ruben carcamoNo ratings yet
- Determination of In-Situ Density by Core Cutter Method: Experiment No 5 DATEDocument5 pagesDetermination of In-Situ Density by Core Cutter Method: Experiment No 5 DATE11520035100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT 2 Dry Density by Core Cutter (2018UGCE005)Document7 pagesEXPERIMENT 2 Dry Density by Core Cutter (2018UGCE005)Golu kumarNo ratings yet
- 2018UGCE040Document2 pages2018UGCE040Praveen OhdarNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument11 pagesReportAbdul latif Abdul latifNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatusDocument2 pagesAIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatussunilNo ratings yet
- Test Title Core CutterDocument8 pagesTest Title Core Cutteraniem_beeNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil TextureDocument6 pagesImportance of Soil Textureshaik shahinaNo ratings yet
- Exp-2 UnitWeight PDFDocument11 pagesExp-2 UnitWeight PDFMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument65 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Laboratory Manualnitin anantNo ratings yet
- Soil Lab ManualDocument39 pagesSoil Lab ManualHuy PanhaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Field Density of Soils by Sand Replacement & Core Cutter MethodDocument9 pagesDetermination of Field Density of Soils by Sand Replacement & Core Cutter MethodIkhwan Z.100% (15)
- Field Density TestDocument2 pagesField Density Testpspayelsarkar2612No ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab For Soil MechanicsDocument27 pagesOpen Ended Lab For Soil Mechanicsعثمان محيب احمدNo ratings yet
- Field Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodDocument2 pagesField Density of Soil by Core Cutter Methodmohd waseemNo ratings yet
- Highway 2Document4 pagesHighway 2hadushNo ratings yet
- 9-In Situ Density by Core Cutter&Sand Repl - MTHDDocument4 pages9-In Situ Density by Core Cutter&Sand Repl - MTHDmuhammad irfanNo ratings yet
- SES-501 Bulk Density and ConepenetrometerDocument12 pagesSES-501 Bulk Density and ConepenetrometerNor579No ratings yet
- New GT Lab PDFDocument56 pagesNew GT Lab PDFDIVYA NATHNo ratings yet
- Soil Lab ManualDocument15 pagesSoil Lab ManualRamsharan DhakalNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Foundation EngineeringDocument39 pagesLab Manual Foundation Engineeringartiraha100% (1)
- LabDocument7 pagesLabMohammad FitriNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Foundation EnggDocument39 pagesLab Manual Foundation EnggsahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Lab ManualDocument39 pagesSoil Mechanics Lab ManualDharmaraaj RajalinggamNo ratings yet
- Determination of In-Situ Unit Weight of Soil: Experiment No 2 & 3 Soil Mechanics Laboratory CE PC 594Document30 pagesDetermination of In-Situ Unit Weight of Soil: Experiment No 2 & 3 Soil Mechanics Laboratory CE PC 594SumanHaldar100% (1)
- Lab Manual 6 and 7Document8 pagesLab Manual 6 and 7Prabesh PokharelNo ratings yet
- Core CutterDocument2 pagesCore CutterkritamNo ratings yet
- Soil 2Document21 pagesSoil 2Priyank GodhatNo ratings yet
- EVT533 Experiment 4 Soil Bulk DensityDocument10 pagesEVT533 Experiment 4 Soil Bulk DensitySyazwan ZainolNo ratings yet
- CE2308 Lab Manual PDFDocument40 pagesCE2308 Lab Manual PDFPeter SingletonNo ratings yet
- Insitu Density TestsDocument9 pagesInsitu Density TestsIsuru Udayanga NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY COMPACTION TEST ImmaDocument9 pagesLABORATORY COMPACTION TEST ImmaIsmail A IsmailNo ratings yet
- Gte Lab Manual PDFDocument36 pagesGte Lab Manual PDFIsrael VenkatNo ratings yet
- SS 12 Lab. Exer 6 Rev Module UpDocument4 pagesSS 12 Lab. Exer 6 Rev Module UpJohn Mark AdorzaNo ratings yet
- Determination of PorosityDocument4 pagesDetermination of PorosityB S Praveen BspNo ratings yet
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestDocument7 pagesStandard Proctor Compaction TestshuhadaNo ratings yet
- Dry Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodDocument8 pagesDry Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodWaqas Sadiq100% (1)
- 10) Core Cutter MethodDocument7 pages10) Core Cutter MethodPn Ekanayaka100% (2)
- Ii - Field Density Test: Historical BackgroundDocument4 pagesIi - Field Density Test: Historical BackgroundSean WasilNo ratings yet
- CIVL354 Notes 2 Field CompactionDocument11 pagesCIVL354 Notes 2 Field CompactionRaj BakhtaniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Relative Density or Density Index of Sand (Is-2720-Part-15)Document3 pagesDetermination of Relative Density or Density Index of Sand (Is-2720-Part-15)muhammad iqbalNo ratings yet
- Soil Science Lab 5Document4 pagesSoil Science Lab 5Joshua Ruel NalzaroNo ratings yet
- Evt533 Soil Bulk DensityDocument15 pagesEvt533 Soil Bulk DensityfatinidayuNo ratings yet
- AGTE-1 Degrevised2Document51 pagesAGTE-1 Degrevised2Vaishali PawarNo ratings yet
- Core Cutter MethodDocument2 pagesCore Cutter MethodVENKATA RANGANADHNo ratings yet
- Group-7 Exp10Document3 pagesGroup-7 Exp10Marc CupayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Soil Testing - (MY REFERENCE)Document34 pagesAssignment 2 - Soil Testing - (MY REFERENCE)YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Basic Physical Properties of SoilDocument20 pagesBasic Physical Properties of SoilTare ManNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Part 2Document23 pagesModule 1 Part 2kichuarfan44No ratings yet
- Quality Control TestsDocument22 pagesQuality Control Testsvarma369vinaNo ratings yet
- Core Cutter TestDocument3 pagesCore Cutter TestManish AryaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Lec1. Geotechnical Properties of SoilDocument41 pages2023 Lec1. Geotechnical Properties of SoilMa. Kate BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Field Density Test: A. Calibration of Mechanical DeviceDocument11 pagesField Density Test: A. Calibration of Mechanical DeviceAnn Bernadette PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Dry Density of Soil in SituDocument29 pagesDetermination of The Dry Density of Soil in SituMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar: Institutes of Technology Department of Civil EngineeringDocument56 pagesUniversity of Gondar: Institutes of Technology Department of Civil EngineeringnahomNo ratings yet
- Porosity of SoilDocument2 pagesPorosity of SoilRamesh KonakallaNo ratings yet
- Draining for Profit, and Draining for HealthFrom EverandDraining for Profit, and Draining for HealthNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion Control : Techniques for Sustainable Land ManagementFrom EverandSoil Erosion Control : Techniques for Sustainable Land ManagementNo ratings yet
- Soil PreparationFrom EverandSoil PreparationNo ratings yet
- Experience CertificateDocument1 pageExperience CertificateprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Experience Certificate: Principal Manoj KumarDocument1 pageExperience Certificate: Principal Manoj KumarprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Experience Certificate MDocument1 pageExperience Certificate MprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Project Based On MergerDocument24 pagesProject Based On MergerPrince RattanNo ratings yet
- Bipartite BodiesDocument2 pagesBipartite BodiesprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Final Report On GrievanceDocument64 pagesFinal Report On GrievanceprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Excel Excel Stuff Monte Carlo Simulation Uncertainty and Risk AnalysisDocument50 pagesExcel Excel Stuff Monte Carlo Simulation Uncertainty and Risk Analysisapi-27174321100% (5)
- Derivatives OdtDocument118 pagesDerivatives OdtprincerattanNo ratings yet
- DividendDocument32 pagesDividendprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Inventory Management: Ramandeep Mba - 3 Sem. Roll No 890829Document28 pagesProject Report ON Inventory Management: Ramandeep Mba - 3 Sem. Roll No 890829akashdeepjoshiNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Mba ProjectDocument24 pagesWorking Capital Mba ProjectprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Work StressDocument9 pagesWork StressprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Information Systems:: Implementation GuidelinesDocument25 pagesInformation Systems:: Implementation GuidelinesprincerattanNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument12 pagesA Presentation On: Hindustan Unilever LimitedprincerattanNo ratings yet
- Personal AppraisalDocument30 pagesPersonal AppraisalKool KaishNo ratings yet
- Indian Textile IndustryDocument16 pagesIndian Textile Industryprincerattan50% (2)
- By Mohamad Shahrizal Bin Alias: Cold Water SupplyDocument18 pagesBy Mohamad Shahrizal Bin Alias: Cold Water Supplynurul atiqahNo ratings yet
- PS 70690 IC Eluent Suppressors PS70690 enDocument19 pagesPS 70690 IC Eluent Suppressors PS70690 enMondommeg SohanemNo ratings yet
- K 2017-08-01 ME H. Pelders S M. Ummelen ME VCL E. Jordaan/hpe 1 of 1Document1 pageK 2017-08-01 ME H. Pelders S M. Ummelen ME VCL E. Jordaan/hpe 1 of 1mokie305No ratings yet
- Ropinirole Extended-Release TabletsDocument4 pagesRopinirole Extended-Release TabletsRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- MDSP Problem Coaching Part 2Document403 pagesMDSP Problem Coaching Part 2Sadam August Dulom100% (1)
- CI Sodium Hypochlorite Compatibility ChartDocument1 pageCI Sodium Hypochlorite Compatibility ChartastromoNo ratings yet
- AR029022.001 (Filtro - ITEM 616A) HHDocument1 pageAR029022.001 (Filtro - ITEM 616A) HHJohan PintoNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Reaction Forces in The Boiler Supports Using The Method of Equivalent Stiffness of Membrane WallDocument16 pagesCalculation of Reaction Forces in The Boiler Supports Using The Method of Equivalent Stiffness of Membrane WallShubha RoyNo ratings yet
- Test of Organic Impurities (Document Guide) 06-24-2017Document3 pagesTest of Organic Impurities (Document Guide) 06-24-2017Erika Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- Aluminium's Corrosion Resistance - Aluminium DesignDocument7 pagesAluminium's Corrosion Resistance - Aluminium DesignCarlos LuNo ratings yet
- 2023-BRL-05-XX-SP-C-1010 - Pavement - P01Document39 pages2023-BRL-05-XX-SP-C-1010 - Pavement - P01François Le RouxNo ratings yet
- Flex Co Rivet HingedDocument4 pagesFlex Co Rivet HingedYuliadi YunusNo ratings yet
- A Calculation of Piston Rod Strength - Bennet, M.CDocument12 pagesA Calculation of Piston Rod Strength - Bennet, M.CLeandro FabrisNo ratings yet
- Krisbow Welding KatalogDocument16 pagesKrisbow Welding Katalogpro.bacotgamingNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation and Biomining Via Microbial Surface AdsorptionDocument6 pagesBioremediation and Biomining Via Microbial Surface AdsorptionTomsonNo ratings yet
- TATSUOKA-2001 BurmisterLectureDocument75 pagesTATSUOKA-2001 BurmisterLectureStefan VogtNo ratings yet
- Graphene PDFDocument373 pagesGraphene PDFJeisson Perez100% (1)
- Joke Katalog PoleringDocument216 pagesJoke Katalog Poleringkharrat samirNo ratings yet
- 2004 - Electrical Resistance Change Method For Monitoring Delaminations of CFRP Laminates Effect of Spacing Between ElectrodesDocument10 pages2004 - Electrical Resistance Change Method For Monitoring Delaminations of CFRP Laminates Effect of Spacing Between ElectrodesDavid AcostaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: Tle - CookeryDocument11 pagesLearning Module: Tle - CookeryMary ChloeNo ratings yet
- Sample Dew Point CalculationDocument3 pagesSample Dew Point Calculationapi-3709413100% (1)
- Metal Film Precision Resistors: Resistive Metal Films and A New Resistor ConceptDocument19 pagesMetal Film Precision Resistors: Resistive Metal Films and A New Resistor ConceptfbaldnerNo ratings yet
- CIGRE - Tutorial Conductor Fatigue B2 AG 06 BangkokDocument37 pagesCIGRE - Tutorial Conductor Fatigue B2 AG 06 BangkokJorge Pinto RochaNo ratings yet
- Saes Q 010 PDFDocument4 pagesSaes Q 010 PDFRoger MallariNo ratings yet
- MasterRheobuild® 716Document3 pagesMasterRheobuild® 716Jagan Mohana Rao ChinnalaNo ratings yet
- Editorial WritingDocument1 pageEditorial WritingSayantan HatiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Week02 Elka1 Diode TheoryDocument25 pagesWeek02 Elka1 Diode TheoryEstika Vriscilla GintingNo ratings yet