Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verb Tenses: Auxiliary Verbs
Uploaded by
AmitSharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb Tenses: Auxiliary Verbs
Uploaded by
AmitSharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
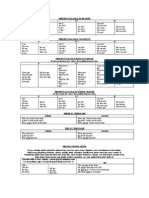
Verb tenses
The tense of a verb tells you when a person did something or when something existed or happened. In English, the main tenses are:
the present (e.g. I am, she laughs, they love, we begin)
the past (e.g. I was, she laughed, they loved, we began)
the future (e.g. I will/shall, she will laugh, they will love, we will/shall begin)
These main tenses can be further subdivided, as follows:
the present continuous she is laughing
the past continuous she was laughing
the future continuous she will be laughing
the present perfect she has laughed
the present perfect continuous she has been laughing
the past perfect she had laughed
the past perfect continuous she had been laughing
the future perfect she will have laughed
the future perfect continuous she will have been laughing
Note that the continuous is also called the progressive.
Different tenses are typically formed either by adding -ed or -ing to the basic form of the verb (known as the stem), or with the help of other
verbs known as auxiliary verbs such as am, was, have, has, had, and will.
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: The Present Simpleor Simple Present. It's Mainly Used in The Following WaysDocument9 pagesVerb Tenses: The Present Simpleor Simple Present. It's Mainly Used in The Following WaysFOANo ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument3 pagesAuxiliary VerbsYoushaibNo ratings yet
- What Is TenseDocument9 pagesWhat Is Tensesobonoj644No ratings yet
- Tenses in English GrammarDocument33 pagesTenses in English Grammarmeri100% (1)
- Middle English MorphologyDocument14 pagesMiddle English MorphologyНаталія Атлас0% (1)
- Auxilliary Verbs: A Verb Used in Forming The Tenses, Moods, and Voices of OtherDocument4 pagesAuxilliary Verbs: A Verb Used in Forming The Tenses, Moods, and Voices of OtherRuby AsadNo ratings yet
- Quick and Easy Way To Learn English Verb TensesDocument5 pagesQuick and Easy Way To Learn English Verb TensesIzem AtlasNo ratings yet
- Simple Present (Present Simple) : - IntroductionDocument23 pagesSimple Present (Present Simple) : - IntroductionSimona VinatoruNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: Form (Forma)Document16 pagesPast Simple: Form (Forma)SandyTatianaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Summary 1-11Document17 pagesTugas Summary 1-11sherinaNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument28 pagesEnglish TensesfaridaNo ratings yet
- Step 1Document31 pagesStep 1api-174052931No ratings yet
- Verb Tenses - NewDocument16 pagesVerb Tenses - NewSai AmruthaNo ratings yet
- The Twelve Tenses of EnglishDocument10 pagesThe Twelve Tenses of EnglishMary Marsheey Jamero ManipisNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses Intermediate LevelDocument3 pagesPresent Tenses Intermediate Levelnagdee.bNo ratings yet
- Regular and Irregular VerbsDocument9 pagesRegular and Irregular Verbstessa17No ratings yet
- Leaf StudyDocument5 pagesLeaf StudyNatália DiasNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument12 pagesSimple Present TenseVanda Love D'javaneisNo ratings yet
- English Auxiliary VerbsDocument7 pagesEnglish Auxiliary VerbsSérgio DominguesNo ratings yet
- The Present Tense (Das Präsens)Document5 pagesThe Present Tense (Das Präsens)Mark CorellaNo ratings yet
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE Prezentacija MojaDocument11 pagesPRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE Prezentacija MojamostarjelicaNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDocument4 pagesVerbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDelgado Maria AngelaNo ratings yet
- English Tenses ConjugationsDocument3 pagesEnglish Tenses ConjugationsJesus PiñaNo ratings yet
- I Finished My Homework Last Night. I Traveled To Spain in 1985. I Got Up at Seven This MorningDocument11 pagesI Finished My Homework Last Night. I Traveled To Spain in 1985. I Got Up at Seven This MorningjahazielbdNo ratings yet
- Lecture - (Tenses)Document35 pagesLecture - (Tenses)Waqas HafeezNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFDocument85 pagesGrammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFKarma Kuenzang WangdiNo ratings yet
- Verbs TypesDocument24 pagesVerbs TypesSairamTirumalaiGovindarajuNo ratings yet
- What Is Happening Now / What Usually Happens:: To WatchDocument8 pagesWhat Is Happening Now / What Usually Happens:: To Watchعبد الرحمان لهواويNo ratings yet
- Unit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Document14 pagesUnit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Johana CamposNo ratings yet
- Historia de La Lengua Inglesa II SYNTAX: VERB PHRASE (TENSE, ASPECT, MOOD AND VOICE)Document19 pagesHistoria de La Lengua Inglesa II SYNTAX: VERB PHRASE (TENSE, ASPECT, MOOD AND VOICE)kapiruxoNo ratings yet
- Tenses UietDocument27 pagesTenses UietMohitNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument119 pagesVerbsDashbayar EmmyNo ratings yet
- Present Tense: Right NowDocument5 pagesPresent Tense: Right NowElizabethNo ratings yet
- Verbos en InglésDocument21 pagesVerbos en InglésISMAEL66KGNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument5 pagesPresent TenseemcdavittNo ratings yet
- Tenses NotesDocument7 pagesTenses NotessasNo ratings yet
- A. Part of Speech: Name: Nurul Aulia Ramadhani HRP NPM: 19052043Document7 pagesA. Part of Speech: Name: Nurul Aulia Ramadhani HRP NPM: 19052043Syarifah Tasya AlhabsyiNo ratings yet
- Handout in Verb TensesDocument5 pagesHandout in Verb TensesZarah CaloNo ratings yet
- Economic EnglishDocument48 pagesEconomic EnglishCristina AlexeNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechJose BrabanteNo ratings yet
- French Basic Grammar TensesDocument1 pageFrench Basic Grammar Tensesrhianniki78% (9)
- Verbs PDFDocument2 pagesVerbs PDFTko ToolNo ratings yet
- Spanish Basics Lesson 2: Lo Básico de Español Lección 2Document6 pagesSpanish Basics Lesson 2: Lo Básico de Español Lección 2Rishav ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Tenses: Course: Functional English 1 Course Code: 103Document66 pagesTenses: Course: Functional English 1 Course Code: 103Nimra AslamNo ratings yet
- The Passive With Progressive AspectDocument4 pagesThe Passive With Progressive Aspectapi-282522988No ratings yet
- Dux Grammar RefresherDocument23 pagesDux Grammar RefresherTony Divine VidzNo ratings yet
- Verbs: 1. History of VerbDocument11 pagesVerbs: 1. History of VerbBwin NetNo ratings yet
- Verbs: 1. History of VerbDocument11 pagesVerbs: 1. History of VerbBwin NetNo ratings yet
- Engleski JezikDocument6 pagesEngleski JezikAdnan PjanicNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction To TensesDocument34 pagesBasic Introduction To TensesPriti PritiNo ratings yet
- Past ContDocument3 pagesPast Contthe amazing sarem the amazing saremNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument9 pagesAdverbsBeepoy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Simple TensesDocument12 pagesSimple TensesHienNo ratings yet
- Book ChapterDocument8 pagesBook ChapterMisbah AwelNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument116 pagesPresent SimplekpmadhunNo ratings yet
- Verbs, or (Verbal) Auxiliaries. Theyauxiliary Verbs Typically Help Express GrammaticalDocument2 pagesVerbs, or (Verbal) Auxiliaries. Theyauxiliary Verbs Typically Help Express GrammaticalFabianBañoNo ratings yet
- Form and Use of The Present ProgressiveDocument11 pagesForm and Use of The Present ProgressiveDiego Acuña VasquezNo ratings yet
- Verb Forms I Ba Grammar NotesDocument19 pagesVerb Forms I Ba Grammar NotesSamuel RufusNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Quazi POSDocument6 pagesTest Paper Quazi POSAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- HCF and LCMDocument13 pagesHCF and LCMdivya1587No ratings yet
- Infosys Paper PatternDocument23 pagesInfosys Paper PatternDr.R.Udaiya Kumar Professor & Head/ECENo ratings yet
- Handout Day 2 Error Replacement 2014Document4 pagesHandout Day 2 Error Replacement 2014AmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Ritu Bhargava - Test Results From AnimeshDocument14 pagesRitu Bhargava - Test Results From AnimeshAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Questioner ShipraDocument7 pagesQuestioner ShipraAmitSharma0% (1)
- Questions Passage SumanDocument7 pagesQuestions Passage SumanAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 25 Vijay.Document7 pagesQuestion Paper 25 Vijay.AmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- WorksheetsDocument4 pagesWorksheetsAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses: Auxiliary VerbsDocument1 pageVerb Tenses: Auxiliary VerbsAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Test On TensesDocument1 pageTest On TensesAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Spot The ErrorDocument1 pageSpot The ErrorAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University Uttar PradeshDocument4 pagesGalgotias University Uttar PradeshAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Verbal Ability 2Document22 pagesVerbal Ability 2AmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Cts Placement Practice Test of ReasoningDocument27 pagesCts Placement Practice Test of ReasoningAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- MCA PaperDocument2 pagesMCA PaperAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- LAHO2001205 SolDocument2 pagesLAHO2001205 SolAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension (Basic Level) - AnswersDocument5 pagesReading Comprehension (Basic Level) - AnswersAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Amit Mock TestDocument10 pagesAmit Mock TestAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Data SufficiencyDocument14 pagesData SufficiencyAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Galgotias University Uttar PradeshDocument4 pagesGalgotias University Uttar PradeshAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- CTS 2004 (PSG and CIT) Yellow Color: Cognizant PaperDocument6 pagesCTS 2004 (PSG and CIT) Yellow Color: Cognizant PaperAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Infosys Test Paper 2 - AnjaliDocument12 pagesInfosys Test Paper 2 - AnjaliAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Monday ME B3, RN - B301 ME B4, RN - B201 Tuesday ME B3, RN - B301 Wednesday ME B4, RN - B201 Thursday ME B3, RN-B301 ME B3, RN - B301 FridayDocument2 pagesMonday ME B3, RN - B301 ME B4, RN - B201 Tuesday ME B3, RN - B301 Wednesday ME B4, RN - B201 Thursday ME B3, RN-B301 ME B3, RN - B301 FridayAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Wipro CAPGEMINI 40 QuestionsDocument4 pagesWipro CAPGEMINI 40 QuestionsAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Blood RelationsDocument2 pagesBlood RelationsAmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Result AnalysisME2011-15,12-16,13-17Document1 pageResult AnalysisME2011-15,12-16,13-17AmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning 1Document4 pagesReasoning 1AmitSharma100% (1)
- Roots To FruitsDocument7 pagesRoots To FruitsAmitSharmaNo ratings yet