Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 11a
Unit 11a
Uploaded by
Aishwarya GoelCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 11a
Unit 11a
Uploaded by
Aishwarya GoelCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 11
Magnetism
Magnets
magnetism force of attraction or
repulsion
not all objects are affected by the force of
magnetism
ex. wood, glass, paper, plastic
common metals affected by magnetism are
iron, nickel, and cobalt
Magnets
poles two ends of a magnet
every magnet has two poles
north (N) pole
south (S) pole
even if you break a magnet in half, each half
will have a north pole and a south pole
Magnets
the north pole of a magnet points North
it is often called North-seeking
Properties of Magnets
if a north pole and a south pole are
brought together, they will attract each
other
opposites attract
Properties of Magnets
if the north pole of one magnet is brought
near the north pole of another magnet,
they will repel each other
if two south poles are brought together,
they will repel each other
Properties of Magnets
like magnetic poles repel each other
unlike magnetic poles attract each other
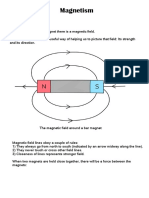
Magnetic Fields
magnetic field area around a magnet
where magnetic forces can act
a magnetic field is made up of magnetic
lines of force
Magnetic Fields
magnetic lines of force lines that show
the shape of a magnetic field
the magnetic lines of force are closest
together at the poles of the magnet
this is where the magnet is strongest
Making a Magnet
some magnets occur in nature
these magnets are called natural
magnets
ex. magnetite (also called lodestone)
Making a Magnet
materials that are not natural magnets
can be magnetized
Making a Magnet
magnetic induction process by which a
material can be made into a magnet
Making a Magnet
some materials are easy to magnetize
ex. iron
Making a Magnet
a material that is easily magnetized
tends to lose its magnetism quickly
a magnet made of this kind of material is
called a temporary magnet
Making a Magnet
materials that are hard to magnetize will
also stay magnetized for a long time
a magnet that is hard to magnetize but
tends to keep its magnetism is called a
permanent magnet
The Earth as a Magnet
William Gilbert
a British scientist
the Earth has north and south poles like a
bar magnet
The Earth as a Magnet
the Earth has a North Magnetic Pole and
a South Magnetic Pole
the North Magnetic Pole is located near the
geographic North Pole
the South Magnetic Pole is located near the
geographic South Pole
The Earth as a Magnet
the North Magnetic Pole is like the south
pole of a bar magnet
the South Magnetic Pole is like the north
pole of a bar magnet
The Earth as a Magnet
the Earth is surrounded by a magnetic
field which extends far into space
magnetosphere region of the Earths
magnetic field
The Earth as a Magnet
the magnetosphere traps charged
particles from the sun
when these particles enter the
atmosphere, an aurora is formed
auroras are also called the northern and
southern lights
Electricity and Magnetism
Hans Oersted
about 200 years ago
an electric current flowing in a wire causes a
compass needle to move
Electricity and Magnetism
an electric current passing through a
wire causes a magnetic field
Electricity and Magnetism
electromagnetism relationship between
electricity and magnetism
Electricity and Magnetism
Michael Faraday (British scientist)
Joseph Henry (American scientist)
when a wire is moved across a magnetic
field, an electric current is induced in the
wire
Electricity and Magnetism
electromagnetic induction process by
which an electric current is produced by
moving a wire in a magnetic field
Electricity and Magnetism
a wire carrying an electric current always
has a magnetic field around it
the magnetic field in a straight wire is not
very strong
if the wire is wound into a coil, the magnetic
field becomes much stronger as the
individual magnetic fields overlap
the greater the number of coils, the stronger the
magnetic field
Electromagnets
electromagnet temporary magnet
made by wrapping a current-carrying
wire around an iron core
the center of an electromagnet is called the
core
it is often made of iron
Electromagnets
as long as current is flowing, an
electromagnet has a magnetic field
when current is turned off, there is no
longer a magnetic field
Electromagnets
there are two ways to make an
electromagnet stronger
increasing the number of coils
increasing the amount of current
Electromagnets
electromagnets are useful because they
can be turned on and off
electromagnets have many important
uses
ex. radios, telephones, computers
Electromagnets
changing the direction of an electric
current causes the poles of an
electromagnet to reverse
this feature is important in the production of
electric motors
Transformers
transformer device in which alternating
current in one coil of wire induces a
current in a second coil
Transformers
a transformer consists of two coils of
wire around a magnet
the first coil, called the primary coil, is
connected to the power source
the second coil, called the secondary coil, is
connected to the load
a load is something that uses electricity, such as
a light bulb or a motor
Transformers
a transformer only works with alternating
current
Transformers
a step-up transformer increases voltage
it consists of more coils of wire in the
secondary coil than the primary coil
Transformers
a step-down transformer decreases
voltage
it consists of more coils of wire in the
primary coil than the secondary coil
Electric Motors
electric motor device that changes
electrical energy into mechanical energy
Electric Motors
an electric motor is made up of an
electromagnet and a permanent magnet
Electric Motors
the electromagnet is free to turn and is
hooked up to a source of alternating
current
changing the direction of an electric current
causes the poles of an electromagnet to
reverse
Electric Motors
attraction and repulsion between the
electromagnet and the permanent
magnet cause the electromagnet to spin
Electric Motors
an electric motor can use direct current if
a special switch is used
Generators
generator device that changes
mechanical energy into electrical energy
a current can be induced in a loop of wire by
spinning the loop inside a magnetic field
due to the changing direction of the wire, an
alternating current is produced
Generators
an electric generator is made up of an
insulated loop of wire and a U-shaped
magnet
spinning the loop of wire in the magnetic
field of the magnet produces an electric
current
Generators
most of the energy we use every day
comes from generators
Generators
mechanical energy for many generators
is supplied by turbines
a turbine is a large wheel that is turned by
moving steam or water
You might also like
- MIG 275R & MIG 350R: Service ManualDocument22 pagesMIG 275R & MIG 350R: Service ManualJaiprakash Sharma100% (5)
- Allarmi enDocument48 pagesAllarmi enjanath kumar50% (2)
- Multisim Digital PrimerDocument62 pagesMultisim Digital PrimerRichard MortimerNo ratings yet
- Syntec InfoDocument14 pagesSyntec InfoGeorgi HelyanNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument45 pagesMagnetismPatel DipenNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument29 pagesMagnetismYoshiro YangNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Is The Property and Interaction of MagnetsDocument13 pagesMagnetism: Is The Property and Interaction of MagnetsLish Is meNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: A Strangely Attractive TopicDocument28 pagesMagnetism: A Strangely Attractive TopicYo100% (1)
- S6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument42 pagesS6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismMichelle LoNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument4 pagesMagnetismnicoaviles725No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen MiayoDocument32 pagesElectromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen Miayo10march1965No ratings yet
- In A Flash: Magnets and ElectricityDocument20 pagesIn A Flash: Magnets and ElectricityJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Magnetism RevisionDocument4 pagesMagnetism RevisiongracelithgoNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument23 pagesMagnetismErrol WaltersNo ratings yet
- G10 MagnetismDocument78 pagesG10 MagnetismTricia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects Class 10 Cbse NotesDocument20 pagesMagnetic Effects Class 10 Cbse NotesAsmita PandeyNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Physics MagnetsDocument6 pagesForm 3 Physics MagnetsChibale Mchere BandaNo ratings yet
- Electricuty and MagneDocument51 pagesElectricuty and MagneVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- 7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Document25 pages7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Haerfing AuwNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of MagnetsDocument24 pagesBasic Principles of MagnetsMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Grd10 Q2 K-12 (Electricity and Magnetism) NOTES AND QUESTIONSDocument9 pagesGrd10 Q2 K-12 (Electricity and Magnetism) NOTES AND QUESTIONSIonacer Viper75% (4)
- ElectromagnetDocument2 pagesElectromagnet10660600No ratings yet
- Physical Chapter 11Document13 pagesPhysical Chapter 11CHAN SEE MILLANo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism PDFDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism PDFNaga RajuNo ratings yet
- Lesson ElectromagnetismDocument67 pagesLesson ElectromagnetismTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument51 pagesMagnetism Notesroxiboxi300No ratings yet
- LESTERDocument11 pagesLESTERLhoraine BaronaNo ratings yet
- 13.1 Magnets and Magnetic MaterialsDocument4 pages13.1 Magnets and Magnetic MaterialscindyNo ratings yet
- Local Media2477199841487123126Document3 pagesLocal Media2477199841487123126Haimen BuisanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism For Printing ModuleDocument24 pagesElectromagnetism For Printing ModuleBob PhigglebottomNo ratings yet
- Science PPT MagnetsDocument8 pagesScience PPT Magnetsapi-313062442No ratings yet
- Date: Form/Class: Subject: TOPIC: Magnetism ObjectivesDocument21 pagesDate: Form/Class: Subject: TOPIC: Magnetism ObjectivesPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current PortfolioDocument3 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current PortfolioAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Artikel Listrik MagnetDocument7 pagesArtikel Listrik MagnetAgnes NovitaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument10 pagesPhysics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentananditaNo ratings yet
- Form 3 or 4 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Notes For WebsiteDocument24 pagesForm 3 or 4 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Notes For Websiteapi-255989257No ratings yet
- 3-5 Physics Elec MagDocument34 pages3-5 Physics Elec MagPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet - 10th GradeDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension Worksheet - 10th GradeAngelica Calamba CalicaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 3: ElectromagnetismDocument28 pagesPhysics Form 5 Chapter 3: ElectromagnetismSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Systems Operation - FundamentalsDocument10 pagesMagnetism: Systems Operation - Fundamentalsrigoberto otinianoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismDocument14 pagesReviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismOP GAMINGNo ratings yet
- IGCSE O Level Magnetism-NotesDocument4 pagesIGCSE O Level Magnetism-NotesSajidMansoorKuriyedamNo ratings yet
- Magnets Magnetic Wire Electricity Solenoid Proportional Current Circuit Electrons Iron Nickel Cobalt CopperDocument2 pagesMagnets Magnetic Wire Electricity Solenoid Proportional Current Circuit Electrons Iron Nickel Cobalt CopperAlyssa Kaye LaganaNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: Magnetic FieldsDocument12 pagesMagnetism: Magnetic FieldsShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Review of Science Test #4Document5 pagesReview of Science Test #4Dariana MercadoNo ratings yet
- MAGNETISM FinalDocument22 pagesMAGNETISM FinalKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Magnetism: (Like Poles Repel, Unlike Poles Attract)Document3 pagesMagnetism: (Like Poles Repel, Unlike Poles Attract)Qui RainNo ratings yet
- ديداكتيك الكهرومغناطسيةDocument2 pagesديداكتيك الكهرومغناطسيةHadil YoubiNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint ElectronicsDocument30 pagesPowerpoint Electronicsjanine jaboneteNo ratings yet
- Electrical Energy Generation and TransmissionDocument59 pagesElectrical Energy Generation and TransmissionLlama jennerNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentMayurItankarNo ratings yet
- Physics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesPhysics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument44 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentjannatuladoniruNo ratings yet
- 1-Magnetism NotesDocument34 pages1-Magnetism NotesSharon DingNo ratings yet
- Delmar Unit 4 Magnetism Sept 2022Document51 pagesDelmar Unit 4 Magnetism Sept 2022Williams UgazNo ratings yet
- Pajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Document4 pagesPajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Jonna PajunarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceDocument18 pagesChapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceGovind DabralNo ratings yet
- To Demonstrate The Phenomena of Magnetism in An ElectromagnetDocument10 pagesTo Demonstrate The Phenomena of Magnetism in An Electromagnetadult_shubhamNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Document21 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Ahmed tarek gaballahNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 2015Document4 pagesPhysics Project 2015harshitNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Word Documentprksht4No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current Class 10thDocument13 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current Class 10thMack TripathiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1Document58 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1iMer22100% (1)
- Compgrammar PolishDocument114 pagesCompgrammar Polish420100% (4)
- The Slavic LanguagesDocument4 pagesThe Slavic LanguagesGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Romanian and Albanian Common Vocabulary-LibreDocument16 pagesRomanian and Albanian Common Vocabulary-LibreGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Russian GrammarDocument141 pagesRussian GrammarMichael Sturgeon, Ph.D.100% (55)
- EndosDocument7 pagesEndosGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- RepProgPh70 - Pitarke Theory SPSPPDocument87 pagesRepProgPh70 - Pitarke Theory SPSPPGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- MIT6 094IAP10 Lec04Document34 pagesMIT6 094IAP10 Lec04Happy2021No ratings yet
- The Synchrotron: Longitudinal Focusing & The Gamma TransitionDocument13 pagesThe Synchrotron: Longitudinal Focusing & The Gamma TransitionGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Ar Ni Er: Av. M Illie Mathy SDocument1 pageAr Ni Er: Av. M Illie Mathy SGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Biases and Information Systems: KeywordsDocument11 pagesDecision-Making Biases and Information Systems: KeywordsGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Molecular FluorescenceDocument7 pagesMolecular FluorescenceGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- StereoisomersDocument17 pagesStereoisomersGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Document38 pagesStereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Gramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oDocument12 pagesValence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument28 pagesNutritionGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- SPEC - LT Switchgear Cub With 400kVA Trans.Document12 pagesSPEC - LT Switchgear Cub With 400kVA Trans.10derNo ratings yet
- Simple GAL ProgrammerDocument7 pagesSimple GAL ProgrammerjaimefpolisNo ratings yet
- Ignition System Prototype Maintenance Manual and Safety ManualDocument15 pagesIgnition System Prototype Maintenance Manual and Safety ManualangeloNo ratings yet
- Planos 830E-5Document27 pagesPlanos 830E-5Kristo LNo ratings yet
- Aux TF 630 KvaDocument7 pagesAux TF 630 KvaUmamaheshwarrao VarmaNo ratings yet
- OSP Document New PDFDocument82 pagesOSP Document New PDFjuminarNo ratings yet
- Agilent AN1364 S-Parameter De-EmbeddingDocument20 pagesAgilent AN1364 S-Parameter De-EmbeddingVedran Ibrahimovic100% (1)
- PTM 1 Strain Gage Io ModuleDocument9 pagesPTM 1 Strain Gage Io ModuleDiogo Henrique HerculanoNo ratings yet
- Polyfuse Report MaterialDocument53 pagesPolyfuse Report Materialgauravpgi4567% (3)
- Tes P 119 05 R0Document8 pagesTes P 119 05 R0boopelectraNo ratings yet
- 400w Psu tl494Document9 pages400w Psu tl494Dhimiter KocaNo ratings yet
- OSCHMANDocument7 pagesOSCHMANapi-3708784100% (1)
- Name: PARDO, Vince Patrick, QUIZON, Fritzgerald, QUEZA, Hendrick Brian Group No.: 8 Section: 3-EED Low Pass Filter (Capacitor)Document6 pagesName: PARDO, Vince Patrick, QUIZON, Fritzgerald, QUEZA, Hendrick Brian Group No.: 8 Section: 3-EED Low Pass Filter (Capacitor)Hendrick Brian QuezaNo ratings yet
- Report Fyp Car PaintDocument64 pagesReport Fyp Car PaintAzka NawazNo ratings yet
- Cinema Act & Hospital LightingDocument3 pagesCinema Act & Hospital LightingBadarul MuneerNo ratings yet
- M1sseries Manual eDocument54 pagesM1sseries Manual eAndrew89No ratings yet
- Eon15p 1Document2 pagesEon15p 1Dennis Brian ModinaNo ratings yet
- Controlador CAN MC33389Document49 pagesControlador CAN MC33389Jorge Martinez PerezNo ratings yet
- Az5b0s 01FDocument6 pagesAz5b0s 01FJC CNo ratings yet
- Fluke 500 Series Battery Analyzers: Technical DataDocument5 pagesFluke 500 Series Battery Analyzers: Technical DataMayurNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Piezoelectric Triboelectric Wearable Nanogenerator Based On Stretchable PVDF Pdms Composite FilmsDocument11 pagesHybrid Piezoelectric Triboelectric Wearable Nanogenerator Based On Stretchable PVDF Pdms Composite FilmsksharpquartetNo ratings yet
- Solar Based Automatic Water Level Sensing and Water Pumping System For Next GenerationDocument5 pagesSolar Based Automatic Water Level Sensing and Water Pumping System For Next GenerationIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Manual Ups Eaton9130Document41 pagesManual Ups Eaton9130Rodrigo Pinillos67% (3)
- Wireless Stick Lite Pinout Diagram: NotesDocument1 pageWireless Stick Lite Pinout Diagram: NotesSKOLLNo ratings yet
- 7ug TMR CatalogDocument16 pages7ug TMR CatalogAkhil ChoureNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Telecommunications DC SystemsDocument39 pagesGuidelines Telecommunications DC SystemsHermanNo ratings yet